Abstract
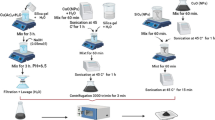
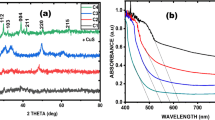
This article reports for the first time a facile, green synthesis of 2D CuO nanoleaves (NLs) using the amino acid, namely aspartic acid, and NaOH by a microwave heating method. The amino acid acts as a complexing/capping agent in the synthesis of CuO NLs. This method resulted in the formation of self-assembled 2D CuO NLs with an average length and width of ~300–400 and ~50–82 nm, respectively. The as-synthesized 2D CuO NLs were built up from the primary CuO nanoparticles by oriented attachment growth mechanism. The CuO NLs were characterized by an X-ray diffraction (XRD) method, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The optical properties were investigated using UV-visible spectroscopy. For the first time, rose bengal and eosin Y dyes were degraded photochemically by solar irradiation using CuO NLs as a photocatalyst. The synthesized CuO NLs act as an efficient photocatalyst in the degradation of rose bengal and eosin Y dye under direct sunlight. The degradation of both the dyes, namely rose bengal and eosin Y, took place within 120 and 45 min, respectively, using CuO NLs as a photocatalyst, whereas commercial CuO, SnO2 quantum dots (QDs), and commercial SnO2 took more than 120 and 45 min for the degradation of rose bengal and eosin Y, respectively. The synthesized CuO NLs showed a superior photocatalytic activity as compared to that of commercial CuO, SnO2 QDs, and commercial SnO2. The reusability of the CuO NLs as a photocatalyst in the degradation of dyes was investigated, and it was evident that the catalytic efficiency decreases to a small extent (5–6 %) after the fifth cycle of operation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharjee A, Ahmaruzzaman M (2015) A novel and green process for the production of tin oxide quantum dots and its application as a photocatalyst for the degradation of dyes from aqueous phase. J Colloid Interface Sci 448:130–139
Chen H, Jhao G, Liu Y (2013) Low-temperature solution synthesis of CuO nanorods with thin diameter. Mater Lett 93:60–63
Cheng Z, Xu J, Zhong H, Chu X, Song J (2011) Hydrogen peroxide-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical CuO flower-like nanostructures. Mater Lett 65:2047–2050
Das D, Nath BC, Phukon P, Dolui SK (2013) Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial behavior of CuO nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B 101:430–433
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Jhare D, Mittal J (2012) Batch and bulk removal of hazardous colouring agent rose bengal by adsorption techniques using bottom ash as adsorbent. RSC Adv 2:8381–8389
Hong ZS, Cao Y, Deng JF (2002) A convenient alcohothermal approach for low temperature synthesis of CuO nanoparticles. Mater Lett 52:34–38
Li Y, Xu M, Pan L, Zhang Y, Guo Z, Bi C (2010) Structural and room-temperature ferromagnetic properties of Fe-doped CuO nanocrystals. J Appl Phys 107:113908–6
Linsebigler L, Lu G, Yates JT (1995) Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem Rev 95:735–758
Pal J, Deb MK, Deshmukh DK, Sen BK (2014) Microwave-assisted synthesis of platinum nanoparticles and their catalytic degradation of methyl violet in aqueous solution. Appl Nanosci 4:61–65
Qin H, Zhang Z, Liu X, Zhang Y, Hu J (2010) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in CuO sol-gel powders and films. J Magn Magn Mater 322:1994–1998
Qin H, Li W, Xia Y, He T (2011) Photocatalytic activity of heterostructures based on ZnO and N-doped ZnO. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:3152–3156
Sangami G, Dharmaraj N (2012) UV-visible spectroscopic estimation of photodegradation of rhodamine-B dye using tin(IV) oxide nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta A 97:847–852
Sankar R, Manikandan P, Malarvizhi V, Fathima T, Shivashangari KS, Ravikumar V (2014) Green synthesis of colloidal copper oxide nanoparticles using Carica papaya and its application in photocatalytic dye degradation. Spectrochim Acta A 121:746–750
Srestha KM, Sorensen CM, Klabunde KJ (2010) Synthesis of CuO nanorods, reduction of CuO into Cu nanorods, and diffuse reflectance measurements of CuO and Cu nanomaterials in the near infrared region. J Phys Chem C 114:14368–14376
Tanasa DE, Piuleac CG, Curteanu S, Popovici E (2013) Photodegradation process of eosin Y using ZnO/SnO2 nanocomposites as photocatalysts: experimental study and neural network modeling. J Mater Sci 48:8029–8040
Wang TX, Xu SH, Yang FX (2012) Green synthesis of CuO nanoflakes from CuCO3·Cu(OH)2 powder and H2O2 aqueous solution. Powder Technol 228:128–130
Xia F, Ou E, Wang L, Wang J (2008) Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over cobalt doped mesoporous SBA-15 under sunlight. Dyes Pigm 76:76–81
Xu M, Wang F, Ding B, Song X, Fang J (2012) Electrochemical synthesis of leaf-like CuO mesocrystals and their lithium storage properties. RSC Adv 2:2240–2243
Yang C, Su X, Wang J, Cao X, Wang S, Zhang L (2013) Facile microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of varied-shaped CuO nanoparticles and their gas sensing properties. Sens Actuators B 185:159–165
Acknowledgments
We, the authors, express our heartfelt thanks and gratitude to the Director, NIT Silchar, and TEQIP-II for providing the lab facilities and scholarship. Our special thanks are extended to NEHU, IIT Bombay, and CSMCRI for providing the TEM, IR, and XRD data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Santiago V. Luis
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Supplementary Information: XRD pattern and TEM image of CuO photocatalyst recovered after 5th cycle are represented in Fig. S1 and S2 in the Supplementary Information (DOCX 4310 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharjee, A., Begum, S., Neog, K. et al. Facile synthesis of 2D CuO nanoleaves for the catalytic elimination of hazardous and toxic dyes from aqueous phase: a sustainable approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 11668–11676 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6355-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6355-4