Abstract
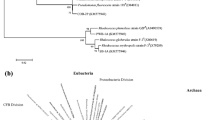
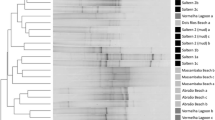
The distribution and diversity of culturable biosurfactant-producing bacteria were investigated in a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) using the Shannon and Simpson’s indices. Twenty wastewater samples were analysed, and from 667 isolates obtained, 32 were classified as biosurfactant producers as they reduced the surface tension of the culture medium (71.1 mN/m), with the lowest value of 32.1 mN/m observed. Certain isolates also formed stable emulsions with diesel, kerosene and mineral oils. The 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) analysis classified the biosurfactant producers into the Aeromonadaceae, Bacillaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, Gordoniaceae and the Pseudomonadaceae families. In addition, numerous isolates carried the surfactin 4′-phosphopantetheinyl transferase (sfp), rhamnosyltransferase subunit B (rhlB) and bacillomycin C (bamC) genes involved in the biosynthesis of surfactin, rhamnolipid and bacillomycin, respectively. While, biosurfactant-producing bacteria were found at all sampling points in the WWTP, the Simpson’s diversity (1 − D) and the Shannon-Weaver (H) indices revealed an increase in bacterial diversity in the influent samples (0.8356 and 2.08), followed by the effluent (0.8 and 1.6094) and then the biological trickling filter (0.7901 and 1.6770) samples. Numerous biosurfactant-producing bacteria belonging to diverse genera are thus present throughout a WWTP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Bahry S, Al-Wahaibi Y, Elshafie A, Al-Bemani A, Joshi S, Al-Makhmari H, Al-Sulaimani H (2013) Biosurfactant production by Bacillus subtilis B20 using date molasses and its possible application in enhanced oil recovery. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 81:141–146
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Arguelles-Arias A, Ongena M, Halimi B, Lara Y, Brans A, Joris B, Fickers P (2009) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GA1 as a source of potent antibiotics and other secondary metabolites for biocontrol of plant pathogens. Microb Cell Fact 8:1–12
Banat IM (1993) The isolation of a thermophilic biosurfactant producing Bacillus sp. Biotechnol Lett 15:591–594
Banat IM, Franzetti A, Gandolfi I, Bestetti G, Martinotti MG, Fracchia L, Smyth TJ, Marchant R (2010) Microbial biosurfactants production, applications and future potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:427–444
Benincasa M, Abalos A, Oliveira I, Manresa A (2004) Chemical structure, surface properties and biological activities of the biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa LBI from soapstock. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 85:1–8
Bento FM, de Oliveira Camargo FA, Okeke BC, Frankenberger WT (2005) Diversity of biosurfactant producing microorganisms isolated from soils contaminated with diesel oil. Microbiol Res 160:249–255
Bodour AA, Miller-Maier RM (1998) Application of a modified drop-collapse technique for surfactant quantitation and screening of biosurfactant-producing microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 32:273–280
Bodour AA, Drees KP, Maier RM (2003) Distribution of biosurfactant-producing bacteria in undisturbed and contaminated arid southwestern soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3280–3287
Bonmatin J, Laprévote O, Peypoux F (2003) Diversity among microbial cyclic lipopeptides: iturins and surfactins. Activity-structure relationships to design new bioactive agents. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 6:541–556
Chrzanowski Ł, Wick L, Meulenkamp R, Kaestner M, Heipieper H (2009) Rhamnolipid biosurfactants decrease the toxicity of chlorinated phenols to Pseudomonas putida DOT‐T1E. Lett Appl Microbiol 48:756–762
Chrzanowski Ł, Dziadas M, Ławniczak Ł, Cyplik P, Białas W, Szulc A, Lisiecki P, Jeleń H (2012a) Biodegradation of rhamnolipids in liquid cultures: effect of biosurfactant dissipation on diesel fuel/B20 blend biodegradation efficiency and bacterial community composition. Bioresour Technol 111:328–335
Chrzanowski Ł, Ławniczak Ł, Czaczyk K (2012b) Why do microorganisms produce rhamnolipids? World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:401–419
Das P, Mukherjee S, Sen R (2008) Antimicrobial potential of a lipopeptide biosurfactant derived from a marine Bacillus circulans. J Appl Microbiol 104:1675–1684
Desai JD, Banat IM (1997) Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:47–64
Drury B, Rosi-Marshall E, Kelly JJ (2013) Wastewater treatment effluent reduces the abundance and diversity of benthic bacterial communities in urban and suburban rivers. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1897–1905
Dusane DH, Zinjarde SS, Venugopalan VP, Mclean RJ, Weber MM, Rahman PK (2010) Quorum sensing: implications on rhamnolipid biosurfactant production. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 27:159–184
Fakruddin M (2012) Biosurfactant: production and application. J Pet Environ Biotechnol
Hashimoto K, Matsuda M, Inoue D, Ike M (2014) Bacterial community dynamics in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant employing conventional activated sludge process. J Biosci Bioeng 118:64–71
Hsieh F, Li M, Lin T, Kao S (2004) Rapid detection and characterization of surfactin-producing Bacillus subtilis and closely related species based on PCR. Curr Microbiol 49:186–191
Jousset A, Lara E, Wall LG, Valverde C (2006) Secondary metabolites help biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0 to escape protozoan grazing. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7083–7090
Juwarkar AA, Nair A, Dubey KV, Singh S, Devotta S (2007) Biosurfactant technology for remediation of cadmium and lead contaminated soils. Chemosphere 68:1996–2002
Juwarkar AA, Dubey KV, Nair A, Singh SK (2008) Bioremediation of multi-metal contaminated soil using biosurfactant—a novel approach. Indian J Microbiol 48:142–146
Kowall M, Vater J, Kluge B, Stein T, Franke P, Ziessow D (1998) Separation and characterization of surfactin isoforms produced by Bacillus subtilis OKB 105. J Colloid Interface Sci 204:1–8
Kuiper I, Lagendijk EL, Pickford R, Derrick JP, Lamers GE, Thomas‐Oates JE, Lugtenberg BJ, Bloemberg GV (2004) Characterization of two Pseudomonas putida lipopeptide biosurfactants, putisolvin I and II, which inhibit biofilm formation and break down existing biofilms. Mol Microbiol 51:97–113
Ławniczak Ł, Marecik R, Chrzanowski Ł (2013) Contributions of biosurfactants to natural or induced bioremediation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:2327–2339
Lazar I, Petrisor I, Yen T (2007) Microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Pet Sci Technol 25:1353–1366
Lourith N, Kanlayavattanakul M (2009) Natural surfactants used in cosmetics: glycolipids. Int J Cosmet Sci 31:255–261
Mandal SM, Barbosa AE, Franco OL (2013) Lipopeptides in microbial infection control: scope and reality for industry. Biotechnol Adv 31:338--345
Mukherjee S, Das P, Sen R (2006) Towards commercial production of microbial surfactants. Trends Biotechnol 24:509–515
Mulligan CN (2005) Environmental applications for biosurfactants. Environ Pollut 133:183–198
Ndlovu T, Le Roux M, Khan W, Khan S (2015) Co-detection of virulent Escherichia coli genes in surface water sources. PLoS One 10:e0116808
Olapade OA, Ronk AJ (2015) Isolation, characterization and community diversity of indigenous putative toluene-degrading bacterial populations with catechol-2, 3-dioxygenase genes in contaminated soils. Microb Ecol 69:59–65
Peypoux F, Bonmatin J, Wallach J (1999) Recent trends in the biochemistry of surfactin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:553–563
Piljac T, Piljac G (2007) Applying rhamnolipids for cosmetic treatment of wrinkles
Piljac A, Stipcevic T, Piljac-Zegarac J, Piljac G (2008) Successful treatment of chronic decubitus ulcer with 0.1% dirhamnolipid ointment. J Cutan Med Surg 12:142–146
Raaijmakers JM, De Bruijn I, Nybroe O, Ongena M (2010) Natural functions of lipopeptides from Bacillus and Pseudomonas: more than surfactants and antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:1037–1062
Ramarathnam R, Bo S, Chen Y, Fernando WD, Xuewen G, De Kievit T (2007) Molecular and biochemical detection of fengycin-and bacillomycin D-producing Bacillus spp., antagonistic to fungal pathogens of canola and wheat. Can J Microbiol 53:901–911
Rawlings D (1995) Restriction enzyme analysis of 16S rRNA genes for the rapid identification of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans strains in leaching environments. Biohydrometallurgical Process 2:9–17
Razafindralambo H, Paquot M, Baniel A, Popineau Y, Hbid C, Jacques P, Thonart P (1996) Foaming properties of surfactin, a lipopeptide biosurfactant from Bacillus subtilis. J Am Oil Chem Soc 73:149–151
Rodrigues L, Banat IM, Teixeira J, Oliveira R (2006) Biosurfactants: potential applications in medicine. J Antimicrob Chemother 57:609–618
Ron EZ, Rosenberg E (2001) Natural roles of biosurfactants. Environ Microbiol 3:229–236
Sen R (2010) Biosurfactants. Springer Science & Business Media
Seydlová G, Svobodová J (2008) Review of surfactin chemical properties and the potential biomedical applications. Cent Eur J Med 3:123–133
Sheppard J, Jumarie C, Cooper D, Laprade R (1991) Ionic channels induced by surfactin in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1064:13–23
Shoeb E, Akhlaq F, Badar U, Akhter J, Imtiaz S (2013) Classification and industrial applications of biosurfactants. Acad Res Int 4:243–252
Shon H, Vigneswaran S, Snyder S (2006) Effluent organic matter (EfOM) in wastewater: constituents, effects, and treatment. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 36:327–374
Silva S, Farias C, Rufino R, Luna J, Sarubbo L (2010) Glycerol as substrate for the production of biosurfactant by Pseudomonas aeruginosa UCP0992. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 79:174–183
Soberón-Chávez G, Maier RM (2011) Biosurfactants: a general overview. In: Biosurfactants. Springer, pp 1--11
Stanković S, Mihajlović S, Draganić V, Dimkić I, Vukotić G, Berić T, Fira Đ (2012) Screening for the presence of biosynthetic genes for antimicrobial lipopeptides in natural isolates of Bacillus sp. Arch Biol Sci 64:1425--1432
Stipcevic T, Piljac A, Piljac G (2006) Enhanced healing of full-thickness burn wounds using di-rhamnolipid. Burns 32:24–34
Tabatabaee A, Assadi MM, Noohi A, Sajadian V (2005) Isolation of biosurfactant producing bacteria from oil reservoirs. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 2:6–12
Thavasi R, Sharma S, Jayalakshmi S (2011) Evaluation of screening methods for the isolation of biosurfactant producing marine bacteria. J Pet Environ Biotechnol S 1:2
Tsuge K, Inoue S, Ano T, Itaya M, Shoda M (2005) Horizontal transfer of iturin A operon, itu, to Bacillus subtilis 168 and conversion into an iturin A producer. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:4641–4648
Van Hamme JD, Singh A, Ward OP (2006) Physiological aspects: part 1 in a series of papers devoted to surfactants in microbiology and biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv 24:604–620
Vollenbroich D, Pauli G, Ozel M, Vater J (1997) Antimycoplasma properties and application in cell culture of surfactin, a lipopeptide antibiotic from Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:44–49
Walter V, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2010) Screening concepts for the isolation of biosurfactant producing microorganisms. In: Biosurfactants. Springer, pp 1-13
Wang Z, Li K, Fingas M, Sigouin L, Menard L (2002) Characterization and source identification of hydrocarbons in water samples using multiple analytical techniques. J Chromatogr 971:173–184
Youssef NH, Duncan KE, Nagle DP, Savage KN, Knapp RM, McInerney MJ (2004) Comparison of methods to detect biosurfactant production by diverse microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 56:339–347
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Research Foundation (Grant number: 90320) for financial support. The authors also wish to thank Mr Vivian Kloppers and the staff members at Stellenbosch municipal wastewater treatment plant for their assistance in the collection of wastewater samples. The Department of Chemistry at Stellenbosch University and Mrs Peta Steyn are thanked for the use of the Du Nouy tensiometer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ndlovu, T., Khan, S. & Khan, W. Distribution and diversity of biosurfactant-producing bacteria in a wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 9993–10004 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6249-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6249-5