Abstract
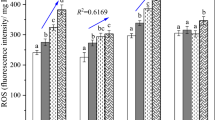
In this study, the influence of soil types on the effect of the commercial form of C-nZVI on tissue concentrations, cellular component, reproduction outcome in Eisenia fetida, and the soil health was investigated. C-nZVI at concentration level of 3 g kg−1 soil showed no effect on the survival of E. fetida in the three soil types. However, varying effects such as concentration-dependent increase in tissue iron concentration, lipid peroxidation, and damage to DNA molecules by C-nZVI were observed. C-nZVI at an exposure concentration of 60 mg kg−1 soil induced oxidative stress in E. fetida. Tissue Fe concentration appeared correlated to the DNA damage. Oxidative stress and DNA damage may explain the toxicity mechanisms of nZVI to E. fetida.

Reactive oxygen species induced by nZVI







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker HM, Anderson BF, Baker EN (2003) Dealing with iron: common structural principles in proteins that transport iron and heme. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:3579–3583
Barbouti A, Doulias P-T, Zhu B-Z, Frei B, Galaris D (2001) Intracellular iron, but not copper, plays a critical role in hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA Damage. Free Radic Biol Med 31:490–498
Beyer WN, Cromartie EJ (1987) A survey of Pb, Cu, Zn, Cd, Cr, As, and Se in earthworms and soil from diverse sites. Environ Monit Assess 8:27–36
Biaglow JE, Kachur AV (1997) The generation of hydroxyl radicals in the reaction of molecular oxygen with polyphosphate complexes of ferrous ion. Radiat Res 148:181–187
Brown PL, Markich SJ (2000) Evaluation of the free ion activity model of metal-organism interaction: extension of the conceptual model. Aquat Toxicol 51:177–194
Case RM, Eisner D, Gurney A, Jones O, Muallem S, Verkhratsky A (2007) Evolution of calcium homeostasis: from birth of the first cell to an omnipresent signalling system. Cell Calcium 42:345–350
Chen P-J, Su C-H, Tseng C-Y, Tan S-W, Cheng C-H (2011) Toxicity assessments of nanoscale zerovalent iron and its oxidation products in medaka (Oryzias latipes) fish. Mar Pollut Bull 63:339–346
Chen P-J, Tan S-W, Wu W-L (2012) Stabilization or oxidation of nanoscale zerovalent iron at environmentally relevant exposure changes bioavailability and toxicity in medaka fish. Environ Sci Technol 46:8431–8439
El-Temsah YS, Joner EJ (2012) Ecotoxicological effects on earthworms of fresh and aged nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) in soil. Chemosphere 89:76–82
Franklin NM, Rogers NJ, Apte SC, Batley GE, Gadd GE, Casey PS (2007) Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata): the importance of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol 41:8484–8490
Gordeeva AV, Zvyagilskaya RA, Labas YA (2003) Cross-talk between reactive oxygen species and calcium in living cells. Biochem Mosc 68:1077–1080
Henle ES, Han Z, Tang N, Rai P, Luo Y, Linn S (1999) Sequence-specific DNA cleavage by Fe2 + −mediated fenton reactions has possible biological implications. J Biol Chem 274:962–971
Homa J, Stürzenbaum SR, Morgan AJ, Plytycz B (2007) Disrupted homeostasis in coelomocytes of Eisenia fetida and Allolobophora chlorotica exposed dermally to heavy metals. Eur J Soil Biol 43(Supplement 1):S273–S280
Johnson RL, Nurmi JT, O’Brien Johnson GS, Fan D, O’Brien Johnson RL, Shi Z, Salter-Blanc AJ, Tratnyek PG, Lowry GV (2013) Field-scale transport and transformation of carboxymethylcellulose-stabilized nano zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 47:1573–1580
Keller AA, Garner K, Miller RJ, Lenihan HS (2012) Toxicity of nano-zero valent iron to freshwater and marine organisms. PLoS ONE 7:e43983
Kirschling TL, Gregory KB, Minkley J, Edwin G, Lowry GV, Tilton RD (2010) Impact of nanoscale zero valent iron on geochemistry and microbial populations in trichloroethylene contaminated aquifer materials. Environ Sci Technol 44:3474–3480
Kızılkaya R (2005) The role of different organic wastes on zinc bioaccumulation by earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L. (Oligochaeta) in successive Zn added soil. Ecol Eng 25:322–331
Klaine SJ, Alvarez PJJ, Batley GE, Fernandes TF, Handy RD, Lyon DY et al (2008) Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1825–1851
Lee C, Kim JY, Lee WI, Nelson KL, Yoon J, Sedlak DL (2008) Bactericidal effect of zero-valent iron nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Environ Sci Technol 42:4927–4933
Li H, Zhou Q, Wu Y, Fu J, Wang T, Jiang G (2009) Effects of waterborne nano-iron on medaka (Oryzias latipes): antioxidant enzymatic activity, lipid peroxidation and histopathology. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:684–692
Li Z, Greden K, Alvarez PJJ, Gregory KB, Lowry GV (2010) Adsorbed polymer and NOM limits adhesion and toxicity of nano scale zerovalent iron to E. coli. Environ Sci Technol 44:3462–3467
Manerikar RS, Apte AA, Ghole VS (2008) In vitro and in vivo genotoxicity assessment of Cr(VI) using comet assay in earthworm coelomocytes. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 25:63–68
McCarty LS, Mackay D (1993) Enhancing ecotoxicological modeling and assessment. Body residues and modes of toxic action. Environ Sci Technol 27:1718–1728
Morgan J, Morgan A (1999) The accumulation of metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn and Ca) by two ecologically contrasting earthworm species ( Lumbricus rubellus and Aporrectodea caliginosa): implications for ecotoxicological testing. Appl Soil Ecol 13:9–20
Opper B, Németh P, Engelmann P (2010) Calcium is required for coelomocyte activation in earthworms. Mol Immunol 47:2047–2056
Phenrat T, Long TC, Lowry GV, Veronesi B (2008) Partial oxidation (“Aging”) and surface modification decrease the toxicity of nanosized zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 43:195–200
Plette ACC, Nederlof MM, Temminghoff EJM, van Riemsdijk WH (1999) Bioavailability of heavy metals in terrestrial and aquatic systems: a quantitative approach. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:1882–1890
Qafoku NP, Ranst EV, Noble A, Baert G (2004) Variable charge soils: their mineralogy, chemistry and management. Adv Agron 84:159–215
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41:905–909
Stohs S, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–336
Valembois P, Lassègues M, Roch P (1992) Formation of brown bodies in the coelomic cavity of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei and attendant changes in shape and adhesive capacity of constitutive cells. Dev Comp Immunol 16:95–101
Whitaker M (2006) Calcium microdomains and cell cycle control. Cell Calcium 40:585–592
Zhang W-X, Elliott DW (2006) Applications of iron nanoparticles for groundwater remediation. Remediat J 16:7–21
Acknowledgments
The first author (BD) is thankful to UniSA for the UPS scholarship and CRCCARE for CRCCARE scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yirsaw, B.D., Mayilswami, S., Megharaj, M. et al. Effect of zero valent iron nanoparticles to Eisenia fetida in three soil types. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 9822–9831 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6193-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6193-4