Abstract
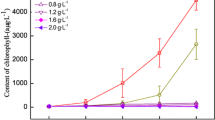
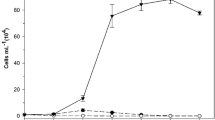
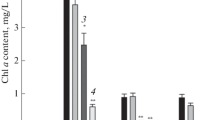
Harmful cyanobacteria bloom contributes to economic loss as well as the threat to human health. Agricultural waste products, particularly straw, have been used to control bloom while arbor plant is the potential candidate for limiting antialgal activity. This study investigated the use of Dracontomelon duperreanum defoliation extract (DDDE) to inhibit the activity of Microcystis aeruginosa. The primary goal of the research was to explore the solution to control cyanobacterial bloom. The photosynthetic activity, cell morphology, membrane integrity, and esterase activity of M. aeruginosa were determined using phytoplankton analyzer pulse amplitude modulation (Phyto-PAM) and flow cytometry before and after exposure to DDDE. The inhibitory rate of M. aeruginosa was about 99.6 % on day 15 when exposed to 2.0 g L−1. A reduction of chlorophyll a (Chl-a) activity and changes in cell membrane suggested the algistatic property of DDDE. Inhibition of photosynthetic activity was reflected by changing mean Chl-a fluorescence intensity (MFI) which was about 52.5 % on day 15 when exposed to 2.0 g L−1 DDDE as well as relative electron transport rates (rETRs) of algal cell. These changes might contribute to the suppression of M. aeruginosa. Algal cell exposed to DDDE may lead to cell volume reduction or slow growth. This resulted in a decreased proportion of normal or swollen granular cells after DDDE treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenburger R, Schmitt-Jansen M, Riedl J (2008) Bioassays with unicellular algae: deviations from exponential growth and its implications for toxicity test results. J Environ Qual 37(1):16–21
Anderson DM, Kaoru Y, White AW (2000) Estimated annual economic impacts from harmful algal blooms (HABs) in the United States. WHOI-2000-11 Woods Hole Oceanogr Inst, Woods Hole, Massachusetts. doi: 10.1575/1912/96
Bailey S, Grossman A (2008) Photoprotection in cyanobacteria: regulation of light harvesting. Photochem Photobiol 84(6):1410–1420
Barrington DJ, Ghadouani A (2008) Application of hydrogen peroxide for the removal of toxic cyanobacteria and other phytoplankton from wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 42(23):8916–8921
Campbell D, Hurry V, Clarke AK, Gustafsson P, Oquist G (1998) Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis of cyanobacterial photosynthesis and acclimation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62(3):667–683
Chen JQ, Guo RX (2014) Inhibition effect of green alga on cyanobacteria by the interspecies interactions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(3):839–842
Choe S, Jung I (2002) Growth inhibition of freshwater algae by ester compounds released from rotted plants. J Ind Eng Chem 8(2):297–304
Churro C, Alverca E, Sam-Bento F, Paulino S, Figueira VC, Bento AJ, Prabhakar S, Lobo AM, Calado AJ, Pereira P (2009) Effects of bacillamide and newly synthesized derivatives on the growth of cyanobacteria and microalgae cultures. J Appl Phycol 21(4):429–442
Codd GA, Morrison LF, Metcalf JS (2005) Cyanobacterial toxins: risk management for health protection. Toxicol Appl Pharm 203(3):264–272
Daniel ET, Ferrier MD, Armbrester EA, Anlauf KA (2002) Inhibition of dinoflagellate growth by extracts of barley straw (Hordeum vulgare). J Appl Phycol 14(4):275–280
Falkowski P, Kiefer DA (1985) Chlorophyll a fluorescence in phytoplankton: relationship to photosynthesis and biomass. J Plankton Res 7(5):715–731
Figueiredo DR, Azeiteiro UM, Esteves SM, Goncalves FJM, Pereira MJ (2004) Microcystin-producing blooms-a serious global public health issue. Ecotox Environ Safe 59(2):151–163
Franklin NM, Stauber JL, Lim RP (2004) Development of multispecies algal bioassays using flow cytometry. Environ Toxicol Chem 23(6):1452–1462
Gibson M, Welch I, Barrett PRF, Ridge I (1990) Barley straw as an inhibitor of algal growth II: laboratory studies. J Appl Phyco 2(3):241–248
Grzymski J, Orrico C, Schofield O (2001) Monochromatic ultraviolet light induced damage to Photosystem II efficiency and carbon fixation in the marine diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana (3H). Photosynth Res 68(3):181–192
Hagström JA, Sengco MR, Villareal TA (2010) Potential methods for managing Prymnesium parvum blooms and toxicity, with emphasis on clay and barley straw: a review. J Am Water Resour Assoc 46(1):187–198
Hong Y, Hu HY, Li FM (2008) Physiological and biochemical effects of allelochemical ethyl 2-methyl acetoacetate (EMA) on cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotox Environ Safe 71(2):527–534
Huang HM, Xiao X, Shi JY, Chen YX (2014) Structure–activity analysis of harmful algae inhibition by congeneric compounds: case studies of fatty acids and thiazolidinediones. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(11):7154–7164
Huang HM, Xiao X, Ghadouani A, Wu JP, Nie ZY, Peng C, Xu XH, Shi JY (2015) Effects of natural flavonoids on photosynthetic activity and cell integrity in Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxins 7(1):66–80
Jančula D, Maršálek B (2012) The toxicity of phthalocyanines to the aquatic plant Lemna minor (duckweed)-testing of 31 compounds. Chemosphere 88(8):962–965
Jiang H, Wu B, Yang B, Xing YZ (2013) Effects of aqueous extract of eucalyptus leaves on the growth and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of two species of marine microalgae. Res Environ Sci 26(11):1186–1193 (in Chinese)
Kong Y, Xu XY, Zhu L, Miao LH (2013) Control of the harmful alga Microcystis aeruginosa and absorption of nitrogen and phosphorus by Candida utilis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169(1):88–99
Macías FA, Oliva RM, Simonet AM, Galindo JCG (1998) What are allelochemicals? In: Olofsdotter M (ed) Allelopathy in rice. IRRI Press, Manilla, Philippines
Murray D, Jefferson B, Jarvis P, Parsons SA (2010) Inhibition of three algae species using chemicals released from barley straw. Environ Technol 31(4):455–466
Nancharaiah YV, Rajadurai M, Venugopalan VP (2007) Single cell level microalgal ecotoxicity assessment by confocal microscopy and digital image analysis. Environ Sci Technol 41(7):2617–2621
Nelder JA, Mead RA (1965) A simplex method for function minimization. Compt J 7(4):308–313
Newman JR, Barrett PRF (1993) Control of Microcystis aeruginosa by decomposing barley straw. J Aquat Plant Manage 31(4):203–206
Ni LX, Hao XY, Li SY, Chen SJ, Ren GX, Zhu L (2011) Inhibitory effects of the extracts with different solvents from three compositae plants on cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosas. Sci China Chemy 54(7):1123–1129
Ni LX, Kumud A, Hao XY, Li SY, Li Y, Li YP (2012) Effects of artemisinin on photosystem II performance of Microcystis aeruginosa by in vivo chlorophyll fluorescence. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89(10):1165–1169
Ou H, Gao NY, Deng Y, Qiao JL, Wang H (2012) Immediate and long-term impacts of UV-C irradiation on photosynthetic capacity, survival and microcystin-LR release risk of Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Res 46(4):1241–1250
Paltt T, Gallegos CL, Harrison WG (1980) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in natural assemblages of marine phytoplankton. J Mar Res 38(4):687–701
Papageorgiou GC, Govindjee (2004) Chl-a fluorescence: a signature of photosynthesis, advances in photosynthesis and respiration. Springer, Dordrecht
Qian HF, Xu XY, Chen W, Jiang H, Jin YX, Liu WP, Fu ZW (2009) Allelochemical stress causes oxidative damage and inhibition of photosynthesis in Chlorella vulgaris. Chemosphere 75(3):368–375
Ralph PJ, Gademann R (2005) Rapid light curves: a powerful tool to assess photosynthetic activity. Aquat Bot 82(3):222–237
Ratkowsky DA (1983) Nonlinear regression modeling: a unified practical approach. Marcel Dekker, New York
Rice EL (1984) Allelopathy, 2nd edn. Academic, Orlando, USA
Ridge I, Walters J, Street M (1999) Algal growth control by terrestrial leaf litter: a realistic tool? Hydrobiologia 395–396:173–180
Rioboo C, O’Connor JE, Prado R, Herrero C, Cid A (2009) Cell proliferation alterations in Chlorella cells under stress conditions. Aquat Toxicol 94(3):229–237
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Genetic assignments, stain histories and properties of pure culture of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111(3):1–61
Street M (1978) Research on the improvement of gravel pits for waterfowl by adding straw. Game Conserv Annu Rev 10:56–61
Su XF, Nong WT (2010) Study on antimicrobial activity of extracts from Dracontomelon duperreanum. China Pharmacy 21(23):2115–2117 (in Chinese)
Su W, Johannes AH, Jia YH, Lu YP, Kong FX (2014) Effects of rice straw on the cell viability, photosynthesis, and growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 32(1):120–129
Tammy AL, Gretchen RB, Stephen MB, Joshua JFH (2015) Environmental influence on cyanobacteria abundance and microcystin toxin production in a shallow temperate lake. Ecotox Environ Safe 114(4):318–328
Tao Y, Zhang XH, Doris WTA, Mao XZ, Yuan K (2010) The effects of sub-lethal UV-C irradiation on growth and cell Integrity of cyanobacteria and green algae. Chemosphere 78(5):541–547
Tao Y, Mao X, Hu J, Mok HOL, Wang L, Au DWT, Zhu J, Zhang X (2013) Mechanisms of photosynthetic inactivation on growth suppression of Microcystis aeruginosa under UV-C stress. Chemosphere 93(4):637–644
Veldhuis MJW, Kraay GW (2000) Application of flow cytometry in marine phytoplankton research: current applications and future perspectives. Sci Mar 64(2):121–134
Wicks RJ, Thiel PG (1990) Environmental factors affecting the production of peptide toxins in floating scums of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa in a hypertrophic African reservoir. Environ Sci Technol 24(9):1413–1418
Xiao X, Chen YX, Liang XQ, Lou LP, Tang XJ (2010) Effects of Tibetan hulless barley efficiently inhibited bloom-Forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Chemosphere 81(9):1118–1123
Xiao X, Han ZY, Chen YX, Liang XQ, Li H, Qian YC (2011) Optimization of FDA-PI method using flow cytometry to measure metabolic activity of the cyanobacteria, Microcystis aeruginosa. Phys Chem Earth 36:424–429
Xiao X, Huang H, Ge Z, Rounge TB, Shi J, Xu X, Li R, Chen YX (2014) A pair of chiral flavonolignans as novel anti-Cyanobacterial allelochemicals derived from barley straw (Hordeum vulgare): characterization and comparison of their anti-Cyanobacterial activities. Environm Microbiol 16(5):1238–1251
Yu Y, Kong F, Wang M, Qian L, Shi X (2007) Determination of short-term copper toxicity in a multispecies microalgal population using flow cytometry. Ecotox Environ Safe 66(1):49–56
Zhang M, Kong FX, Xing P, Tan X (2007) Effects of interspecific interactions between Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella pyrenoidosa on their growth and physiology. Int Rev Hydrobiol 92(3):281–290
Zhang D, Xie P, Liu Y, Qiu T (2009) Transfer, distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in the aquatic food web in Lake Taihu, China, with potential risks to human health. Sci of the Total Environ 407(7):2191–2199
Zhu JC, Zhou L, Zhu J, Gao JS (2015) Allelopathic effects of Anthurium on cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Research of Environ Sci 28(10):1638–1644 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No. 51378316 and the Science, Industry, Trade and Information Technology Commission of Shenzhen Municipality, Grant Nos. 20130331151242230 and 201504301657307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Jiang, C., Szeto, Yt. et al. Effects of Dracontomelon duperreanum defoliation extract on Microcystis aeruginosa: physiological and morphological aspects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 8731–8740 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6119-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6119-1