Abstract
Consumption of water polluted by faecal contaminants is responsible for 2 million deaths annually, most of which occur in developing countries without adequate sanitation. In tropical aquatic systems, streambeds can be reservoirs of persistent pathogenic bacteria and high rainfall can lead to contaminated soils entering streams and to the resuspension of sediment-bound microbes in the streambed. Here, we present a novel method using fallout radionuclides (7Be and 210Pbxs) to estimate the proportions of Escherichia coli, an indicator of faecal contamination, associated with recently eroded soil particles and with the resuspension of streambed sediments. We show that using these radionuclides and hydrograph separations we are able to characterize the proportion of particles originating from highly contaminated soils and that from the resuspension of particle-attached bacteria within the streambed. We also found that although overland flow represented just over one tenth of the total flood volume, it was responsible for more than two thirds of the downstream transfer of E. coli. We propose that data obtained using this method can be used to understand the dynamics of faecal indicator bacteria (FIB) in streams thereby providing information for adapted management plans that reduce the health risks to local populations.

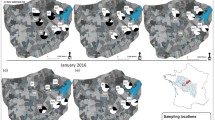
Graphical abstract showing (1) the main water flow processes (i.e. overland flow, groundwater return flow, blue arrows) and sediment flow components (i.e. resuspension and soil erosion, black arrows) during floods in the Houay Pano catchment; (2) the general principle of the method using fallout radionuclide markers (i.e. 7Be and 210Pbxs) to estimate E. coli load from the two main sources (i.e. streambed resuspension vs soil surface washoff); and 3) the main results obtained during the 15 May 2012 storm event (i.e. relative percentage contribution of each process to the total streamflow, values in parentheses)



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bricquet J-P, Boonsaner A, Phommassack T, Toan TD (2003) Statistical analysis of long series rainfall data: a regional study in Southeast Asia. In: IWMI (Hrsg.), IWMI Seminar on Scientific Cooperation. IWMI South East Asia. Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand, pp 83–89
Byappanahalli MN, Fujioka RS (1998) Evidence that tropical soil environment can support the growth of Escherichia coli. Water Sci Technol 38:171–174
Byappanahalli MN, Nevers MB, Korajkic A, Staley ZR, Harwood VJ (2012) Enterococci in the environment. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 76:685–706
Causse J, Billen G, Garnier J, Henri-des-Tureaux T, Olasa X, Thammahacksa C, Latsachak KO, Soulileuth B, Sengtaheuanghoung O, Rochelle-Newall E, Ribolzi O (2015) Field and modelling studies of Escherichia coli loads in tropical streams of montane agro-ecosystems. J Hydro Environ Res. doi: 10.1016/j.jher.2015.03.003
Chan YM, Thoe W, Lee JHW (2015) Field and laboratory studies of Escherichia coli decay rate in subtropical coastal water. J Hydro Environ Res 9:1–14
Cho KH, Pachepsky YA, Kim JH, Kim JW, Park MH (2012) The modified SWAT model for predicting fecal coliforms in the Wachusett Reservoir Watershed, USA. Water Res 46:4750–4760
Collins RU, Neal C (1998) The hydrochemical impacts of terraced agriculture, Nepal. Sci Total Environ 212:233–243
Ekklesia E, Shanahan P, Chua LHC, Eikaas HS (2015) Temporal variation of faecal indicator bacteria in tropical urban storm drains. Water Res 68:171–181
Evrard O, Nemery J, Gratiot N, Duvert C, Ayrault S, Lefevre I, Poulenard J, Prat C, Bonte P, Esteves M (2010) Sediment dynamics during the rainy season in tropical highland catchments of central Mexico using fallout radionuclides. Geomorphology 124:42–54
Garzio-Hadzick A, Shelton DR, Hill RL, Pachepsky YA, Guber AK, Rowland R (2010) Survival of manure-borne E. coil in streambed sediment: effects of temperature and sediment properties. Water Res 44:2753–2762
Genereux DP, Hooper RP (1998) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in rainfall-runoff-studies. In: McDonnell JJ, Kendall C (eds) Isotopes tracers in catchment hydrology. Elsevier Science B.V, Amsterdam, pp 319–346
Goto DK, Yan T (2011) Effects of land uses on fecal indicator bacteria in the water and soil of a tropical watershed. Microbes Environ 26:254–260
Gourdin E, Evrard O, Huon S, Lefèvre I, Ribolzi O, Reyss J-L, Sengtaheuanghoung O, Ayrault S (2014a) Suspended sediment dynamics in a Southeast Asian mountainous catchment: combining river monitoring and fallout radionuclide tracers. Journal of Hydrology 519, Part B: 1811–1823
Gourdin E, Evrard O, Huon S, Reyss JL, Ribolzi O, Bariac T, Sengtaheuanghoung O, Ayrault S (2014b) Spatial and temporal variability of Be-7 and Pb-210 wet deposition during four successive monsoon storms in a catchment of northern Laos. J Environ Radioact 136:195–205
Gourdin E, Huon S, Evrard O, Ribolzi O, Bariac T, Sengtaheuanghoung O, Ayrault S (2015) Sources and export of particle-borne organic matter during a monsoon flood in a catchment of northern Laos. Biogeosciences 12:1073–1089
Guiteras R, Levinsohn J, Mobarak AM (2015) Encouraging sanitation investment in the developing world: a cluster-randomized trial. Science: aaa0491
Hrdinka T, Novický O, Hanslík E, Rieder M (2012) Possible impacts of floods and droughts on water quality. J Hydro Environ Res 6:145–150
Huon S, de Rouw A, Bonté P, Robain H, Valentin C, Lefèvre I, Girardin C, Le Troquer Y, Podwojewski P, Sengtaheuanghoung O (2013) Long-term soil carbon loss and accumulation in a catchment following the conversion of forest to arable land in northern Laos. Agric Ecosyst Environ 169:43–57
Ishii S, Sadowsky MJ (2008) Escherichia coli in the environment: implications for water quality and human health. Microbes Environ 23:101–108
Kim JW, Pachepsky YA, Shelton DR, Coppock C (2010) Effect of streambed bacteria release on E. coli concentrations: monitoring and modeling with the modified SWAT. Ecol Model 221:1592–1604
Kirchner JW (2003) A double paradox in catchment hydrology and geochemistry. Hydrol Process 17:871–874
Lemee R, Rochelle-Newall E, Van Wambeke F, Pizay MD, Rinaldi P, Gattuso JP (2002) Seasonal variation of bacterial production, respiration and growth efficiency in the open NW Mediterranean Sea. Aquat Microb Ecol 29:227–237
Matisoff G, Wilson CG, Whiting PJ (2005) The 7Be/210Pbxs ratio as an indicator of suspended sediment age or fraction new sediment in suspension. Earth Surf Process Landf 30:1191–1201
Muirhead RW, Davies-Colley RJ, Donnison AM, Nagels JW (2004) Faecal bacterial yields in artificial flood events: quantifying in-stream stores. Water Res 38:1215–1224
Nguyen TMH, Le TPQ, Garnier J, Janeau J-L, Rochelle-Newall E (2015) Variability of faecal indicator bacteria (FIB) and die-off rates in the Red River, North Vietnam. J Hydro Environ Res (in press)
Oliver DM, Clegg CD, Heathwaite AL, Haygarth PM (2007) Preferential attachment of Escherichia coli to different particle size fractions of an agricultural grassland soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 185:369–375
Pachepsky YA, Garzio-Hadzick A, Shelton DR, Hadzick ZZ, Hill RL (2011) Survival of E. coli O157:H12 in creek sediments after inoculation and re-inoculation. Int J Environ Pollut 46:234–245
Pachepsky YA, Shelton DR (2011) Escherichia coli and fecal coliforms in freshwater and estuarine sediments. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 41:1067–1110
Pandey PK, Soupir ML, Haddad M, Rothwell JJ (2012) Assessing the impacts of watershed indexes and precipitation on spatial in-stream E. coli concentrations. Ecol Indic 23:641–652
Patin J, Mouche E, Ribolzi O, Chaplot V, Sengtahevanghoung O, Latsachak KO, Soulileuth B, Valentin C (2012) Analysis of runoff production at the plot scale during a long-term survey of a small agricultural catchment in Lao PDR. J Hydrol 426:79–92
Ribolzi O, Moussa R, Gaudu JC, Valles V, Voltz M (1997) Stream water regime change at autumn recharge on a Mediterranean farmed catchment using a natural tracer. Comptes Rendus De L Academie Des Sciences Serie Ii Fascicule a-Sciences De La Terre Et Des Planetes 324:985–992
Ribolzi O, Andrieux P, Valles V, Bouzigues R, Bariac T, Voltz M (2000) Contribution of groundwater and overland flows to storm flow generation in a cultivated Mediterranean catchment. Quantification by natural chemical tracing. J Hydrol 233:241–257
Ribolzi O, Cuny J, Sengsoulichanh P, Mousques C, Soulileuth B, Pierret A, Huon S, Sengtaheuanghoung O (2011a) Land use and water quality along a Mekong tributary in Northern Lao PDR. Environ Manag 47:291–302
Ribolzi O, Patin J, Bresson LM, Latsachack KO, Mouche E, Sengtaheuanghoung O, Silvera N, Thiebaux JP, Valentin C (2011b) Impact of slope gradient on soil surface features and infiltration on steep slopes in northern Laos. Geomorphology 127:53–63
Rochelle-Newall EJ, Nguyen TMH, Le TPQ, Sengtaheuanghoung O, Ribolzi O (2015) A short review of faecal indicator bacteria in tropical aquatic ecosystems: knowledge gaps and future directions. Front Microbiol 6:308
Saqalli M, Jourdren M, Maestripieri N, Guillerme S, Maire E, Soulileuth B, Latsachach K, Sounyafong P, Tammahuxsa L, Sengtaheuanghoung O, Ribolzi O, Becerra S (2015) Backward waters, modern waters: perception-based regional mapping territory uses and water-related sanitary stakes in Luang Phabang area (Lao PDR). Appl Geogr 60:184–193
Soil Survey Staff (1999) Soil taxonomy. A basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. USDA-NRCS
Stumpf CH, Piehler MF, Thompson S, Noble RT (2010) Loading of fecal indicator bacteria in North Carolina tidal creek headwaters: hydrographic patterns and terrestrial runoff relationships. Water Res 44:4704–4715
Sturma A, Becerra S (2012) L’assainissement à Mayotte à quel prix ? Entre vulnérabilité institutionnelle et sociale. In: Raynaud L, Poirot-Delpech S (eds) Par-delà le local et le global: Pour une socio-anthropologie de l’environnement. L’Harmattan, Paris, pp 207–223
Suter E, Juhl A, O’Mullan G (2011) Particle association of Enterococcus and total bacteria in the Lower Hudson River Estuary, USA. J Water Resour Prot 3:715–725
Taylor A, Blake WH, Couldrick L, Keith-Roach MJ (2012) Sorption behaviour of beryllium-7 and implications for its use as a sediment tracer. Geoderma 187–188:16–23
Taylor A, Blake WH, Smith HG, Mabit L, Keith-Roach MJ (2013) Assumptions and challenges in the use of fallout beryllium-7 as a soil and sediment tracer in river basins. Earth Sci Rev 126:85–95
Unanue M, Ayo B, Azúa I, Barcina I, Iriberri J (1992) Temporal variability of attached and free-living bacteria in coastal waters. Microb Ecol 23:27–39
Vigiak O, Ribolzi O, Pierret A, Sengtaheuanghoung O, Valentin C (2008) Trapping efficiencies of cultivated and natural riparian vegetation of northern Laos. J Environ Qual 37:889–897
WHO (2012) World Health Organisation global data repository, World Health Organisation, http://apps.who.int/ghodata/
World Bank (2009) Economic impacts of sanitation in Lao PDR
Yakirevich A, Pachepsky YA, Guber AK, Gish TJ, Shelton DR, Cho KH (2013) Modeling transport of Escherichia coli in a creek during and after artificial high-flow events: three-year study and analysis. Water Res 47:2676–2688
Ziegler AD, Sutherland RA, Giambelluca TW (2000) Partitioning total erosion on unpaved roads into splash and hydraulic components: the roles of interstorm surface preparation and dynamic erodibility. Water Resour Res 36:2787–2791
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Lao Department of Agriculture Land Management (DALAM) and the MSEC project (Multi-Scale Environment Changes) for their support. They are also grateful to Keo Oudone Latsachack, Bounsamai Soulileuth, Marie Arnoux and Elian Gourdin for their help during field and laboratory work. This work was financed by the French Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique EC2CO/BIOHEFECT program (Belcrue and Belkong projects) as well as by the French National Research Agency (TecItEasy project; ANR-13-AGRO-0007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribolzi, O., Evrard, O., Huon, S. et al. Use of fallout radionuclides (7Be, 210Pb) to estimate resuspension of Escherichia coli from streambed sediments during floods in a tropical montane catchment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 3427–3435 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5595-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5595-z