Abstract
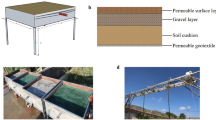
In this paper, the laboratory-scale permeable pavement layers, including a surface permeable brick layer, coarse sand bedding layers (thicknesses = 2, 3.5, and 5 cm), and single-graded gravel sub-base layers (thicknesses = 15, 20, 25, and 30 cm), were built to evaluate stormwater infiltration and surface runoff pollution reduction performance. And, the infiltration rate (I) and concentrations of suspended solids (SS), total phosphorus (TP), chemical oxygen demand (COD), ammonia nitrogen, and total nitrogen (TN) were measured under the simulated rainfall intensity of 72.4 mm/h over duration of 60 min. The results indicate that the thickness factor primarily influences the infiltration rate and pollutant removal rate. The highest steady infiltration rate was for surface brick layer 51.0 mm/h, for 5-cm sand bedding layer 32.3 mm/h, and for 30-cm gravel sub-base layer 42.3 mm/h, respectively. The SS average removal rate was relative higher (79.8∼98.6 %) for all layers due to the interception and filtration. The average removal rates of TP and COD were for surface layer 71.2 and 24.1 %, for 5-cm bedding layer 54.8 and 9.0 %, and for 20-cm sub-base layer 72.2 and 26.1 %. Ammonia nitrogen and TN cannot steadily be removed by layers according to the experiment results. The optimal thickness of bedding sands was 5 cm, and that of sub-base gravels was 20∼30 cm.

ᅟ
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bean EZ, Hunt WF, Bidelspach DA (2007) Evaluation of four permeable pavement sites in eastern North Carolina for runoff reduction and water quality impacts. J Irrig Drain E-Asce 133:583–592
Brattebo BO, Booth DB (2003) Long-term stormwater quantity and quality performance of permeable pavement systems. Water Res 37:4369–4376
Brezonik PL, Stadelmann TH (2002) Analysis and predictive models of stormwater runoff volumes, loads, and pollutant concentrations from watersheds in the Twin Cities metropolitan area, Minnesota, USA. Water Res 36(7):1743–1757
Cates EL, Westphal MJ, Cox JH, Calabria J, Patch SC (2009) Field evaluation of a proprietary storm-water treatment system: removal efficiency and relationships to peak flow, season, and dry time. J Environ Eng-Asce 135:511–517
Collins KA, Hunt WF, Hathaway JM (2008) Hydrologic comparison of four types of permeable pavement and standard asphalt in eastern north carolina. J Hydrol Eng 13:1146–1157
Coughlin JP, Campbell CD, Mays DC (2012) Infiltration and clogging by sand and clay in a pervious concrete pavement system. J Hydrol Eng 17:68–73
Davies JW, Pratt CJ, Scott MA (2002) Laboratory study of permeable pavement systems to support hydraulic modelling. Proc. of the 9th International Conf. on Urban Drainage (9ICUD), ASCE, Reston
Dierkes C, Kuhlmann L, Kandasamy J, Angelis G (2002) Pollution retention capability and maintenance of permeable pavements. In: proceedings of Ninth International Conference on Urban Drainage, American Society of Civil Engineers, 1-13
Dreelin EA, Fowler L, Carroll CR (2006) A test of porous pavement effectiveness on clay soils during natural storm events. Water Res 40:799–805
Eck BJ, Winston RJ, Hunt WF, Barrett ME (2012) Water quality of drainage from permeable friction course. J Environ Eng-Aace 138:174–181
Fassman EA, Blackbourn S (2010) Urban runoff mitigation by a permeable pavement system over impermeable soils. J Hydrol Eng 15:475–485
Geller G (1997) Horizontal subsurface flow systems in the German speaking countries: summary of long-term scientific and practical experience: recommendations. Water Sci Technol 35:157–166
Gilbert JK, Clausen JC (2006) Stormwater runoff quality and quantity from asphalt, paver, and crushed stone driveways in Connecticut. Water Res 40:826–832
Gnecco I, Berretta C, Lanza LG, La Barbera P (2005) Storm water pollution in the urban environment of Genoa, Italy. Atmos Res 77(1-4):60–73
Han J (2007) Process of ammonium ion-sieve's molding and its application on removal of ammonia in reclaimed water. Dissertation, Tianjin University (in Chinese)
Hou CL (2008) Study on the treatment of polluted river water by constructed rapid infiltration system. Dissertation, Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology (in Chinese)
Hu K (2009) Research on the water quality evaluation and use of rain on city area. Dissertation, Harbin Institute of Technology (in Chinese)
Kuang X, Fu Y (2013) Coupled infiltration and filtration behaviours of concrete porous pavement for stormwater management. Hydrol Process 27:532–540
Li Z, Fu K, Xia QB (2007) Modification of natural zeolite and adsorption of ammonia nitrogen by modified natural zeolite. J South Chin Univ Technol (Nat Sci Edit) 35:6–10 (in Chinese)
Liu XP (2008) Study on the water-effects of unsaturated-soil roadbed and water-transfer characteristics in the roadbed. Dissertation, Hunan University (in Chinese)
Lv G, Hao XY (2008) Review on influential factors of soil infiltration characteristics. Chin Agric Sci Bull 24:494–499 (in Chinese)
Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China (2008) Engineering Technical Code for Rain Utilization in Building and Sub-District (GB 50400-2006). China Architecture & Building Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Nnadi EO, Coupe SJ, Sanudo-Fontaneda LA, Rodriguez-Hernandez J (2014) An evaluation of enhanced geotextile layer in permeable pavement to improve stormwater infiltration and attenuation. Int J Pavement Eng 15:925–932
Pan AJ, Zhang SH, Chen JG, Ding YY (2010) Study and application on the comprehensive utilization technology of urban rainwater. China Water & Power Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Park DG, Sandoval N, Lin W, Kim H, Cho YH (2014) A case study: evaluation of water storage capacity in permeable block pavement. Ksce J Civ Eng 18:514–520
Pezzaniti D, Beecham S, Kandasamy J (2009) Influence of clogging on the effective life of permeable pavements. P I Civil Eng-Wat M 162:211–220
Rodriguez-Hernandez J, Castro-Fresno D, Fernandez-Barrera AH, Vega-Zamanillo A (2012) Characterization of infiltration capacity of permeable pavements with porous asphalt surface using cantabrian fixed infiltrometer. J Hydrol Eng 17:597–603
Rushton BT (2001) Low-impact parking lot design reduces runoff and pollutant loads. J Water Res Pl-Asce 127:172–179
Sanudo-Fontaneda LA, Rodriguez-Hernandez J, Vega-Zamanillo A, Castro-Fresno D (2013) Laboratory analysis of the infiltration capacity of interlocking concrete block pavements in car parks. Water Sci Technol 67:675–681
Sanudo-Fontaneda LA, Charlesworth SM, Castro-Fresno D, Andres-Valeri VCA, Rodriguez-Hernandez J (2014a) Water quality and quantity assessment of pervious pavements performance in experimental car park areas. Water Sci Technol 69:1526–1533
Sanudo-Fontaneda LA, Rodriguez-Hernandez J, Calzada-Perez MA, Castro-Fresno D (2014b) Infiltration Behaviour of Polymer-Modified Porous Concrete and Porous Asphalt Surfaces used in SuDS Techniques. Clean-Soil Air Water 42:139–145
Shen LQ, Che W, Li HY, He WH, Li SQ (2009) Urban road rainwater runoff pollution and its control measures in China. China Water Wastewater 25(4):23–28 (in Chinese)
Srimurali M, Pragathi A, Karthikeyan J (1998) A study on removal of fluorides from drinking water by adsorption onto low-cost materials. Environ Pollut 99:285–289
Tota-Maharaj K, Scholz M (2010) Efficiency of permeable pavement systems for the removal of urban runoff pollutants under varying environmental conditions. Environ Prog Sustain 29:358–369
Xiong GX (2007) Research on the behavior and removal mechanism of phosphorus in wetland. Dissertation, Guangdong University of Technology (in Chinese)
Yang X, You XY, Ji M, Nima C (2013) Influence factors and prediction of stormwater runoff of urban green space in Tianjin, China: laboratory experiment and quantitative theory model. Water Sci Technol 67:869–876
Zhang QG (2005) Study on the analysis methods of rainfall infiltration capacity. Dissertation, Shandong University (in Chinese)
Zhang SN, Li XJ (2008) Pollution feature of road surface runoff in urban district of Tianjin. Environ Sci Manag 33(2):25–28 (in Chinese)
Zhou YH (2007) The Simulation and control on stormwater runoff pollution of urban residential district. Dissertation, Hu Nan University (in Chinese)
Zhu T (1999) Phosphate sorption and chemical characteristics of lightweight aggregates (LWA)-potential filter media in treatment wetlands. Water Sci Technol 35:103–108
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51308305), the National Water Pollution Control and Management Technology Major Projects of China (2014ZX07203-009), and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of China. It is also very thankful for the Tianjin Urban Construction Design Institute for their help during the experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, ZG., Lv, ZW., Zhang, Y. et al. Stormwater infiltration and surface runoff pollution reduction performance of permeable pavement layers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 2576–2587 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5466-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5466-7