Abstract
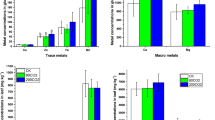
Predicting the soil-to-plant transfer of metals in the context of global warming has become a major issue for food safety. It requires a better understanding of how the temperature alters the bioavailability of metals in cultivated soils. This study focuses on one agricultural soil contaminated by Cd, Zn and Pb. DGT measurements were performed at 10, 20 and 30 °C to assess how the bioavailability of metals was affected by a rise in soil temperature. A lettuce crop was cultivated in the same conditions to determine if the soil-to-plant transfer of metals increased with a rise in soil temperature. A gradual decline in Cd and Zn bioavailability was observed from 10 to 30 °C, which was attributed to more intense complexation of metals in the pore water at higher temperatures. Together with its aromaticity, the affinity of dissolved organic matter (DOM) for metals was indeed suspected to increase with soil temperature. One main output of the present work is a model which satisfactorily explains the thermal-induced changes in the characteristics of DOM reported in Cornu et al. (Geoderma 162:65–70, 2011) by assuming that the mineralization of initial aliphatic compounds followed a first-order reaction, increased with soil temperature according to the Arrhenius law, and due to a priming effect, led to the appearance of aromatic molecules. The soil-to-plant transfer of Cd and Zn was promoted at higher soil temperatures despite a parallel decrease in Cd and Zn bioavailability. This suggests that plant processes affect the soil-to-plant transfer of Cd and Zn the most when the soil temperature rises.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almas AR, Singh BR (2001) Plant uptake of cadmium-109 and zinc-65 at different temperature and organic matter levels. J Environ Qual 30:869–877
Almas A, Singh BR, Salbu B (1999) Mobility of cadmium-109 and zinc-65 in soil influenced by equilibration time, temperature, and organic matter. J Environ Qual 28:1742–1750
Amery F, Degryse F, Degeling W, Smolders E, Merckx R (2007) The copper-mobilizing-potential of dissolved organic matter in soils varies 10-fold depending on soil incubation and extraction procedures. Environ Sci Technol 41:2277–2281
Antoniadis V, Alloway BJ (2001) Availability of Cd, Ni and Zn to ryegrass in sewage sludge-treated soils at different temperatures. Water Air Soil Pollut 132:201–214
Bade R, Oh S, Shin WS (2012) Diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) for the prediction of bioavailability of heavy metals in contaminated soils to earthworm (Eisenia foetida) and oral bioavailable concentrations. Sci Total Environ 416:127–136
Barrow NJ (1992) A brief discussion on the effect of temperature on the reaction of inorganic ions with soil. J Soil Sci 43:37–45
Chin YP, Aiken GR, Danielsen KM (1997) Binding of pyrene to aquatic and commercial humic substances: the role of molecular weight and aromaticity. Environ Sci Technol 31:1630–1635
Cornu JY, Denaix L (2006) Prediction of zinc and cadmium phytoavailability within a contaminated agricultural site using DGT. Environ Chem 3:61–64
Cornu JY, Denaix L, Schneider A, Pellerin S (2008) Temporal variability of solution Cd2+ concentration in metal-contaminated soils as affected by soil temperature: consequences on lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) exposure. Plant Soil 307:51–65
Cornu JY, Schneider A, Jezequel K, Denaix L (2011) Modelling the complexation of Cd in soil solution at different temperatures using the UV-absorbance of dissolved organic matter. Geoderma 162:65–70
Cox LM, Boersma L (1967) Transpiration as a function of soil temperature and soil water stress. Plant Physiol 42:550–556
Davranche M, Bollinger JC, Bril H (2003) Effect of reductive conditions on metal mobility from wasteland solids: an example from the Mortagne-du-Nord site (France). Appl Geochem 18:383–394
Fest EPMJ, Temminghoff EJM, Comans RNJ, vanRiemsdijk WH (2008) Partitioning of organic matter and heavy metals in a sandy soil: effects of extracting solution, solid to liquid ratio and pH. Geoderma 146:66–74
Fontaine S, Bardoux G, Benest D, Verdier B, Mariotti A, Abbadie L (2004) Mechanisms of the priming effect in a savannah soil amended with cellulose. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:125–131
Fritioff A, Kautsky L, Greger M (2005) Influence of temperature and salinity on heavy metal uptake by submersed plants. Environ Pollut 133:265–274
Groenenberg JE, Koopmans GF, Comans RNJ (2010) Uncertainty analysis of the nonideal competitive adsorption-Donnan model: effects of dissolved organic matter variability on predicted metal speciation in soil solution. Environ Sci Technol 44:1340–1346
Gustafsson JP (2012) Visual MINTEQ version 3.0. http://rymd.lwr.kth.se/English/OurSoftware/vminteq/
Hart JJ, Welch RM, Norvell WA, Sullivan LA, Kochian LV (1998) Characterization of cadmium binding, uptake, and translocation in intact seedlings of bread and durum wheat cultivars. Plant Physiol 116:1413–1420
IPCC AR5 WG1 (2013) In: Stocker TF et al. (eds) Climate Change 2013: the physical science basis. Working Group 1 (WG1) contribution to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 5th Assessment Report (AR5), Cambridge University Press
Kinniburgh DG, Milne CJ, Benedetti MF, Pinheiro JP, Filius J, Koopal LK, vanRiemsdijk WH (1996) Metal ion binding by humic acid: application of the NICA-Donnan model. Environ Sci Technol 30:1687–1698
Kuzyakov Y (2002) Review: factors affecting rhizosphere priming effects. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 165:382–396
Li Y, Zhang Q, Wang R, Gou X, Wang H, Wang S (2012) Temperature changes the dynamics of trace element accumulation in Solanum tuberosum L. Clim Chang 112:655–672
Lu LI, Ke S, Tian XE, Yang T, Li Q, He ZI (2009) Cadmium uptake and xylem loading are active processes in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J Plant Physiol 166:579–587
Luo J, Cheng H, Ren J, Davison W, Zhang H (2014) Mechanistic insights from DGT and soil solution measurements on the uptake of Ni and Cd by radish. Environ Sci Technol 48:7305–7313
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic, London
Martınez CE, Jacobson AR, McBride MB (2003) Aging and temperature effects on DOC and elemental release from a metal contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 122:135–143
McNicol RD, Beckett PHT (1985) Critical tissue concentrations of potentially toxic elements. Plant Soil 85:107–129
Merckx R, Brans K, Smolders E (2001) Decomposition of dissolved organic carbon after soil drying and rewetting as an indicator of metal toxicity in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 33:235–240
Milne CJ, Kinniburgh DG, VanRiemsdijk WH, Tipping E (2003) Generic NICA-Donnan model parameters for metal-ion binding by humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 37:958–971
Miyasak S, Grunes D (1997) Root zone temperature and calcium effects on phosphorus, sulfur, and micronutrients in winter wheat forage. Agron J 89:742–748
Nolan AL, Zhang H, McLaughlin MJ (2005) Prediction of zinc, cadmium, lead, and copper availability to wheat in contaminated soils using chemical speciation, diffusive gradients in thin films, extraction, and isotopic dilution techniques. J Environ Qual 34:496–507
Pourghasemian N, Ehsanzadeh P, Greger M (2013) Genotypic variation in safflower (Carthamus spp.) cadmium accumulation and tolerance affected by temperature and cadmium levels. Environ Exp Bot 87:218–226
Prasad MNV (2004) Heavy metal stress in plants. Springer, Berlin
Quenea K, Lamy I, Winterton P, Bermond A, Dumat C (2009) Interactions between metals and soil organic matter in various particle size fractions of soil contaminated with waste water. Geoderma 149:217–223
Rey-Castro C, Mongin S, Huidobro C, David C, Salvador J, Garces JL, Galceran J, Mas F, Puy J (2009) Effective affinity distribution for the binding of metal ions to a generic fulvic acid in natural waters. Environ Sci Technol 43:7184–7191
Sauvé S, Hendershot W, Allen HE (2000) Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: dependence on pH, total metal burden and organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 34:1125–1131
Weishaar JL, Aiken GR, Bergamaschi BA, Fram MS, Fujii R, Mopper K (2003) Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ Sci Technol 37:4702–4708
Yin Y, Impellitteri CA, You SJ, Allen HE (2002) The importance of organic matter distribution and exact soil: solution ratio on the desorption of heavy metals from soils. Sci Total Environ 287:107–119
Yu XZ, Peng XY, Xing LQ (2010) Effect of temperature on phytoextraction of hexavalent and trivalent chromium by hybrid willows. Ecotoxicology 19:61–68
Zhang H, Zhao FJ, Sun B, Davison W, McGrath SP (2001) A new method to measure effective soil solution concentration predicts copper availability to plants. Environ Sci Technol 35:2602–2607
Zhao FJ, Hamon RE, Lombi E, McLaughlin MJ, McGrath SP (2002) Characteristics of cadmium uptake in two contrasting ecotypes of the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. J Exp Bot 53:535–543
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Sylvie Bussière, Cécile Fontaine, Alain Vives and Stéphane Thunot for their technical assistance. Financial support of this work was provided by the region Aquitaine (France) and the ToxNucE programme (CEA-CNRS-INRA-INSERM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cornu, JY., Denaix, L., Lacoste, J. et al. Impact of temperature on the dynamics of organic matter and on the soil-to-plant transfer of Cd, Zn and Pb in a contaminated agricultural soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 2997–3007 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5432-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5432-4