Abstract
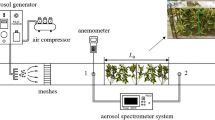
Particulate matter (PM) pollution has been increasingly becoming serious in Beijing and has drawn the attention of the local government and general public. This study was conducted during early spring of 2013 and 2014 to monitor the concentration of PM at three different land surfaces (bare land, urban forest, and lake) in the Olympic Park in Beijing and to analyze its effect on the concentration of meteorological factors and the dry deposition onto different land cover types. The results showed that diurnal variation of PM concentrations at the three different land surfaces had no significant regulations, and sharp short-term increases in PM10 (particulate matter having an aerodynamic diameter <10 μm) occurred occasionally. The concentrations also differed from one land cover type to another at the same time, but the regulation was insignificant. The most important meteorological factor influencing the PM concentration is relative humidity; it is positively correlated with the PM concentration. While in the forests, the wind speed and irradiance also influenced the PM concentration by affecting the capture capacity of trees and dry deposition velocity. Other factors were not correlated with or influenced by the PM concentration. In addition, the hourly dry deposition in unit area (μg/m2) onto the three types of land surfaces and the removal efficiency based on the ratio of dry deposition and PM concentration were calculated. The results showed that the forest has the best removal capacity for both PM2.5 (particulate matter having an aerodynamic diameter <2.5 μm) and PM10 because of the faster deposition velocity and relatively low resuspension rate. The lake’s PM10 removal efficiency is higher than that of the bare land because of the relatively higher PM resuspension rates on the bare land. However, the PM2.5 removal efficiency is lower than that of the bare land because of the significantly lower dry deposition velocity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato F, Pandolfi M, Viana M (2009) Spatial and chemical patterns of PM10 in road dust deposited in urban environment. Atmos Environ 43(9):1650–1659
Balestrini R, Arisci S, Brizzio MC, Mosello R, Rogora M, Tagliaferri A (2007) Dry deposition of particles and canopy exchange: comparison of wet, bulk and throughfall deposition at five forest sites in Italy. Atmos Environ 41(4):745–756
Baumgardner D, Varela S, Escobedo FJ, Chacalo A, Ochoa C (2012) The role of a peri-urban forest on air quality improvement in the Mexico city megalopolis. Environ Pollut 163:174–183
Beckett KP, Freer-Smith PH, Taylor G (1998) Urban woodlands: their role in reducing the effects of particulate pollution. Environ Pollut 99(3):347–360
Beckett KP, Freer-Smith P, Taylor G (2000) Effective tree species for local air quality management. J Arboric 26(1):12–19
Beckett KP, Freer-Smith PH, Taylor G (2006) Particulate pollution capture by urban trees: effect of species and wind speed. Glob Chang Biol 6:995–1003
Brack CL (2002) Pollution mitigation and carbon sequestration by an urban forest. Environ Pollut 116:S195–S200
Cavanagh JE, Zawar-Reza P, Wilson JG (2009) Spatial attenuation of ambient particulate matter air pollution within an urbanised native forest patch. Urban For Urban Green 8(1):21–30
Chamberlain AC (1975) The movement of particles in plant communities. Veg Atmos 1:155–203
Chen H, Liu CL (2014) Assessment of the effect of PM2.5 reduction by plain afforestation project in beijing based on dry deposition model. Chin J Ecol 33(11):2897–2904
Cheng M, Horng C, Lin Y (2007) Characteristics of atmospheric aerosol and acidic gases from urban and forest sites in central Taiwan. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79(6):674–677
Croxford B, Penn A, Hillier B (1996) Spatial distribution of urban pollution: civilizing urban traffic. Sci Total Environ 189:3–9
Derwent RG (1996) EPAQS recommendations--can they be implemented. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 63rd national society for clean Air environmental protection conference and exhibition. National Society for Clean Air, Brighton
Dockery DW, Pope CA, Xu X, Spengler JD, Ware JH, Fay ME (1993) An association between air pollution and mortality in six US cities. N Engl J Med 329(24):1753–1759
Dzierżanowski K, Popek R, Gawrońska H, Sæbø A, Gawroński SW (2011) Deposition of particulate matter of different size fractions on leaf surfaces and in waxes of urban forest species. Int J Phytoremediation 13(10):1037–1046
Edwards R (1996) Smog blights babies in the womb. New Sci 152(2052):4
Erisman JW, Draaijers G (2003) Deposition to forests in Europe: most important factors influencing dry deposition and models used for generalisation. Environ Pollut 124(3):379–388
Erisman JW, Grennfelt P, Sutton M (2003) The European perspective on nitrogen emission and deposition. Envion Int 29(2–3):311–325
Escobedo FJ, Nowak DJ (2009) Spatial heterogeneity and air pollution removal by an urban forest. Landsc Urban Plan 90:102–110
Escobedo FJ, Wagner JE, Nowak DJ, De la Maza CL, Rodriguez M, Crane DE (2008) Analyzing the cost effectiveness of Santiago, Chile’s policy of using urban forests to improve air quality. J Environ Manag 86(1):148–157
Fisher R (1955) Statistical method and scientific induction. J R Stat 17(1):69–87
Freer-Smith P, El-Khatib A, Taylor G (2004) Capture of particulate pollution by trees: a comparison of species typical of semi-arid areas with european and north american species. Water Air Soil Pollut 155:173–187
Great B (1995) Asthma and outdoor Air pollution. HMSO, London
Grimm EC (1988) Data analysis and display. Springer, Netherlands
Khan FI, Abbasi SA (2000) Attenuation of gaseous pollutants by greenbelts. Environ Monit Assess 64(2):457–475
Khong KS, Liu W (2002) Calculation of critical values for dunnet and Tamhane’s step-up multiple test procedure. Stat Prob Lett 49(4):411–416
MacKenzie JJ, El-Ashry MT (1989) Air pollution’s toll on forests and crops. Yale University Press, New Haven
McDonald AG, Bealey WJ, Fowler D, Dragosits U, Skiba U, Smith RI (2007) Quantifying the effect of urban tree planting on concentrations and depositions of PM < sub > 10 in two UK conurbations. Atmos Environ 41(38):8455–8467
Nowak DJ, Crane DE, Stevens JC (2006) Air pollution removal by urban trees and shrubs in the united states. Urban For Urban Green 4:115–123
Nowak DJ, Hirabayashi S, Bodine A (2013) Modeled PM2.5 removal by trees in ten US. Cities and associated health effects. Environ Pollut 178:395–402
Ould-Dada Z (2002) Dry deposition profile of small particles within a model spruce canopy. Sci Total Environ 286(1):83–96
Petroff A, Mailliat A, Amielh M, Anselmet F (2008) Aerosol dry deposition on vegetative canopies. Part I: review of present knowledge. Atmos Environ 42(16):3625–3653
Pullman M (2009) Conifer PM2.5 deposition and re-suspension in wind and rain events. Cornell University, Ithaca
Reinap A, Wiman BL, Svenningsson B, Gunnarsson S (2009) Oak leaves as aerosol collectors: relationships with wind velocity and particle size distribution. Experimental results and their implications. Trees 23(6):1263–1274
Ruijgrok W, Tieben H, Eisinga P (1997) The dry deposition of particles to a forest canopy: a comparison of model and experimental results. Atmos Environ 31(3):399–415
Sabin LD, Hee Lim J, Teresa Venezia M, Winer AM, Schiff KC, Stolzenbach KD (2006) Dry deposition and resuspension of particle-associated metals near a freeway in Los Angeles. Atmos Environ 40(39):7528–7538
Shan Y, Jingping C, Liping C, Zhemin S, Xiaodong Z, Dan W (2007) Effects of vegetation status in urban green spaces on particle removal in a street canyon atmosphere. Acta Ecol Sin 27(11):4590–4595
Shannigrahi AS, Fukushima T, Sharma RC (2004) Anticipated air pollution tolerance of some plant species considered for green belt development in and around an industrial/urban area in India: an overview. Int J Environ Stud 61(2):125–137
Slinn SA, Slinn WGN (1980) Predictions for particle deposition on nature waters. Atmos Environ 14:1013–1016
Tallis M, Taylor G, Sinnett D (2011) Estimating the removal of atmospheric particulate pollution by the urban tree canopy of London under current and future environments. Landsc Urban Plan 103:129–138
Tiwary A, Morvan HP, Colls JJ (2006) Modelling the size-dependent collection efficiency of hedgerows for ambient aerosols. J Aerosol Sci 37(8):990–1015
Tiwary A, Reff A, Colls JJ (2008) Collection of ambient particulate matter by porous vegetation barriers: sampling and characterization methods. J Aerosol Sci 39(1):40–47
Vedal S (1995) Health effects of inhalable particles: Implications for British Columbia: the ministry
Wang XF (1999) Determination of concentrations of elements in the atmospheric aerosol of the urban and rural areas of beijing in winter. Biol Trace Elem Res 71(1):203–208
Wang YC (2011) Carbon sequestration and foliar dust retention by woody plants in the greenbelts along two major Taiwan highways. Ann Appl Biol 159(2):244–251
Watkins LH (1991) Air pollution from road vehicles. HMSO, London
Williams RM (1982) A model for the dry deposition of particles to nature water surfaces. Atmos Environ 16(8):1933–1938
Willis KG, Garrod G, Scarpa R, Powe N, Lovett A, & Bateman IJ (2003) The social and environmental benefits of forests in Great Britain. Newcastle University, Centre for Research in Environmental Appraisal and Management
Wuyts K, Verheyen K, De Schrijver A, Cornelis WM, Gabriels D (2008) The impact of forest edge structure on longitudinal patterns of deposition, wind speed, and turbulence. Atmos Environ 42(37):8651–8660
Yang J, McBride J, Zhou J, Sun Z (2005) The urban forest in beijing and its role in air pollution reduction. Urban For Urban Green 3(2):65–78
Zhang W, Sun Y, Zhuang G, Xu D (2006) Characteristics and seasonal variations of PM2. 5, PM10, and TSP aerosol in beijing. Biomed Environ Sci 19(6):461
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by The Forestry Public Welfare Project of China (201304301), Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Project (Z141100006014031) and Youth Foundation of Beijing Municipal Bureau of Landscape and Forestry (20100014120011). Thanks to two anonymous reviewers and editor for their help in improving a previous version of this manuscript. Jiakai Liu and Lichun Mo contributed equally to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Mo, L., Zhu, L. et al. Removal efficiency of particulate matters at different underlying surfaces in Beijing. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 408–417 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5252-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5252-6