Abstract
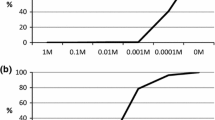
Hair shampoos are among the most commonly used chemicals in everyday life. Since shampoos are a major component of domestic and municipal wastewater, they may affect plants when irrigated with wastewater. However, their effects on plants have never been investigated in detail. The present study was aimed to evaluate the effect of some commonly used hair shampoos on seed germination and seedling vigor of Brassica napus. Seeds of Brassica napus were exposed to different concentrations of hair shampoos, i.e., 0 (control), 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, and 10 %. The obtained results revealed that germination was not very sensitive to shampoo stress and was significantly inhibited only at the highest tested concentration (10 %) of shampoo except in the case of one shampoo where it was inhibited at concentration of 1 % or above. The other tested parameters of Brassica napus were comparatively more sensitive than germination to shampoo stress. However, at lower concentrations of shampoos, stimulatory effects were also observed in some cases. Although no exact data is available on shampoo concentration in wastewater used for irrigation, it is unlikely that shampoo concentration in irrigation water reach so high and pose adversity to plants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleavia (2012) Are the products in your home dangerous? Special Health Report. URL: http://aleavia.com/uploads/newsletter_aleavia3reduced.pdf
Azizullah A, Richter P, Häder D-P (2011a) Ecotoxicological evaluation of wastewater samples from Gadoon Amazai Industrial Estate (GAIE), Swabi, Pakistan. Int J Environ Sci 1(5):959–976
Azizullah A, Khattak MNK, Richter P, Häder D-P (2011b) Water pollution in Pakistan and its impact on public health—a review. Environ Int 37:479–497
Bewley DJ, Black M (1994) Seeds: physiology of development and germination. Plenum Press, New York
Bradford JK (1995) Water relations in seed germination. In: Kigel J, Galili G (eds) Seed development and germination. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, p 351–396
Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2002) NH4+ toxicity in higher plants: a critical review. J Plant Physiol 159:567–584. doi:10.1078/0176-1617-0774
Campion MJ, Hobson-Jobson (2012) The words English owes to India BBC News. 11 July 2012
Chawla G, Viswanathan PN, Devi S (1987) Biochemical studies on the toxicity of linear alkyl benzene sulphonate to Scenedesmus quadricauda in culture. Environ Exp Bot 27:311–319
Danilov RA, Ekelund NGA (2001) Effects of Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, Zn2+ and pentachlorophenol on photosynthesis and motility in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in short-term exposure experiments. BMC Ecol 1:1
EPA (2005) Protecting water quality from agricultural runoff. Fact Sheet No. EPA-841-F-05-001. Environmental Protection Agency
Finkel R, Cubeddu LX, Clark MA (2009) Pharmacology, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, p 411
Kagalwala AY, Kavitha K (2012) International journal of life sciences and biotechnology and pharma research Hyderabad, India
Khan JA (2011) Marketing plan 1. URL: http://www.scribd.com/doc/72244711/Marketing-Plan-1#scribd
Laine DC (2007) North Carolina Department of Agriculture: plant nutrients
Lamore SD, Cabello CM, Wondrak GT (2010) The topical antimicrobial zinc pyrithione is a heat shock response inducer that causes DNA damage and PARP-dependent energy crisis in human skin cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 15(3):309–322
Lee LW (2011) Organic shampoo. Home guide. URL: http://homeguides.sfgate.com/organic-shampoo-78367.html
Leung S, Gironella A, Trigo C, Bhushan A, Daniels CK, Lai JCK (2007) Cationic surfactants and other factors that affect enzymatic activities and transport. Proc Inst Mech Eng H J Eng Med 221(2):153–160
Mandal RA, Yadav BKV (2009) Reduced emission avoiding deforestation and forest degradation (REDD) initiatives in Nepal
Markina ZV, Aizdaicher NA (2007) Influence of laundry detergents on the abundance dynamics and physiological state of the benthic microalga Attheya ussurensis (Bacillariophyta) in laboratory culture. Russ J Mar Biol 33:391–398
Markina ZV, Aizdaycher NA (2010) Influence of the ariel detergent on the growth and physiological state of the unicellular algae Dunaliella salina (Chlorophyta) and Plagioselmis prolonga (Cryptophyta). Hydrobiol J 46:49–56
Moya I, Silvestri M, Vallon O, Cinque G, Bassi R (2001) Time-resolved fluorescence analysis of the photosystem II antenna proteins in detergent micelles and liposomes. Biochemistry 40:12552–12561
Miller JG (2005) The essential role of culture in developmental psychology. New Dir Child Adolesc Dev 2005:33–41
Movahedian H, Bina B, Asghari GH (2005) Toxicity evaluation of wastewater treatment plant effluents using Daphnia magna. Iranian J Environ Health Sci Eng 2:1–4
Nyberg H, Koskimies-Soininen K (1984) The phospholipid fatty acids of Porphyridium purpureum cultured in the presence of Triton X-100 and sodium desoxycholate. Phytochemistry 23:2489–2493
Osmond CB, Bjorkman O, Anderson DJ (1980) Physiological processes in plant ecology. Toward a synthesis with Atriplex. Springer-Verlag, New York
Reeder NL, Kaplan J, Xu J, Youngquist RS, Wallace J, Hu P, Saunders CW (2011) Zinc pyrithione inhibits yeast growth through copper influx and inactivation of iron-sulfur proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:5753–5760
Richardson D, Plewa J, Wagner D, Schoeny R, Demarini M (2007) Occurrence, genotoxicity, and carcinogenicity of regulated and emerging disinfection by-products in drinking water: a review and roadmap for research. Mutat Res 636(1–3):178–242
Richter E, Wick A, Ternes TA, Coors A (2013) Ecotoxicity of climbazole, a fungicide contained in antidandruff shampoo. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:2816–2825
Robbins CR, Robbins CR (2002) Chemical and physical behavior of human hair, 4th edn. Springer, New York
Rosen M J, Kunjappu JT (2012) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena. John Wiley & Sons
Sánchez-Bayo F, Goka K (2005) Unexpected effects of zinc pyrithione and imidacloprid on Japanese medaka fish (Oryzias latipes). Aquat Toxicol 74(4):285–293
Schnuch A, Geier J, Utur W, Frosch PJ (1998) Patch testing with preservatives, antimicrobials and industrial biocides: results from a multicentre study. Br J Dermatol 137:467–476
Simon EW (1984) Early events in germination. In: Murray DR (ed) Seed physiology. Academic Press, Australia
Uhvits R (1946) Effect of osmotic pressure on water absorption and germination of alfalfa seeds. Am J Bot 33:278–284
Warne MSJ, Schifko AD (1999) Toxicity of laundry detergent components to a freshwater cladoceran and their contribution to detergent toxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 44:196–206
Werner JE, Finkelstein RR (1995) Arabidopsis mutants with reduced response to NaCl and osmotic stress. Physiol Plant 93: 659–666
West L (2006) World water day: a billion people worldwide lack safe drinking water. URL: envi-ronment.about.com
Yamada T, Alpers DH et al. (2009) Textbook of gastroenterology (5th ed.). Chichester, West Sussex: Blackwell Pub. ISBN 978-1-4051-6911-0
Yuan L, Loqué D, Kojima S, Rauch S, Ishiyama K et al (2007) The organization of high affinity ammonium uptake in Arabidopsis roots depends on the spatial arrangement and biochemical properties of AMT1-type transporters. Plant Cell 19:2636–2652
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to all the staff at the department of Botany, KUST, for their support. We also acknowledge KUST for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naeem, F., Ahmed, F., Kanwal, M. et al. Phytotoxicity evaluation of some commonly used shampoos using Brassica napus L.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 15164–15170 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5054-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5054-x