Abstract
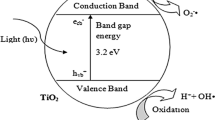
To better understand the potential impacts of metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs) on Gram(+) Bacillus subtilis and Gram(−) Escherichia coli (K12) bacteria, eight different nanosized titanium dioxide (TiO2) suspensions with five different concentrations were used. Water quality parameters (pH, temperature, and ionic strength), light sources, and light intensities were also changed to achieve different environmental conditions. The photosensitive TiO2 NPs were found to be harmful to varying degrees under ambient conditions, with antibacterial activity increasing with primary particle sizes from 16 to 20 nm. The presence of light was a significant factor under most conditions tested, presumably due to its role in promoting generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). However, bacterial growth inhibition was also observed under dark conditions and different water quality parameters, indicating that undetermined mechanisms additional to photocatalytic ROS production were responsible for toxicity. The results also indicated that nano-TiO2 particles in the absence and the presence of photoactivation induced lipid peroxidation and cellular respiration disruption.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams LK, Lyon DY, Alvarez PJJ (2006) Comparative eco-toxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Res 40:3527–3532
Battin T, Kammer FVD, Weilhartner A, Ottofuelling S, Hofmann T (2009) Nanostructured TiO2: transport behavior and effects on aquatic microbial communities under environmental conditions. Environ Sci Technol 43(21):8098–8104
Caballero L, Whitehead KA, Allen NS, Verran J (2009) Inactivation of Escherichia coli on immobilized TiO2 using fluorescent light. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 202(2–3):92–98
Cheng CL, Sun DS, Chu WC, Tseng YH, Ho HC, Wang JB, Chung PH, Chen JH, Tsai PJ, Lin NT, Yu MS, Chang HH (2009) The effects of the bacterial interaction with visible-light responsive titania photocatalyst on the bactericidal performance. J Biomed Sci 16(7):10
Cho M, Chung H, Choi W, Yoon J (2004) Linear correlation between inactivation of E. coli and OH radical concentration in TiO2 photocatalytic disinfection. Water Res 38(4):1069–1077
Christensen PA, Curtis TP, Egerton TA, Kosa SAM, Tinlin JR (2003) Photoelectrocatalytic and photocatalytic disinfection of E. coli suspensions by titanium dioxide. Appl Cat B Environ 41(4):371–386
Clément L, Hurel C, Marmier N (2013) Toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to cladocerans, algae, rotifers and plants—effects of size and crystalline structure. Chemosphere 90(3):1083–1090
Coleman HM, Marquis CP, Scott JA, Chin SS, Amal R (2005) Bactericidal effects of titanium dioxide-based photocatalysts. Chem Eng J 113(1):55–63
Dadjour MF, Ogino C, Matsumura S, Shimizu N (2005) Kinetics of disinfection of Escherichia coli by catalytic ultrasonic irradiation with TiO2. Biochem Eng J 25:243–248
Dong CD, Liao YL, Kao CM, Chen CW, Lin HY, Huang CP (2007) Preparation of crystalline nanosized titania by microemulsion: evaluation of process variables. J Adv Ox Technol 10(2):399–404
Erdem A, Cha D, Huang CP (2007) Chapter 9: Growth and some enzymatic responses of E. coli to photocatalytic TiO2. In: Grassian VH, editor. Nanoscience and nanotechnology: environmental and health impact: Wiley. p 496.
Erdem A, Metzler D, Cha D, Huang CP (2014) Inhibition of bacteria by photocatalytic nano-TiO2 particles in the absence of light. Int J Environ Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s13762-014-0729-2
Foster HA, Ditta IB, Varghese S (2011) Photocatalytic disinfection using titanium dioxide: spectrum and mechanism of antimicrobial activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1847–1868
Gogniat G, Thyssen M, Denis M, Pulgarin C, Dukan S (2006) The bactericidal effect of TiO2 photocatalysis involves adsorption onto catalyst and the loss of membrane integrity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 258(1):18–24
Gumy D, Rincon AG, Hajdu R, Pulgarin C (2006a) Solar photocatalysis for detoxification and disinfection of water: different types of suspended and fixed TiO2 catalysts study. Sol Energy 80(10):1376–1381
Gumy D, Morais C, Pulgarin C, Giraldo S, Hajdu R, Kiwi J (2006b) Catalytic activity of commercial of TiO2 powders for the abatement of the bacteria (E. coli) under solar simulated light: influence of the isoelectric point. Appl Cat B Environ 63(1–2):76–84
Handy RD, Shaw BJ (2007) Toxic effects of nanoparticles and nanomaterials: implications for public health, risk assessment and the public perception of nanotechnology. Health Risk Soc 9(2):125–144
Hu C, Guo J, Qu J, Hu X (2007) Photocatalytic degradation of pathogenic bacteria with AgI/TiO2 under visible light irradiation. Langmuir 23(9):4982–4987
Huang N, Xiao Z, Huang D, Yuan C (1998) Photochemical disinfection of Escherichia coli with a TiO2 colloid solution and a self-assembled TiO2 thin film. Supramol Sci 5:559–564
Huang Z, Maness P-C, Blake DM, Wolfrum EJ, Smolinski SL, Jacoby WA (2000) Bactericidal mode of titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 130:163–170
Kikuchi Y, Sunada K, Iyoda T, Hashimoto K, Fujishima A (1997) Photocatalytic bactericidal effect of TiO2 thin films: dynamic view of the active oxygen species responsible for the effect. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 106(1–3):51–56
Lee NA, Yoon M, Song NW (2012) Photochemical properties and cytotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles depending on the degree of agglomeration. XX IMEKO World Congress, Metrology for Green Growth, Busan, Republic of Korea
Lin X, Li J, Ma S, Liu G, Yang K et al (2014) Toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to Escherichia coli: effects of particle size, crystal phase and water chemistry. PLoS One 9(10), e110247
Liu HL, Yang TCK (2003) Photocatalytic inactivation of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus helveticus by ZnO and TiO2 activated with ultraviolet light. Process Biochem 39(4):475–481
Maness PC, Smolinski S, Blake DM, Huang Z, Wolfrum EJ, Jacoby WA (1999) Bactericidal activity of photocatalytic TiO2 reaction: toward an understanding of its killing mechanism. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(9):4094–4098
Matsunaga T, Tomoda R, Nakajima T, Wake H (1985) Photoelectrochemical sterilization of microbial cells by semiconductor powders. FEMS Microbiol Lett 29(1–2):211–214
Matsunaga T, Tomoda R, Nakajima T, Wake H, Nakamura N, Komine T (1988) Continuous-sterilization system that uses photosemiconductor powders. Appl Environ Microbiol 54(6):1330–1333
McCullagh C, Robertson JMC, Bahnemann DW, Robertson PKJ (2007) The application of TiO2 photocatalysis for disinfection of water contaminated with pathogenic micro-organisms: a review. Res Chem Intermed 33(3–5):359–375
Metzler DM, Li M, Erdem A, Huang CP (2011) Responses of algae to photocatalytic nano-TiO2 particles with an emphasis on the effect of particle size. Chem Eng J 170:538–546
Metzler DM, Erdem A, Tseng YH, Huang CP (2012) Responses of algal cells to engineered nanoparticles measured as algal cell population, chlorophyll a, and lipid peroxidation: effect of particle size and type. Int J Nanotechnol 2012:1–12
Moore MN (2006) So nanoparticles present ecotoxicological risks for the health of the aquatic environment? Environ Int 32:967–976
Nadtochenkoa VA, Rincon AG, Stanca SE, Kiwi J (2005) Dynamics of E. coli membrane cell peroxidation during TiO2 photocatalysis studied by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and AFM microscopy. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 169:131–137
Nesic J, Rtimi S, Laub D, Roglic GM, Pulgarin C, Kiwi J (2014) New evidence for TiO2 uniform surfaces leading to complete bacterial reduction in the dark: critical issues. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 123:593–599
Othman SH, Rashid SA,Ghazi TIM, Abdullah N (2012) Dispersion and stabilization of photocatalytic TiO2 nanoparticles in aqueous suspension for coatings applications. J Nanomater. 2012: doi:10.1155/2012/718214
Pagnout C, Jomini S, Dadhwal M, Caillet C, Thomas F, Bauda P (2012) Role of electrostatic interactions in the toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles toward Escherichia coli. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 92:315–321
Pal A, Pehkonen SO, Yu LE, Ray MB (2007) Photocatalytic inactivation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria using fluorescent light. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 186(2–3):335–341
Pigeot-Rémy S, Simonet F, Errazuriz-Cerda E, Lazzaroni JC, Atlan D, Guillard C (2011) Photocatalysis and disinfection of water: identification of potential bacterial targets. Appl Catal B Environ 104(3–4):390–398
Schneider J, Matsuoka M, Takeuchi M, Zhang J, Horiuchi Y, Anpo M, Bahnemann DW (2014) Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: mechanisms and materials. Chem Rev 114(19):9919–9986
Simon-Deckers A, Loo S, Mayne-L’Hermite M, Herlin-Boime N, Menguy N, Reynaud C, Gouget B, Carriere M (2009) Size-, composition- and shape-dependent toxicological impact of metal oxide nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes toward bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 43:8423–8429
Skocaj M, Filipic M, Petkovic J, Novak S (2011) Titanium dioxide in our everyday life; is it safe? Radiol Oncol 45(4):227–247
Sohaebuddin SK, Thevenot PT, Baker D, Eaton JW, Tang L (2010) Nanomaterial cytotoxicity is composition, size, and cell type dependent. Part Fibre Toxicol 7(22):1–17
Sökmen M, Candan F, Sümer Z (2001) Disinfection of E. coli by the Ag-TiO2/UV system: lipidperoxidation. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 143(2–3):241
Swayamprava D, Sunandan S, Suresh N, Mukherjee C, Mukherjee A (2012) A comparative cytotoxicity study of TiO2 nanoparticles under light and dark conditions at low exposure concentrations. Toxicol Res 1:116–130
Swetha S, Singh MK, Minchitha KU, Balakrishna RG (2012) Elucidation of cell killing mechanism by comparative analysis of photoreactions on different types of bacteria. J Photochem Photobiol 88(2):414–422
Tseng YH, Lin HY, Kuoc CS, Lic YY, Huang CP (2006) Thermostability of nano-TiO2 and its photocatalytic activity. React Kinet Catal Lett 89(1):63–69
Valduga G, Bertoloni G, Reddi E, Jori G (1993) Effect of extracellularly generated singlet oxygen on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J Photochem Photobiol B 21(1):81–86
von Moos N, Slaveykova VI (2014) Oxidative stress induced by inorganic nanoparticles in bacteria and aquatic microalgae—state of the art and knowledge gaps. Nanotoxicology 8(6):605–630
Wei C, Lin WY, Zainal Z, Williams NE, Zhu K, Kruzic AP, Smith RL, Rajeshwar K (1994) Bactericidal activity of TiO2 photocatalyst in aqueous-media—toward a solar-assisted water disinfection system. Environ Sci Technol 28(5):934–938
Zhukova LV, Kiwi J, Nikandrov VV (2012) TiO2 nanoparticles suppress Escherichia coli cell division in the absence of UV irradiation in acidic conditions. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 97:240–247
Acknowledgments
The materials presented in this paper were based upon work supported by US EPA under STAR Project Grant No. R-83172101. The nanomaterials used in this study came from the following suppliers: Degussa Corp. and Nanostructured and Amorphous Materials, Inc.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Cinta Porte
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erdem, A., Metzler, D., Cha, D.K. et al. The short-term toxic effects of TiO2 nanoparticles toward bacteria through viability, cellular respiration, and lipid peroxidation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 17917–17924 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5018-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5018-1