Abstract
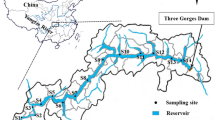
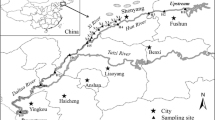
Lakes along the Yangzte River are very important for inhabitants due to their ecosystem service values. In this study, the level of eight endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs) was studied in the Honghu Lake and East Dongting Lake. In each lake, 21 water samples and 21 sediment samples were collected. The total concentrations of eight EDCs in surface water (47.60–419.82 ng L−1, mean value: 225.65 ng L−1) and sediments (202.71–635.36 ng g−1 dry weight (dw), mean value 371.90 ng g−1 dw) of Honghu Lake were significantly higher than those in surface water (43.52–394.21 ng L−1, mean value 153.03 ng L−1) and sediment (70.01–464.63 ng g−1 dw, mean value 238.42 ng g−1 dw) in East Dongting Lake. 4-Nonylphenol (NP), 4-octylphenol (OP), and bisphenol A (BPA) in surface water and sediments were main EDCs in two lakes. No correlation relationships were found between concentrations of EDCs in water and sediment from two lakes. The concentrations of OP and 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) in sediments of Honghu Lake had significant positive correlation with the content of total organic carbon (TOC). The concentrations of EDCs in outlet of Honghu Lake were comparable to those in the main lake, whereas the EDCs in outlet of East Dongting Lake were lower than those in the main lake. The EDCs in Honghu Lake and East Dongting Lake may have a significant potential biological effect on fish based on the estimation of EDC estrogenicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahel M, Giger W (1993) Partitioning of alkylphenols and alkylphenol polyethoxylates between water and organic solvents. Chemosphere 26:1471–1478
Auriol M, Filali-Meknassi Y, Tyagi RD, Adams CD, Surampalli RY (2006) Endocrine disrupting compounds removal from wastewater, a new challenge. Process Biochem 41:525–539
Ban X, Wu QZ, Pan BZ, Du Y, Feng Q (2014) Application of composite water quality identification index on the water quality evaluation in spatial and temporal variations: a case study in Honghu Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 186:4237–4247
Boekhorst DGJT, Smits TJM, Yu X, Li L, Lei G, Zhang C (2010) Implementing integrated river basin management in China. Ecol Soc 15(2):23, http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol15/iss2/art23
Céspedes R, Petrovic M, Raldúa D, Saura Ú, Piña B, Lacorte S, Viana P, Barceló D (2004) Integrated procedure for determination of endocrine-disrupting activity in surface waters and sediments by use of the biological technique recombinant yeast assay and chemical analysis by LC–ESI-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 378:697–708
Chang HS, Choo KH, Lee B, Choi SJ (2009) The methods of identification, analysis, and removal of endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in water. J Hazard Mater 172:1–12
Chouhan S, Yadav SK, Prakash J, Swati SSP (2014) Effect of bisphenol A on human health and its degradation by microorganisms: a review. Ann Microbiol 64:13–21
Dong R (2014) Effects of EDCs on sex as demonstrated by feminization of artificially reared southern catfish. Southwest University, Chongqing, China, Dissertation
Esteban S, Gorga M, Petrovic M, González-Alonso S, Barceló D, Valcárcel Y (2014) Analysis and occurrence of endocrine-disrupting compounds and estrogenic activity in the surface waters of Central Spain. Sci Total Environ 466–467:939–951
Falconer IR, Chapman HF, Moore MR, Ranmuthugala G (2006) Endocrine-disrupting compounds: a review of their challenge to sustainable and safe water supply and water reuse. Environ Toxicol 21:181–191
Gutendorf B, Westendorf J (2001) Comparison of an array of in vitro assays for the assessment of the estrogenic potential of natural and synthetic estrogens, phytoestrogens and xenoestrogens. Toxicology 166:79–89
Harries JE, Sheahan DA, Jobling S, Matthiessen P, Neall P, Sumpter JP, Tylor T, Zaman N (1997) Estrogenic activity in five United Kingdom rivers detected by measurement of vitellogenesis in caged male trout. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:534–542
Huang D, Wan Q, Li L, Wang T, Lu S, Ou F, Tian Q (2013) Changes of water quality and eutrophic state in recent 20 years of Dongting Lake. Res J Environ Sci 26:27–33 (In Chinese)
Jin SW, Yang FX, Xu Y, Dai HP, Liu WP (2013) Risk assessment of xenoestrogens in a typical domestic sewage-holding lake in China. Chemosphere 93:892–898
Lai KM, Johnson KL, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2000) Binding of waterborne steroid estrogens to solid phases in river and estuarine systems. Environ Sci Technol 34:3890–3894
Li ZY, Li DH, Oh JR, Je JG (2004) Seasonal and spatial distribution of nonylphenol in Shihwa Lake, Korea. Chemosphere 56:611–618
Lu GH, Yan ZH, Wang YH, Chen W (2011) Assessment of estrogenic contamination and biological effects in Lake Taihu. Ecotoxicology 20:974–981
Pan BZ, Wang HJ, Liang XM, Wang HZ (2011) Macrozoobenthos in Yangtze floodplain lakes: patterns of density, biomass, and production in relation to river connectivity. J N Am Benthol Soc 30:589–602
Petrovic M, Sole M, Lopez de Alda MJ, Barcelo D (2002) Endocrine disruptors in sewage treatment plants, receiving river waters, and sediments: integration of chemical analysis and biological effects on feral carp. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:2146–2156
Pinto PIS, Estevao MD, Power DM (2014) Effects of estrogens and estrogenic disrupting compounds on fish mineralized tissues. Mar Drugs 12:4474–4494
Pojana G, Bonfà A, Busetti F, Collarin A, Marcomini A (2004) Estrogenic potential of the Venice, Italy, lagoon waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1874–1880
Qian Y, Zheng MH, Zhang B, Gao LR, Liu WB (2006) Determination and assessment of HCHs and DDTs residues in sediments from Lake Dongting, China. Environ Monit Assess 116:157–167
Qin D, Luo Y, Huang Z, Hu J, Fan J, Liao Y (2012) Pollution status and source analysis of water environment in Dongting Lake. Environ Sci Technol 35:193–198 (In Chinese)
Ru H, Liu X, Huang X, Ning Y, Wang H (2008) Diversity of fish species and its spatio-temporal variations in Lake Dongting, a large Yangtze-connected lake. J Lake Sci 20:93–99 (In Chinese)
Ruili S, Zhengyu BAO, Min Z, Shengying Q, Shuxun XIE (2007) Temporal-spatial evolution of water quality in Lake Dongting, China. J Lake Sci 19:677–682 (In Chinese)
Seki M, Yokota H, Matsubara H, Tsuruda Y, Maeda M, Tadokoro H, Kobayashi K (2002) Effect of ethinylestradiol on the reproduction and induction of vitellogenin and testis-ova in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1692–1698
Soares A, Guieysse B, Jefferson B, Cartmell E, Lester JN (2008) Nonylphenol in the environment: a critical review on occurrence, fate, toxicity and treatment in wastewaters. Environ Int 34:1033–1049
Solé M, López de Alda MJ, Castillo M, Porte C, Ladegaard-Pedersen K, Barceló D (2000) Estrogenicity determination in sewage treatment plants and surface waters from the Catalonian area (NE Spain). Environ Sci Technol 34:5076–5083
Tao L, Fang F, Lei WX, Bo WC, Soc IC (2009) Effect of enclosure culture on water quality: a case study in lake Honghu, Hubei province, China. 2009 International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology. Proceedings IEEE Computer Soc, Los Alamitos 2:237–240
Viglino L, Aboulfadl K, Prévost M, Sauvé S (2008) Analysis of natural and synthetic estrogenic endocrine disruptors in environmental waters using online preconcentration coupled with LC-APPI-MS/MS. Talanta 76:1088–1096
Wan R, Yang G, Wang X, Qin N, Dai X (2014) Progress of research on the relationship between the Yangtze River and its connected lakes in the middle reaches. J Lake Sci 26:1–8 (In Chinese)
Wang B, Huang B, Jin W, Wang Y, Zhao SM, Li FR, Hu P, Pan XJ (2012) Seasonal distribution, source investigation and vertical profile of phenolic endocrine disrupting compounds in Dianchi Lake, China. J Environ Monit 14:1275–1282
Wu CX, Huang XL, Witter JD, Spongberg AL, Wang KX, Wang D, Liu JT (2014) Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products and associated environmental risks in the central and lower Yangtze river, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:19–26
Yang G, Ma R, Zhang L, Jiang J, Yao S, Zhang M, Zeng H (2010) Lake status, major problems and protection strategy in China. J Lake Sci 22:799–810 (In Chinese)
Yeomans JC, Bremner JM (1988) A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19:1467–1476
Yuan LX, Qi SH, Wu XG, Wu CX, Xing XL, Gong XY (2013) Spatial and temporal variations of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in water and sediments from Honghu Lake, China. J Geochem Explor 132:181–187
Zgola-Grzeskowiak A, Grzeskowiak T, Rydlichowski R, Lukaszewski Z (2010) Concentrations of endocrine disrupting alkylphenols and their mono- and diethoxylates in sediments and water from artificial Lake Malta in Poland. Tenside Surfactants Deterg 47:222–227
Zhu Y, Jiahu J, Zhandong S, Qun H, Hongjuan W, Yunkai Z (2008) Character and assessment of heavy metals in the sediments from Lake Dongting. J Lake Sci 20:477–485 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This project was supported in part by the Foundation of Key Laboratory of Yangtze River Water Environment, Ministry of Education (Tongji University), China (No. YRWEF201402), Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering Science (Wuhan University), China (No. 2013B115), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2014CFA114), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31400113), Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 2015282), and the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Y329671K01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Cao, X., Zhang, M. et al. Occurrence and distribution of endocrine-disrupting compounds in the Honghu Lake and East Dongting Lake along the Central Yangtze River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 17644–17652 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4980-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4980-y