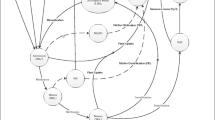
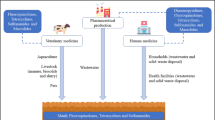
Abstract
Antibiotic use in the early 1900 vastly improved human health but at the same time started an arms race of antibiotic resistance. The widespread use of antibiotics has resulted in ubiquitous trace concentrations of many antibiotics in most environments. Little is known about the impact of these antibiotics on microbial processes or “non-target” organisms. This mini-review summarizes our knowledge of the effect of synthetically produced antibiotics on microorganisms involved in biogeochemical cycling. We found only 31 articles that dealt with the effects of antibiotics on such processes in soil, sediment, or freshwater. We compare the processes, antibiotics, concentration range, source, environment, and experimental approach of these studies. Examining the effects of antibiotics on biogeochemical processes should involve environmentally relevant concentrations (instead of therapeutic), chronic exposure (versus acute), and monitoring of the administered antibiotics. Furthermore, the lack of standardized tests hinders generalizations regarding the effects of antibiotics on biogeochemical processes. We investigated the effects of antibiotics on biogeochemical N cycling, specifically nitrification, denitrification, and anammox. We found that environmentally relevant concentrations of fluoroquinolones and sulfonamides could partially inhibit denitrification. So far, the only documented effects of antibiotic inhibitions were at therapeutic doses on anammox activities. The most studied and inhibited was nitrification (25–100 %) mainly at therapeutic doses and rarely environmentally relevant. We recommend that firm conclusions regarding inhibition of antibiotics at environmentally relevant concentrations remain difficult due to the lack of studies testing low concentrations at chronic exposure. There is thus a need to test the effects of these environmental concentrations on biogeochemical processes to further establish the possible effects on ecosystem functioning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Vithanage M, Kim K, Cho J-S, Lee YH, Joo YK, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Inhibitory effect of veterinary antibiotics on denitrification in groundwater: a microcosm approach. ScientificWorldJournal. doi:10.1155/2014/879831
Alighardashi A, Pandolfi D, Potier O, Pons MN (2009) Acute sensitivity of activated sludge bacteria to erythromycin. J Hazard Mater 172:685–692. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.051
Allen HK, Donato J, Wang HH, Cloud-Hansen KA, Davies J, Handelsman J (2010) Call of the wild: antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:251–259. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2312
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–69
Andersson DI, Hughes D (2014) Microbiological effects of sublethal levels of antibiotics. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:465–478. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3270
Baath E, Olsson S, Tunlid A (1988) Growth of bacteria in the rhizoplane and the rhizosphere of rape seedlings. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53(6):355–360. doi:10.1016/0378-1097(88)90501-0
Backhaus T, Altenburger R, Boedeker W, Faust M, Scholze M, Grimme LH (2000) Predictability of the toxicity of a multiple mixture of dissimilarly acting chemicals to Vibrio fischeri. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(9):2348–2356. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2000)019<2348:pottoa>2.3.co;2
Bell KY, Bandy JJ, Finnegan BJ, Keen O, Mauter MS, Parker AM, Sima LC, Stretz HA (2013) Emerging pollutants - part II: treatment. Water Environ Res 85:2022–2071. doi:10.2175/106143013x13698672323308
Bressan CR, Kunz A, Schmidell W, Soares HM (2013) Toxicity of the colistin sulfate antibiotic used in animal farming to mixed cultures of nitrifying organisms. Water Air Soil Pollut 224(3):1–9. doi:10.1007/s11270-013-1441-4
Carlson CA, Ingraham JL (1983) Comparison of denitrification by Pseudomonas stutzeri, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas denitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol 45(4):1247–1253
Campos JL, Garrido JM, Mendez R, Lema JM (2001) Effect of two broad-spectrum antibiotics on activity and stability of continuous nitrifying system. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 95:1–10. doi:10.1385/abab:95:1:01
Carucci A, Cappai G, Piredda M (2006) Biodegradability and toxicity of pharmaceuticals in biological wastewater treatment plants. J Environ Sci Health A 41:1831–1842. doi:10.1080/10934520600779000
Claus H, Martin HH, Jantos CA, Konig H (2000) A search for beta-lactamase in chlamydiae, mycoplasmas, planctomycetes, and cyanelles: bacteria and bacterial descendants at different phylogenetic positions and stages of cell wall development. Microbiol Res 155:1–6
Conkle JL, White JR (2012) An initial screening of antibiotic effects on microbial respiration in wetland soils. J Environ Sci Health A 47:1381–1390. doi:10.1080/10934529.2012.672315
Costanzo SD, Murby J, Bates J (2005) Ecosystem response to antibiotics entering the aquatic environment. Mar Pollut Bull 51:218
Crane M, Watts C, Boucard T (2006) Chronic aquatic environmental risks from exposure to human pharmaceuticals. Sci Total Environ 367:23–41. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.04.010
Cui H, Wang SP, Fu J, Zhou ZQ, Zhang N, Guo L (2014) Influence of ciprofloxacin on microbial community structure and function in soils. Biol Fertil Soils 50(6):939–947. doi:10.1007/s00374-014-0914-y
Dalsgaard T, Thamdrup B, Canfield DE (2005) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in the marine environment. Res Microbiol 156(4):457–464. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2005.01.011
Davies J, Ryan KS (2012) Introducing the parvome: bioactive compounds in the microbial world. ACS Chem Biol 7:252–259. doi:10.1021/cb200337h
Demoling LA, Baath E, Greve G, Wouterse M, Schmitt H (2009) Effects of sulfamethoxazole on soil microbial communities after adding substrate. Soil Biol Biochem 41:840–848. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.02.001
Ducklow H (2008) Microbial services: challenges for microbial ecologists in a changing world. Aquat Microb Ecol 53:13–19. doi:10.3354/ame01220
Fernandez I, Mosquera-Corral A, Campos JL, Mendez R (2009) Operation of an anammox SBR in the presence of two broad-spectrum antibiotics. Process Biochem 44:494–498. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2009.01.001
Finley RL, Collignon P, Larsson DGJ, McEwen SA, Li XZ, Gaze WH, Reid-Smith R, Timinouni M, Graham DW, Topp E (2013) The scourge of antibiotic resistance: the important role of the environment. Clin Infect Dis 57:704–710. doi:10.1093/cid/cit355
Fountoulakis M, Drillia P, Stamatelatou K, Lyberatos G (2004) Toxic effect of pharmaceuticals on methanogienesis. Wa Sci Technol 50(5):335–340
Gatica J, Cytryn E (2013) Impact of treated wastewater irrigation on antibiotic resistance in the soil microbiome. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3529–3538. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1505-4
Gu JD (2014) Assessment of ecosystem health and ecotoxicology through chemical analysis and modeling. Ecotoxicology 23:475–479. doi:10.1007/s10646-014-1206-x
Hansen PK, Lunestad BT, Samuelsen OB (1992) Effects of oxytetracycline, oxolinic acid, and flumequine on bacteria in an artificial marine fish farm sediment. Can J Microbiol 38:1307–1312
Hou L, Yin G, Liu M, Zhou J, Zheng Y, Gao J, Zong H, Yang Y, Gao L, Tong C (2015) Effects of sulfamethazine on denitrification and the associated N2O release in estuarine and coastal sediments. Environ Sci Technol 49:326–33. doi:10.1021/es504433r
Ingvorsen K, Nielsen MY, Joulian C (2003) Kinetics of bacterial sulfate reduction in an activated sludge plant. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 46:129–137
Juliastuti SR, Baeyens J, Creemers C (2003) Inhibition of nitrification by heavy metals and organic compounds: the ISO 9509 test. Environ Eng Geosci 20(2):79–90. doi:10.1089/109287503763336511
Klaver AL, Matthews RA (1994) Effects of oxytetracycline on nitrification in a model aquatic system. Aquaculture 123:237–247
Katipoglu-Yazan T, Pala-Ozkok I, Ubay-Cokgor E, Orhon D (2013) Acute impact of erythromycin and tetracycline on the kinetics of nitrification and organic carbon removal in mixed microbial culture. Bioresour Technol 144:410–419. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.121
Kleineidam K, Sharma S, Kotzerke A, Heuer H, Thiele-Bruhn S, Smalla K, Wilke BM, Schloter M (2010) Effect of sulfadiazine on abundance and diversity of denitrifying bacteria by determining nirK and nirS genes in two arable soils. Microb Ecol 60:703–707. doi:10.1007/s00248-010-9691-9
Knapp CW, Engemann CA, Hanson ML, Keen PL, Hall KJ, Graham DW (2008) Indirect evidence of transposon-mediated selection of antibiotic resistance genes in aquatic systems at low-level oxytetracycline exposures. Environ Sci Technol 42:5348–5353. doi:10.1021/es703199g
Kotzerke A, Fulle M, Sharma S, Kleineidam K, Welzl G, Lamshoft M, Schloter M, Wilke BM (2011) Alterations in total microbial activity and nitrification rates in soil due to amoxicillin-spiked pig manure. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174:56–64. doi:10.1002/jpln.200900210
Kotzerke A, Sharma S, Schauss K, Heuer H, Thiele-Bruhn S, Smalla K, Wilke BM, Schloter M (2008) Alterations in soil microbial activity and N-transformation processes due to sulfadiazine loads in pig-manure. Environ Pollut 153:315–322. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.08.020
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR (2001) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: a model for molecular microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:485–529
Kümmerer K (2009a) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment - a review - part I. Chemosphere 75:417–434. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.086
Kümmerer K (2009b) The presence of pharmaceuticals in the environment due to human use - present knowledge and future challenges. J Environ Manag 90:2354–2366. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.01.023
Larsson DGJ (2014) Pollution from drug manufacturing: review and perspectives. Philos T Roy Soc B 369:20130571. doi:10.1098/rstb.2013.0571
Liu B, Li Y, Zhang X, Wang J, Gao M (2014) Combined effects of chlortetracycline and dissolved organic matter extracted from pig manure on the functional diversity of soil microbial community. Soil Biol Biochem 74:148–155. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.03.005
Lotti T, Cordola M, Kleerebezem R, Caffaz S, Lubello C, van Loosdrecht MCM (2012) Inhibition effect of swine wastewater heavy metals and antibiotics on anammox activity. Water Sci Technol 66:1519–1526. doi:10.2166/wst.2012.344
Luczkiewicz A, Felis E, Ziembinska A, Gnida A, Kotlarska E, Olanczuk-Neyman K, Surmacz-Gorska J (2013) Resistance of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus spp. to selected antimicrobial agents present in municipal wastewater. J Water Health 11:600–612. doi:10.2166/wh.2013.130
Murray RE, Knowles R (1999) Chloramphenicol inhibition of denitrifying enzyme activity in two agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(8):3487–3492
Nesme J, Cecillon S, Delmont TO, Monier JM, Vogel TM, Simonet P (2014) Large-scale metagenomic-based study of antibiotic resistance in the environment. Curr Biol 24:1096–1100. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.036
Nordberg M, Templeton DM, Andersen O, Duffus JH (2009) Glossary of terms used in ecotoxicology (IUPAC recommendations 2009). Pure Appl Chem 81:829–970. doi:10.1351/pac-rec-08-07-09
Näslund J, Hedman JE, Agestrand C (2008) Effects of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin on the bacterial community structure and degradation of pyrene in marine sediment. Aquat Toxicol 90:223–227
Philippot L, Hallin S (2005) Finding the missing link between diversity and activity using denitrifying bacteria as a model functional community. Curr Opin Microbiol 8(3):234–239
Prosser JI (1989) Autotrophic nitrification in bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol 30:125–181
Reichel R, Rosendahl I, Peeters ETHM, Focks E, Groeneweg J, Bierl R, Schlichting A, Amelung W, Thiele-Bruhn S (2013) Effects of slurry from sulfadiazine- (SDZ) and difloxacin- (DIF) medicated pigs on the structural diversity of microorganisms in bulk and rhizosphere soil. Soil Biol Biochem 62:82–91. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.03.007
Rico A, Dimitrov MR, Van Wijngaarden RPA, Satapornvanit K, Smidt H, Van den Brink PJ (2014) Effects of the antibiotic enrofloxacin on the ecology of tropical eutrophic freshwater microcosms. Aquat Toxicol 147:92–104. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.12.008
Roose-Amsaleg C, Yan C, Hoang AM, Laverman AM (2013) Chronic exposure of river sediments to environmentally relevant levels of tetracycline affects bacterial communities but not denitrification rates. Ecotoxicology 22:1467–1478. doi:10.1007/s10646-013-1133-2
Rosendahl I, Siemens J, Kindler R, Groeneweg J, Zimmermann J, Czerwinski S, Lamshoeft M, Laabs V, Wilke BM, Vereecken H, Amelung W (2012) Persistence of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic difloxacin in soil and lacking effects on nitrogen turnover. J Environ Qual 41:1275–1283. doi:10.2134/jeq2011.0459
Schauss K, Focks A, Heuer H, Kotzerke A, Schmitt H, Thiele-Bruhn S, Smalla K, Wilke BM, Matthies M, Amelung W, Klasmeier J, Schloter M (2009) Analysis, fate and effects of the antibiotic sulfadiazine in soil ecosystems. Trends Anal Chem 28:612–618
Schmidt S, Winter J, Gallert C (2012) Long-term effects of antibiotics on the elimination of chemical oxygen demand, nitrification, and viable bacteria in laboratory-scale wastewater treatment plants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 63:354–364. doi:10.1007/s00244-012-9773-4
Schmieder R, Edwards R (2012) Insights into antibiotic resistance through metagenomic approaches. Future Microbiol 7:73–89. doi:10.2217/fmb.11.135
Servais P, Passerat J (2009) Antimicrobial resistance of fecal bacteria in waters of the Seine river watershed (France). Sci Total Environ 408:365–372. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.09.042
Shen T, Stieglmeier M, Dai J, Urich T, Schleper C (2013) Responses of the terrestrial ammonia-oxidizing archaeon Ca. Nitrososphaera viennensis and the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosospira multiformis to nitrification inhibitors. FEMS Microbiol Lett 344:121–129. doi:10.1111/1574-6968.12164
Spieck E, Lipski A (2011) Cultivation, growth physiology, and chemotaxonomy of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria. In Martin G. Klotz, editor: Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 486, Burlington: Academic Press, 2011, pp. 109–130. ISBN: 978-0-12-381294-0 Elsevier Inc. Academic Press
Stewart PS (2002) Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacterial biofilms. Int J Med Microbiol 292:107–113. doi:10.1078/1438-4221-00196
Strous M, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (1999) Key physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3248–3250
Thiele-Bruhn S (2003) Pharmaceutical antibiotic compounds in soils - a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 166:145–167. doi:10.1002/jpln.200390023
Thiele-Bruhn S, Beck IC (2005) Effects of sulfonamide and tetracycline antibiotics on soil microbial activity and microbial biomass. Chemosphere 59:457–465. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.01.023
Toth JD, Feng Y, Dou Z (2011) Veterinary antibiotics at environmentally relevant concentrations inhibit soil iron reduction and nitrification. Soil Biol Biochem 43:2470–2472. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.09.004
Tourna M, Stieglmeier M, Spang A, Konneke M, Schintlmeister A, Urich T, Engel M, Schloter M, Wagner M, Richter A, Schleper C (2011) Nitrososphaera viennensis, an ammonia oxidizing archaeon from soil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:8420–8425. doi:10.1073/pnas.1013488108
Treusch AH, Leininger S, Kletzin A, Schuster SC, Klenk HP, Schleper C (2005) Novel genes for nitrite reductase and Amo-related proteins indicate a role of uncultivated mesophilic crenarchaeota in nitrogen cycling. Environ Microbiol 7(12):1985–1995
Underwood JC, Harvey RW, Metge DW, Repert DA, Baumgartner LK, Smith RL, Roane TM, Barber LB (2011) Effects of the antimicrobial sulfamethoxazole on groundwater bacterial enrichment. Environ Sci Technol 45:3096–3101. doi:10.1021/es103605e
Wunder DB, Tan DT, LaPara TM, Hozalski RM (2013) The effects of antibiotic cocktails at environmentally relevant concentrations on the community composition and acetate biodegradation kinetics of bacterial biofilms. Chemosphere 90:2261–2266. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.031
Yamamura S, Watanabe K, Suda W, Tsuboi S, Watanabe M (2014) Effect of antibiotics on redox transformations of arsenic and diversity of arsenite-oxidizing bacteria in sediment microbial mommunities. Environ Sci Technol 48:350–357. doi:10.1021/es403971s
Yan C, Dinh QT, Chevreuil M, Garnier J, Roose-Amsaleg C, Labadie P, Laverman AM (2013) The effect of environmental and therapeutic concentrations of antibiotics on nitrate reduction rates in river sediment. Water Res 47:3654–3662. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.025
Yergeau E, Sanschagrin S, Waiser MJ, Lawrence JR, Greer CW (2012) Sub-inhibitory concentrations of different pharmaceutical products affect the meta-transcriptome of river biofilm communities cultivated in rotating annular reactors. Environ Microbiol Rep 4(3):350–359. doi:10.1111/j.1758-2229.2012.00341.x
Zumft WG (1997) Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:533–616
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the constructive comments of four journal reviewers and Ben Abbott for proofreading the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roose-Amsaleg, C., Laverman, A.M. Do antibiotics have environmental side-effects? Impact of synthetic antibiotics on biogeochemical processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 4000–4012 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4943-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4943-3