Abstract
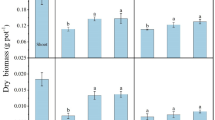
Intensive agricultural system with high input of fertilizer results in high agricultural output. However, excessive fertilization in intensive agricultural system has great potential to cause nitrate and heavy metal accumulation in soil, which is adverse to human health. The main objective of the present study was to observe the effects of intercropping and inoculation of endophytic bacterium Acinetobacter calcoaceticus Sasm3 on phytoremediation of combined contaminated soil in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). The results showed that with Sasm3 inoculation, the biomass of rape was increased by 10–20 % for shoot, 64 % for root, and 23–29 % for seeds while the nitrate accumulation in rape was decreased by 14 % in root and by 12 % in shoot. The cadmium concentration in rape increased significantly with mono-inoculating treatment, whereas it decreased significantly after intercropping treatment. By denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and real-time quantitative PCR analysis, the diversity of bacterial community and the number of nirS and nirK gene copies increased significantly with inoculation or/and intercropping treatment. In conclusion, the endophytic bacterium Sasm3-inoculated intercropping system not only improved the efficiency of clearing cadmium from soil without obstructing crop production, but also improved the quality of crop.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bedoussac L, Justes E (2010) The efficiency of a durum wheat-winter pea intercrop to improve yield and wheat grain protein concentration depends on N availability during early growth. Plant Soil 330:19–35
Berg G, Smalla K (2009) Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. Fems Microbiol Ecol 68:1–13
Betencourt E, Duputel M, Colomb B, Desclaux D, Hinsinger P (2012) Intercropping promotes the ability of durum wheat and chickpea to increase rhizosphere phosphorus availability in a low P soil. Soil Biol Biochem 46:181–190
Cassman KG (1999) Ecological intensification of cereal production systems: yield potential, soil quality, and precision agriculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:5952–5959
Cataldo D, Maroon M, Schrader L, Youngs V (1975) Rapid colorimetric determination of nitrate in plant tissue by nitration of salicylic acid 1. Commun Soil Sci Plan Anal 6:71–80
Chan TYK (2011) Vegetable-borne nitrate and nitrite and the risk of methaemoglobinaemia. Toxicol Lett 200:107–108
Cunningham SD, Ow DW (1996) Promises and prospects of phytoremediation. Plant Physiol 110:715
Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A, Rusanowska P, Zielińska M, Bernat K, Wojnowska-Baryła I (2014) Structure of nitrogen-converting communities induced by hydraulic retention time and COD/N ratio in constantly aerated granular sludge reactors treating digester supernatant. Bioresour Technol 154:162–170
Deng D, Shu W, Zhang J, Zou H, Lin Z, Ye Z, Wong M (2007) Zinc and cadmium accumulation and tolerance in populations of Sedum alfredii. Environ Pollut 147:381–386
Deng DM, Deng JC, Li JT, Zhang J, Hu M, Lin Z, Liao B (2008) Accumulation of zinc, cadmium, and lead in four populations of Sedum alfredii growing on lead/zinc mine spoils. J Integr Plant Biol 50:691–698
Dineshkumar N, Saravanakumar C, Vasanth M, Muralidhar M, Alavandi SV (2014) Genetic and physiological characterization of denitrifying bacteria from brackishwater shrimp culture ponds of India. Int Biodeter Biodegr 92:49–56
el Zahar HF, Marol C, Berge O, Rangel-Castro JI, Prosser JI, Balesdent J, Heulin T, Achouak W (2008) Plant host habitat and root exudates shape soil bacterial community structure. ISME J 2:1221–1230
Hanafi A, Papasolomontos A (1999) Integrated production and protection under protected cultivation in the Mediterranean region. Biotechnol Adv 17:183–203
Hauggaard-Nielsen H, Jensen ES (2005) Facilitative root interactions in intercrops. Plant Soil 274:237–250
Huang SW, Jin JY (2008) Status of heavy metals in agricultural soils as affected by different patterns of land use. Environ Monit Assess 139:317–327
Ishikawa K, Ohmori T, Miyamoto H, Ito T, Kumagai Y, Sonoda M, Matsumoto J, Miyamoto H, Kodama H (2013) Denitrification in soil amended with thermophile-fermented compost suppresses nitrate accumulation in plants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1349–1359
Ju XT, Kou CL, Zhang FS, Christie P (2006) Nitrogen balance and groundwater nitrate contamination: comparison among three intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environ Pollut 143:117–125
Ju XT, Kou CL, Christie P, Dou ZX, Zhang FS (2007) Changes in the soil environment from excessive application of fertilizers and manures to two contrasting intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environ Pollut 145:497–506
Khan Z, Doty S (2011) Endophyte-assisted phytoremediation. Curr Top Plant Biol 12:97–105
Kramer SB, Reganold JP, Glover JD, Bohannan BJ, Mooney HA (2006) Reduced nitrate leaching and enhanced denitrifier activity and efficiency in organically fertilized soils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:4522–4527
Lefèvre I, Marchal G, Meerts P, Corréal E, Lutts S (2009) Chloride salinity reduces cadmium accumulation by the Mediterranean halophyte species Atriplex halimus L. Environ Exp Bot 65:142–152
Li L, Sun J, Zhang F, Li X, Yang S, Rengel Z (2001) Wheat/maize or wheat/soybean strip intercropping: I yield advantage and interspecific interactions on nutrients. Field Crop Res 71:123–137
Li S, Li L, Zhang F, Tang C (2004) Acid phosphatase role in chickpea/maize intercropping. Ann Bot 94:297–303
Li TQ, Yang XE, Jin XF, He ZL, Stoffella PJ, Hu QH (2005) Root responses and metal accumulation in two contrasting ecotypes of Sedum alfredii Hance under lead and zinc toxic stress. J Environ Sci Heal A 40:1081–1096
Li N, Li Z, Zhuang P, Zou B, McBride M (2009) Cadmium uptake from soil by maize with intercrops. Water Air Soil Pollut 199:45–56
Li HY, Wei DQ, Shen M, Zhou ZP (2012) Endophytes and their role in phytoremediation. Fungal Divers 54:11–18
Li XG, Wang XX, Dai CC, Zhang TL, Xie XG, Ding CF, Wang HW (2014) Effects of intercropping with Atractylodes lancea and application of bio-organic fertiliser on soil invertebrates, disease control and peanut productivity in continuous peanut cropping field in subtropical China. Agrofor Syst 88:41–52
Long XX, Zhang YG, Jun D, Zhou QX (2009) Zinc, cadmium and lead accumulation and characteristics of rhizosphere microbial population associated with hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance under natural conditions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:460–467
Long XX, Chen XM, Chen YG, Wong-Jonathan WC, Wei ZB, Wu QT (2011) Isolation and characterization endophytic bacteria from hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance and their potential to promote phytoextraction of zinc polluted soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:1197–1207
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Luo Y, Freitas H (2011) Inoculation of endophytic bacteria on host and non-host plants—effects on plant growth and Ni uptake. J Hazard Mater 195:230–237
Maarit Niemi R, Heiskanen I, Wallenius K, Lindström K (2001) Extraction and purification of DNA in rhizosphere soil samples for PCR-DGGE analysis of bacterial consortia. J Microbiol Methods 45:155–165
Magalhães CM, Machado A, Matos P, Bordalo AA (2011) Impact of copper on the diversity, abundance and transcription of nitrite and nitrous oxide reductase genes in an urban European estuary. Fems Microbiol Ecol 77:274–284
Mastretta C, Barac T, Vangronsveld J, Newman L, Taghavi S, Dvd L (2006) Endophytic bacteria and their potential application to improve the phytoremediation of contaminated environments. Biotechnol Genet Eng 23:175–188
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Ozkan B, Kurklu A, Akcaoz H (2004) An input–output energy analysis in greenhouse vegetable production: a case study for Antalya region of Turkey. Biomass Bioenerg 26:89–95
Pan FS, Chen B, Ma XX, Yang XE, Feng Y (2014) Isolation and characterization of a specific endophytic bacterium from the Cd hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance. Acta Sci Circumst 34:449–456
Priemé A, Braker G, Tiedje JM (2002) Diversity of nitrite reductase (nirK and nirS) gene fragments in forested upland and wetland soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1893–1900
Pulford ID, Watson C (2003) Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated land by trees—a review. Environ Int 29:529–540
Quinton JN, Catt JA (2007) Enrichment of heavy metals in sediment resulting from soil erosion on agricultural fields. Environ Sci Technol 41:3495–3500
Rajkumar M, Ae N, Freitas H (2009) Endophytic bacteria and their potential to enhance heavy metal phytoextraction. Chemosphere 77:153–160
Rajkumar M, Sandhya S, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2012) Perspectives of plant-associated microbes in heavy metal phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 30:1562–1574
Salt DE, Blaylock M, Kumar NP, Dushenkov V, Ensley BD, Chet I, Raskin I (1995) Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Nat Biotechnol 13:468–474
Sanford RA, Wagner DD, Wu Q, Chee-Sanford JC, Thomas SH, Cruz-García C, Rodríguez G, Massol-DeyáA KKK, Ritalahti KM (2012) Unexpected nondenitrifier nitrous oxide reductase gene diversity and abundance in soils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:19709–19714
Sheng XF, Xia JJ, Jiang CY, He LY, Qian M (2008) Characterization of heavy metal-resistant endophytic bacteria from rape (Brassica napus) roots and their potential in promoting the growth and lead accumulation of rape. Environ Pollut 156:1164–1170
Smalla K, Wieland G, Buchner A, Zock A, Parzy J, Kaiser S, Roskot N, Heuer H, Berg G (2001) Bulk and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities studied by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis: plant-dependent enrichment and seasonal shifts revealed. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4742–4751
Van Overbeek L, Van Elsas JD (2008) Effects of plant genotype and growth stage on the structure of bacterial communities associated with potato (Solanum tuberosum L). Fems Microbiol Ecol 64:283–296
Wang Y, Shi J, Wang H, Lin Q, Chen X, Chen Y (2007) The influence of soil heavy metals pollution on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and community composition near a copper smelter. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 67:75–81
Wang K, Huang H, Zhu Z, Li T, He Z, Yang X, Alva A (2013) Phytoextraction of metals and rhizoremediation of PAHs in co-contaminated soil by co-planting of Sedum alfredii with ryegrass (Lolium perenne) or castor (Ricinus communis). Int J Phytoremed 15:283–298
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Weyens N, Croes S, Dupae J, Newman L, van der Lelie D, Carleer R, Vangronsveld J (2010) Endophytic bacteria improve phytoremediation of Ni and TCE co-contamination. Environ Pollut 158:2422–2427
Wu Q, Wei Z, Ouyang Y (2007) Phytoextraction of metal-contaminated soil by Sedum alfredii H: effects of chelator and co-planting. Water Air Soil Pollut 180:131–139
Yang X, Long X, Ye H, He Z, Calvert D, Stoffella P (2004) Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Zn-hyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance). Plant Soil 259:181–189
Zhang F, Li L (2003) Using competitive and facilitative interactions in intercropping systems enhances crop productivity and nutrient-use efficiency. Plant Soil 248:305–312
Zhang X, Lin L, Zhu Z, Yang X, Wang Y, An Q (2013) Colonization and modulation of host growth and metal uptake by endophytic bacteria of Sedum alfredii. Int J Phytoremed 15:51–64
Zhou X, Yu G, Wu F (2011) Effects of intercropping cucumber with onion or garlic on soil enzyme activities, microbial communities and cucumber yield. Eur J Soil Biol 47:279–287
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the projects from The “863” Project by The Ministry of Science and Technology of China (no. 2012AA101405), Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21177107), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY15D010002), and The Fundamental Research Funds for The Central Universities (2014QNA6011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Highlights
An intercropping system to remediate the combined contaminated soil.
Endophytic bacterium Sasm3 promoted plant growth and cadmium absorption.
Sasm3-inoculated intercropping decreased the plant nitrate absorption.
Soil bacterial diversity contributed to the promotion of phytoremediation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, B., Ma, X., Liu, G. et al. An endophytic bacterium Acinetobacter calcoaceticus Sasm3-enhanced phytoremediation of nitrate–cadmium compound polluted soil by intercropping Sedum alfredii with oilseed rape. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 17625–17635 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4933-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4933-5