Abstract
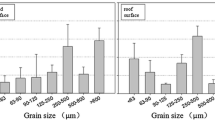
Roofs and roads, accounting for a large portion of the urban impervious land surface, have contributed significantly to urban nonpoint pollution. In this study, in Beijing, China, roof and road runoff are sampled to measure the suspended solids (SS), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) contained in particles with different sizes. The SS content in the road runoff (151.59 mg/L) was sevenfold that in the roof runoff (21.13 mg/L, p < 0.05). The SS contained more coarse particulates in the roof runoff than in road runoff. The small particulates in the range of 0.45–50 μm consisted of 59 % SS in the roof runoff and 94 % SS in the road runoff. P was mainly attached to particle sizes of 10–50 μm in the roof (73 %) and road (48 %) runoffs, while N was mainly in a dissolved phase state in both runoffs. So, the different associations of N and P raise a challenge in preventing stormwater pollution in urban environments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anta J, Pena E, Suárez J, Cagiao J (2006) A BMP selection process based on the granulometry of runoff solids in a separate urban catchment. Water SA 32(3):419–428
Aryal RK, Furumai H, Nakajima F, Boller M (2005) Dynamic behavior of fractional suspended solids and particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in highway runoff. Water Res 39(20):5126–5134
Beijng Municipal Bureau of Statistics (BMBS) and NBS Survey Office in Beijing (NBSSOB). 2014 Beijing statistical yearbook [EB/OL]. China Statistics Press, Beijing, http://www.bjstats.gov.cn/nj/main/2014-tjnj/CH/content/mV91_0417.htm, 2014.09
Brezonik PL, Stadelmann TH (2002) Analysis and predictive models of stormwater runoff volumes, loads, and pollutant concentrations from watersheds in the Twin Cities metropolitan area, Minnesota, USA. Water Res 36:1743–1757
Clark DL, Asplund R, Ferguson J, Mar BW (1981) Composite sampling of highway runoff. J Environ Eng Div 107(EE5):1067–1081, ASCE
Conley DJ, Paerl HW, Howarth RW, Boesch DF, Seitzinger SP, Havens KE, Lancelot C, Linkens GE (2009) Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323:1014–1015
Correll DL (1998) The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: a review. J Environ Qual 27:261–266
Du GS, Wu YM, Yang ZS, Wu DW, Liu J (2005) Analysis of water quality on urban rivers and lakes in Beijing. J Lake Sci 17(4):373–377 (in Chinese)
Fang GC, Chang KF, Lu CS, Bai HL (2004) Estimation of PAHs dry deposition and BaP toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) study at urban, industry park and rural sampling sites in central Taiwan, Taichung. Chemosphere 55:787–796
Furumai H, Baimer H, Boller M (2002) Dynamic behavior of suspended pollutions and particle size distribution in the highway runoff. Water Sci Technol 46:413–418
Gan HY, Zhou MN, Li DQ, Zhou YZ (2008) Quality characterization and impact assessment of highway runoff in urban and rural area of Guangzhou, China. Environ Monit Assess 140(1–3):147–159
Gastaldini MCC, Silva ARV (2013) Pollutant distribution on urban surfaces: case study in southern Brazil. J Environ Eng 139(2):269–276
Gilbert JK, Clausen JC (2006) Stormwater runoff quality and quantity from asphalt, paver, and crushed stone driveways in Connecticut. Water Res 40:826–832
Goonetilleke A, Egodawatta P, Kitchen B (2009) Evaluation of pollutant build-up and wash-off from selected land uses at the Port of Brisbane, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 58(2):213–221
Gromaire MC, Garnaud S, Gonzalez A, Chebbo G (1999) Characterization of Urban Runoff Pollution in Paris. Water Sci Technol 39(2):1–8
Ha SY, Kim GB, Yim UH, Shim WJ, Hong SH, Han GM (2012) Particle-size distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban road dust of Masan, Korea. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 63(2):189–198
Han YH, Lau SL, Kayhanian M, Stenstrom MK (2006) Characteristics of highway stormwater runoff. Water Environ Res 78(12):2377–2388
Herngren L, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA (2005) Understanding heavy metal and suspended solids relationships in urban stormwater using simulated rainfall. J Environ Manag 78:149–158
Hou PQ (2012) Research on the pollution characteristics and influencing factors of urban roof runoff and road runoff [D]. Research Centre for Eco-Environmental Sciences. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing
Huang J, Du PF, Ao CT, Lei MH, Zhang DQ, Ho MH, Wang ZS (2007) Characterization of surface runoff from a subtropics urban catchment. J Environ Sci 19(2):148–152
Jing HW, Hua L, Sun CH, Guo J (2008) Analysis on urban lakes’ eutrophication status in Beijing. J Lake Sci 30(3):357–363 (in Chinese)
Lee JH, Bang KW (2000) Characterisation of urban stormwater runoff. Water Res 34(6):1773–1780
Lee JY, Bak G, Han M (2012) Quality of roof-harvested rainwater – comparison of different roofing materials. Environ Pollut 162:422–429
Li LQ, Yin CQ, He QC, Kong LL (2007) First flush of storm runoff pollution from an urban catchment in China. J Environ Sci 19:295–299
Liu XJ, Ju XT, Zhang Y, He C, Kopsch J, Fusuo Z (2006) Nitrogen deposition in agroecosystems in the Beijing area. Agric Ecosyst Environ 113:370–377
Liu A, Egodawatta P, Guan YT et al (2013) Influence of rainfall and catchment characteristics on urban stormwater quality. Sci Total Environ 444:255–262
Maniquiz MC, Lee S, Lee E, Kim L (2009) Development of linear regression model for metals from transportation land uses. Water Sci Technol 59(12):2495–2501
Miguntanna NP, Liu A, Egodawatta P, Goonetilleke A (2013) Characterising nutrients wash-off for effective urban stormwater treatment design. J Environ Manag 120:61–67
Murakami M, Nakajima F, Furumai H (2005) Size- and density-distributions and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban road dust. Chemosphere 61(6):783–791
Novotny V, Witte JW (1997) Ascertaining aquatic ecological risks of urban stormwater discharges. Water Res 31(10):2573–2585
Opher T, Friedler E (2010) Factors affecting highway runoff quality. Urban Water J 7(3):155–172
Pitte R, Morquecho R (2005) Stormwater quality as described in the National Stormwater Quality Database (NSQD). 10th International Conference on Urban Drainage. Copenhagen/Denmark: 21–26
Ren YF, Wang XK, Ouyang ZY, Zheng H, Duan XM, Miao H (2008) Stormwater runoff quality from different surfaces in an urban catchment in Beijing, China. Water Environ Res 80(8):719–724
Roberts AD, Prince SD, Jantz CA, Goetz SJ (2009) Effects of projected future urban land cover on nitrogen and phosphorus runoff to Chesapeake Bay. Ecol Eng 35:1758–1772
Roger S, Montrejaud-vignoles M, Andral MC, Herremans L, Fortune JP (1998) Mineral, physical and chemical analysis of the solid matter carried by motorway runoff water. Water Res 32:1119–1125
Sansalone JJ, Buchberger S (1995) An infiltration device as a best management practice for immobilizing heavy metals in urban highway runoff. Water Sci Technol 32(4):119–125
Sansalone JJ, Buchberger SG (1997) Partitioning and first flush of metals in urban roadway storm water. J Environ Eng 123:134–143
Sansalone JJ, Kim JY (2008) Transport of particulate matter fractions in urban source area pavement surface runoff. J Environ Qual 37(5):1883–1893
Schiff KC, Tiefenthaler LL (2011) Seasonal flushing of pollutant concentrations and loads in urban stormwater 1. J Am Water Resour Assoc 47(1):136–142
Sheng Y, Ying G, Sansalone J (2008) Differentiation of transport for particulate and dissolved water chemistry load indices in rainfall-runoff from urban source area water-sheds. J Hydrol 361:144–158
State Environmental Protection Agency of China (1989) Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analyzing Method, 3rd edn. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, China
Taylor GD, Fletcher TD, Wong THF, Breen PF, Duncan HP (2005) Nitrogen composition in urban runoff: implications for stormwater management. Water Res 39(10):1982–1989
Vaze J, Chiew FHS (2002) Experimental study of pollutant accumulation on an urban road surface. Urban Water 4:378–389
Vaze J, Chiew FHS (2004) Nutrient load associated with different sediment sizes in the urban stormwater and surface pollutions. J Environ Eng 30:391–396
Wang X, Li JQ, Li YX, Shen ZY, Wang X, Yang ZF, Lou IC (2014) Is urban development an urban river killer? A case study of Yongding Diversion Channel in Beijing, China. J Environ Sci China 26(6):1232–1237
Zhao HT, Li XY, Wang XM, Tain D (2010) Grain size distribution of road-deposited sediment and its contribution to heavy metal pollution in urban runoff in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 183(1–3):203–210
Zhou D, Bi CJ, Chen ZL, Yu ZJ, Wang J, Han JC (2013) Phosphorus loads from different urban storm runoff sources in southern China: a case study in Wenzhou City. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(11):8227–8236
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (Grant No. 41230633 and 41030744).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(XLSX 24 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Ren, Y., Wang, X. et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus associating with different size suspended solids in roof and road runoff in Beijing, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 15788–15795 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4743-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4743-9