Abstract
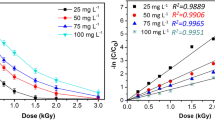
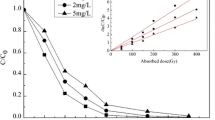
Gamma irradiation-induced decomposition of ciprofloxacin (CIP) was elucidated with different additives, such as CO3 2−, NO3 −, NO2 −, humic acid, methanol, 2-propanol, and tert-butanol. The results show that low initial concentration and acidic condition were favorable for CIP removal during γ irradiation. By contrast, radiolytic decomposition of CIP was inhibited with the addition of anions and organic additives. As a strong carcinogen, Cr6+ was especially mixed with CIP to produce combined pollution. It is noteworthy that the removal of the mixture of CIP and Cr6+ presented a synergistic effect; the degradation efficiency of the two pollutants was markedly improved compared to that of the single pollutant during γ irradiation. Based on the results of quantum chemical calculations and LC-MS analysis, we determined seven kinds of degradation intermediates and presented the CIP degradation pathways, which were mainly attributed to the oxidation process of hydroxyl radicals OH· and the direct decomposition of CIP molecules.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
An T, Yang H, Li G, Song W, Cooper WJ, Nie X (2010) Kinetics and mechanism of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in degradation of ciprofloxacin in water. Appl Catal B Environ 94:288–294
Andrieu M, Rico A, Phu TM, Phuong NT, Van den Brink PJ (2015) Ecological risk assessment of the antibiotic enrofloxacin applied to Pangasius catfish farms in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Chemosphere 119:407–414
Basfar AA, Khan HM, Al-Shahrani AA (2005) Trihalomethane treatment using gamma irradiation: kinetic modeling of single solute and mixtures. Radiat Phys Chem 72:555–563
Basfar AA, Mohamed KA, Al-Abduly AJ, Al-Shahrani AA (2009) Radiolytic degradation of atrazine aqueous solution containing humic substances. Ecotox Environ Safe 72:948–953
Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Jambor JL (1997) In-situ remediation of Cr (VI)-contaminated groundwater using permeable reactive walls: laboratory studies. Environ Sci Technol 31:3348–3357
Borrely SI, Cruz AC, Del Mastro NL, Sampa MHO, Somessari ES (1998) Radiation processing of sewage and sludge. A review. Prog Nucl Energ 33:3–21
Buxton GV, Greenstock CL, Helman WP, Ross AB (1988) Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (·OH/·O− in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem Ref Data 17:513–886
Cho JY, Chung BY, Lee KB, Lee GH, Hwang SA (2014) Decomposition reaction of the veterinary antibiotic ciprofloxacin using electron ionizing energy. Chemosphere 117:158–163
De Bel E, Dewulf J, Witte BD, Van Langenhove H, Janssen C (2009) Influence of pH on the sonolysis of ciprofloxacin: biodegradability, ecotoxicity and antibiotic activity of its degradation products. Chemosphere 77:291–295
De Witte B, Dewulf J, Demeestere K, Van Langenhove H (2009) Ozonation and advanced oxidation by the peroxone process of ciprofloxacin in water. J Hazard Mater 161:701–708
De Witte B, Van Langenhove H, Demeestere K, Saerens K, De Wispelaere P, Dewulf J (2010) Ciprofloxacin ozonation in hospital wastewater treatment plant effluent: effect of pH and H2O2. Chemosphere 78:1142–1147
Garcia-Käufer M, Haddad T, Bergheim M, Gminski R, Gupta P, Mathur N, Kümmerer K, Mersch-Sundermann V (2012) Genotoxic effect of ciprofloxacin during photolytic decomposition monitored by the in vitro micronucleus test (MNvit) in HepG2 cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(5):1719–1727
Getoff N (1996) Radiation-induced degradation of water pollutants—state of the art. Radiat Phys Chem 47:581–593
Getoff N (2002) Factors influencing the efficiency of radiation-induced degradation of water pollutants. Radiat Phys Chem 65:437–446
Guo ZB, Dong QY, He DL, Zhang CZ (2012a) Gamma radiation for treatment of bisphenol A solution in presence of different additives. Chem Eng J 183:10–14
Guo ZB, Zhou F, Zhao YF, Zhang CZ, Liu FL, Bao CX, Lin MY (2012b) Gamma irradiation-induced sulfadiazine degradation and its removal mechanisms. Chem Eng J 191:256–262
Hirsch R, Ternes T, Haberer K, Kratz KL (1999) Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 225(1):109–118
Kümmerer K (2008) Pharmaceuticals in the environment: sources, fate, effects and risks. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg. 1–200
Kümmerer K, Al-Ahmad A, Mersch-Sundermann V (2000) Biodegradability of some antibiotics, elimination of the genotoxicity and affection of wastewater bacteria in a simple test. Chemosphere 40:701–710
Leung HW, Minh TB, Murphy MB, Lam JC, So MK, Martin M, Richardson BJ (2012) Distribution, fate and risk assessment of antibiotics in sewage treatment plants in Hong Kong, South China. Environ Int 42:1–9
Li H, Zhang D, Han X, Xing B (2014) Adsorption of antibiotic ciprofloxacin on carbon nanotubes: pH dependence and thermodynamics. Chemosphere 95:150–155
Liu SY, Chen YP, Yu HQ, Zhang SJ (2005) Kinetics and mechanisms of radiation-induced degradation of acetochlor. Chemosphere 59:13–19
Moriwaki H, Takagi Y, Tanaka M, Tsuruho K, Okitsu K, Maeda Y (2005) Sonochemical decomposition of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid. Environ Sci Technol 39:3388–3392
Polesel F, Lehnberg K, Dott W, Trapp S, Thomas KV, Plósz BG (2015) Factors influencing sorption of ciprofloxacin onto activated sludge: experimental assessment and modelling implications. Chemosphere 119:105–111
Singh A, Kremers W (2002) Radiolytic dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls using alkaline 2-propanol solutions. Radiat Phys Chem 6:467–472
Tai YP, Luo XD, Mo CH, Li YW, Wu XL, Liu XY (2011) Occurrence of quinolone and sulfonamide antibiotics in swine and cattle manures from large-scale feeding operations of Guangdong Province Chinese. Chin J Environ Sci 32:1188–1193 (in Chinese)
Vasconcelos TG, Kümmerer K, Henriques DM, Martins AF (2009) Ciprofloxacin in hospital effluent: degradation by ozone and photoprocesses. J Hazard Mater 169:1154–1158
Wang J, Wang J (2007) Application of radiation technology to sewage sludge processing: a review. J Hazard Mater 143:2–7
Wang RS, Xu QJ, Zhang X, Wei QS, Yan CZ (2012) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in typical township water sources in Dongjiang River Basin. Environ Sci 33:3083–3088 (in Chinese)
Watkinson AJ, Murby EJ, Costanzo SD (2007) Removal of antibiotics in conventional and advanced wastewater treatment: Implications for environmental discharge and wastewater recycling. Water Res 41:4164–4176
Wu HM, Bao BR (2002) Radiation technology applied in environmental field. Chemical Industry Press, China. 1–319 (in Chinese)
Xu J, Xu Y, Wang H, Guo C, Qi H, He Y, Zhang Y, Li XC, Meng W (2014) Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a sewage treatment plant and its effluent-receiving river. Chemosphere 119:1379–1385
Yahya MS, Oturan N, El Kacemi K, El Karbane M, Aravindakumar CT, Oturan A (2014) Oxidative degradation study on antimicrobial agent ciprofloxacin by electro-Fenton process: kinetics and oxidation products. Chemosphere 117:447–454
Yang JF, Ying GG, Zhao JL, Tao R, Su HC, Chen F (2010) Simultaneous determination of four classes of antibiotics in sediments of the Pearl Rivers using RRLC–MS/MS. Sci Total Environ 408:3424–3432
Yuan SJ, Zheng Z, Mou YY, Yu X, Zhao YF (2005) The removal of chromium (VI) in water by gamma-irradiation. China Environ Sci 25:655–659 (in Chinese)
Zhang JB, Zheng Z, Zhao T, Yu X, Zhao YF, Tang DY, Xu Y (2007) Humic acid removal in water by γ-irradiation. Environ Chem 26:749–752 (in Chinese)
Zhou Z, Jiang JQ (2014) Reaction kinetics and oxidation products formation in the degradation of ciprofloxacin and ibuprofen by ferrate (VI). Chemosphere 119:95–100
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41373023 and 21473092), Jiangsu Province research prospective joint research project (BY2013007-03), Jiangsu Province Environmental Protection research project (2014t016), Jiangsu Province “333 high-level talents project” and “Six major talent Summit,” Jiangsu Specially-Appointed Professor program (R2013T08), and A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Highlight
1. We investigated the effect of different kinds of additives on CIP radiolytic removal.
2. The degradation of the mixture containing CIP and a strong carcinogen Cr6+ was conducted in order to seek for a new method for treating combined pollution.
3. CIP removal was mainly controlled by OH· oxidation and CIP direct decomposition on the basis of quantum chemical calculations and LC-MS analysis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Z., Zhu, S., Zhao, Y. et al. Radiolytic decomposition of ciprofloxacin using γ irradiation in aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 15772–15780 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4715-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4715-0