Abstract
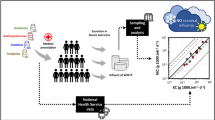
In recent years, it has been demonstrated that sewage-based epidemiology can deliver interesting information on trends in illicit drug consumption. However, until now, no real evidence exists that the measured concentrations of drugs in sewage can be exactly correlated with the amounts of drugs used by a specific population. This study aimed therefore at correlating detailed monthly prescription figures of 11 pharmaceuticals (atenolol, bisoprolol, citalopram, fluoxetine, venlafaxine, losartan, telmisartan, valsartan, carbamazepine, metformin, and tramadol) with measured concentrations of these compounds in influent sewage from five sewage treatment plants in Belgium. For 7 out of the 11 substances, a ratio between loads calculated from the prescription figures and loads calculated from measured concentrations in the range of 0.30–3.00 was observed. For four pharmaceuticals (atenolol, bisoprolol, telmisartan, and venlafaxine), the observed relationship was less pronounced. The manuscript gives an overview of the possible uncertainties that are related with the calculated correlations. This study highlights the need for gathering all the necessary information regarding sewage sampling, stability of substances in sewage, pharmacokinetics, and analytical method performance when sewage-based epidemiology studies are performed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baselt RC (2011) Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man, 9th edn. Biomedical Publications, Foster
Boxall ABA, Keller VDJ, Straub JO, Monteiro SC, Fussell R, Williams RJ (2014) Exploiting monitoring data in environmental exposure modelling and risk assessment of pharmaceuticals. Environ Int 73:176–185
Brausch JM, Connors KA, Brooks BW, Rand GM (2012) Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: a review of recent toxicological studies and considerations for toxicity testing. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 218:1–99
Carballa M, Omil F, Lema JM (2008) Comparison of predicted and measured concentrations of selected pharmaceuticals, fragrances and hormones in Spanish sewage. Chemosphere 72:1118–1123
Castiglioni S, Bijlsma L, Covaci A, Emke E, Hernández F, Reid M, Ort C, Thomas KV, van Nuijs ALN, de Voogt P, Zuccato E (2013) Evaluation of uncertainties associated with the determination of community drug use through the measurement of sewage drug biomarkers. Environ Sci Technol 47:1452–1460
Castiglioni S, Thomas KV, Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Vandam L, Griffiths P (2014) Testing wastewater to detect illicit drugs: state of the art, potential and research needs. Sci Total Environ 487:613–620
Fatta-Kassinos D, Meric S, Nikolaou A (2011) Pharmaceutical residues in environmental waters and wastewater: current state of knowledge and future research. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:251–275
Hernandez F, Ibanez M, Portoles T, Cervera MI, Sancho JV, Lopez FJ (2015) Advancing towards universal screening for organic pollutants in water. J Haz Mat 282:86–95
Huerta B, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Barceló D (2012) Pharmaceuticals in biota in the aquatic environment: analytical methods and environmental implications. Anal Bioanal Chem 404:2611–2624
Lai FY, Ort C, Gartner C, Carter S, Prichard J, Kirkbride P, Bruno R, Hall W, Eaglesham G, Mueller JF (2011) Refining the estimation of illicit drug consumption from wastewater analysis: co-analysis of prescription pharmaceuticals and uncertainty assessment. Water Res 45:4437–4448
Morasch B, Bonvin F, Reiser H, Grandjean D, de Alencastro LF, Perazzolo C, Chèvre N, Kohn T (2010) Occurrence and fate of micropollutants in the Vidy Bay of lake Geneva, Switzerland. Part II: micropollutant removal between wastewater and raw drinking water. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:1658–1668
Ort C, Lawrence MG, Reungoat J, Mueller JF (2010a) Sampling for PPCPs in wastewater systems: a comparison of different sampling modes and optimization strategies. Environ Sci Technol 44:6289–6296
Ort C, Lawrence MG, Rieckermann J, Joss A (2010b) Sampling for PPCPs and illicit drugs in wastewater systems: are your conclusions valid?, A critical review. Environ Sci Technol 44:6024–6035
Petrovic M, Farré M, Lopez de Alda M, Perez S, Postigo C, Köck M, Radjenovic J, Gros M, Barcelo D (2010) Recent trends in the liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of organic contaminants in environmental samples. J Chromatogr A 1217:4004–4017
Physicians’ Desk Reference (2014) PDR Network, Montvale, New Jersey
Richardson S (2010) Environmental mass spectrometry: emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal Chem 82:4742–4774
Richardson S, Ternes TA (2011) Water analysis: emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal Chem 83:4614–4648
Stangier J, Schmid J, Turck D, Switek H, Verhagen A, Peeters PAM, van Marle SP, Tamminga WJ, Sollie FAE, Jonkma JHG (2000) Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of intravenously and orally administered [14C] telmisartan in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 40:1312–1322
Tarcomnicu I, van Nuijs ALN, Simons W, Bervoets L, Blust R, Jorens PG, Neels H, Covaci A (2011) Simultaneous determination of 15 top-prescribed pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in influent wastewater by reversed-phase liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 83:795–803
Tauxe-Wuersch A, De Alencastro LF, Grandjean D, Tarradellas J (2005) Occurrence of several acidic drugs in sewage treatment plants in Switzerland and risk assessment. Water Res 39:1761–1772
ter Laak TL, Kooij PJF, Tolkamp H, Hofman J (2014) Different compositions of pharmaceuticals in Dutch and Belgian rivers explained by consumption patterns and treatment efficiency. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12843–12855
van Nuijs ALN, Tarcomnicu I, Simons W, Bervoets L, Blust R, Jorens PG, Neels H, Covaci A (2010) Optimization and validation of a hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of 13 top-prescribed pharmaceuticals in influent wastewater. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:2211–2222
van Nuijs ALN, Castiglioni S, Tarcomnicu I, Postigo C, Lopez de Alda M, Neels H, Zuccato E, Barcelo D, Covaci A (2011) Illicit drug consumption estimations derived from wastewater analysis: a critical review. Sci Total Environ 409:3564–3577
van Nuijs ALN, Abdellati K, Bervoets L, Blust R, Jorens PG, Neels H, Covaci A (2012) The stability of illicit drugs and metabolites in wastewater, an important issue for sewage epidemiology? J Haz Mat 239–240:19–23
Verlicchi P, Al Aukidy M, Zambello E (2012) Occurrence of pharmaceutical compounds in urban wastewater: removal, mass load and environmental risk after a secondary treatment—a review. Sci Total Environ 429:123–155
Verlicchi P, Al Aukidy M, Jelic A, Petrovic M, Barcelo D (2014) Comparison of measured and predicted concentrations of selected pharmaceuticals in wastewater and surface water: a case study of a catchment area in the Po Valley (Italy). Sci Total Environ 470–471:844–854
World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology (2012) ATC classification index with DDDs, 2013. Oslo, Norway
Acknowledgments
The Flanders Scientific Funds for Research (FWO) is acknowledged for the financial support through FWO research project G.0177.09M. Alexander van Nuijs acknowledges FWO for his scholarship. The authors would like to thank Alain Vandelannoote (Aquafin, Belgium) for his support with the sampling of sewage. Dr. Christoph Ort (Eawag, Switzerland) is acknowledged for his help with data analysis and presentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hongwen Sun
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 23 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Nuijs, A.L.N., Covaci, A., Beyers, H. et al. Do concentrations of pharmaceuticals in sewage reflect prescription figures?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 9110–9118 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4066-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4066-2