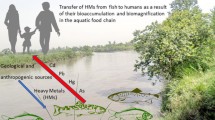
Abstract
In the present study, the bioaccumulation of six heavy metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, and Zn) in Hediste (Nereis) diversicolor (O.F. Müller, 1776) and also in the muscle and liver of Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758) collected from seven stations in the Bafa Lake was investigated. Sediment samples were also collected in each site to assess heavy metal levels and to provide additional information on pollution of the lake. The mean concentrations of heavy metals in sediment, H. diversicolor, and muscle and liver of the fish were found to be in the magnitude of Cr>Pb>Zn>Cu>Cd>Hg, Zn>Cu>Cr>Pb>Hg>Cd, Zn>Cu>Pb>Cr >Hg>Cd, and Cu>Zn>Cr>Cd>Pb>Hg, respectively. Hg, Cu, and Zn in H. diversicolor and Hg and Zn in muscle and also Hg, Cd, Cu, and Zn in liver of fish accumulated in a higher degree than in sediment. There was no clear relationship between metal concentrations in sediments, polychaetes, and fish, except Cr. According to international criteria and Turkish regulations, Pb and Zn values in edible muscle of the fish collected from stations S6 and S5 exceeded the food safety limits, respectively. The results of this study suggest that these sentinel species can be considered as good anthropogenic biological indicators for heavy metal pollution along the Bafa Lake.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah M, Abdallah M (2008) Biomonitoring study of heavy metals in biota and sediments in the South Eastern coast of Mediterranean Sea. Environ Monit Assess 146:139–145
Abdel-Moneim MA, Khaled AM, Iskander MF (1994) A study on the levels of some heavy metals in El-Mex, West of Alexandria, Egypt. Proc. 4th Conf. of the Envir. Prot. Is a must, 10–12 May, pp:155–174
Abowei JFN (2010) Salinity, dissolved oxygen, pH and surface water temperature conditions in Nkoro River, Niger Delta, Nigeria. Adv J Food Sci Technol 2:36–40
Alam MA, Gomes A, Sarkar SK, Shuvaeva OV, Vishnevetskaya NS, Gustaytis MA et al (2010) Trace metal bioaccumulation by soft-bottom polychaetes (Annelida) of Sundarban Mangrove Wetland, India and their potential use as contamination indicator. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85(5):492–496
Anonymous (1996) Handbook of quality control on fish products. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Ankara (In Turkish)
Bahnasawy M, Khidr A, Dheina N (2009) Seasonal variations of heavy metal concentrations in Mullet, Mugil cephalus and Liza ramada (Mugilidae) from Lake Manzala, Egypt. J Appl Sci Res 5(7):845–852
Bardarudeen T, Damodaran KT, Sajan K, Padmalal D (1996) Texture and geochemistry of the sediments of a tropical mangrove ecosystem, southwest coast of India. Environ Geol 27:164–169
Başyiğit B, Tekin-Özan S (2013) Concentartions of some heavy metals in water, sediment and tissues of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) form Karataş Lake related to Physicochemical parameters, fish size and seasons. Pol J Environ Stud 22(3):633–644
Berthet B, Mouneyrac C, Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Berthelot Y, Rainbow PS, Smith BD (2003) Accumulation and soluble binding of cadmium, copper, and zinc in the polychaete Hediste diversicolor from coastal sites with different trace metal bioavailabilities. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45(4):468–478
Boyd CE, Lichtkoppler F (1979) Water quality management in fishpond, Research and Dev, vol 22. International Centre for Aquaculture and Agriculture (I.C.A.A.), Experimental station Auburn University, Alabama, pp 45–47
Cajaraville MP, Bebianno MJ, Blasco J, Porte C, Sarasquete C, Viarengo A (2000) The use of biomarkers to assess the impact of pollution in coastal environments of the Iberian Peninsula: a practical approach. Sci Total Environ 247(2–3):295–317
Canbek M, Demir TA, Uyanoglu M, Bayramoglu G, Emiroglu Ö, Arslan N et al (2007) Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and some Cyprinidae species from the Porsuk River, Turkey. J Appl Biol Sci 1(3):91–95
Chapman D (1992) Water quality assessments. A guide to the use of biota, sediments and water in environmental monitoring. UNESCO/WHO/UNEP, Chapman and Hall, London, pp 371–460
Chapman PM, Wang FY (2001) Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(1):3–22
Chen KP, Jiao JJ (2008) Metal concentration and mobility in marine sediment and groundwater in costal reclamation areas: a case of study in Shenzhen, China. Environ Pollut 151(3):576–584
Chouba L, Kraiem M, Njimi W, Tissaoui C, Thompson J, Flower R (2007) Seasonal variation of heavy metals (Cd, Pb, and Hg) in sediments and mullet, Mugil cephalus (Mugilidae) from the Ghar EL-Melh lagoon (Tunisia). Transit Waters Bull 4:45–52
Degnon RG, Dahouenon-Ahoussi E, Adjou ES, Soumanou MM, Dolganova NV, Sohounhloue DCK (2012) Heavy metal contamination of the Nokoué Lake (Southern Benin) and the dynamic of their distribution in organs of some fish’s species (Mugil cephalus L. and Tilapia guineensis). J Anim Sci Adv 2(7):589–595
Depledge MH, Rainbow PS (1990) Comp Biochem Physiol C: Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 97:1–7
Díez G, Soto M, Canton L, Vaquero C, Marigomez I (2000) Hediste (Nereis) diversicolor as bioindicator of metal and organic chemical bioavailability: a field study. Ecotoxicol Environ Restor 3:7–15
Dora EC, Sunlu U, Ergen (2007) Heavy metal concentrations in Hediste diversicolor (Polychaeta) and sediments from Homa Lagoon (Izmir Bay-Turkey). Rapp Comm int Mer Medit 38:253
Dural M, Göksu MZL, Özak AA (2007) Investigation of heavy metal levels in economically ımportant fish species captured from the Tuzla Lagoon. Food Chem 102:415–421
Durou C, Poirier L, Amiard JC, Budzinski H, Gnassia-Barelli M, Lemenach K et al (2007) Biomonitoring in a clean and a multi-contaminated estuary based on biomarkers and chemical analyses in the endobenthic worm Nereis diversicolor. Environ Pollut 148:445–458
European Commission (2011) Commission Regulation (EU) No 420/2011 of 29 April 2011 Amending Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. 30.4.2011. Off J Eur Union L 111:3–6
Farrugio H, Quignard JP (1974) Biologie de Mugil ramada et Mugil labrosus du lac de Tunis. Bull Inst Océanogr Pêche Salammbô 3:1–4
Ferreira M, Moradas-Ferreira P, Reis-Henriques MA (2005) Oxidative stress biomarkers in two resident species, mullet (Mugil cephalus) and flounder (Platichthys flesus), from a polluted sitein River Douro Estuary. Portugal Aquat Toxicol 71:39–48
Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) (1983) Manual of Methods in Aquatic Environmental Research, part 9. Analyses of metals and organochlorines in fish. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper, 212
Frangipane G, Volpi Ghirardini A, Collavini F, Zaggia L, Pesce A, Tagliapietra D (2005) Heavy metals in Hediste diversicolor (Polychaeta: Nereididae) and salt marsh sediments from the lagoon of Venice (Italy). Chem Ecol 21(6):441–454
Gochfeld M (2003) Cases of mercury exposure, bioavailability and absorption. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 56(1):174–179
Gomes T, Gonzalez-Rey M, Rodríguez-Romero A, Trombini C, Rıba I, Blasco J et al (2013) Biomarkers in Nereis diversicolor (Polychaeta: Nereididae) as management tools for environmental assessment on the southwest Iberian coast. Sci Mar 77S1:69–78
Gürer İ, Yıldız E (2008) Türkiye’nin sulak alan politikalarına genel bir bakış: Sultan sazlığı sulak alanı örneği, TMMOB, 2. Su Politikaları Kongresi Bildiriler 335–345
Hach Publication (1988) Procedures for Water and Waste-Water Analysis. p. 392
Häkanson L, Jansson M (1983) Principles of Lake Sedimentology. Springer Verlag, New York, p 316
Hateley JG, Grant A, Jones NV (1989) Heavy metal tolerance in estuarine populations of Nereis diversicolor. In: Ryland JS, Tyler PA (eds) Reproduction, genetics and distribution of marine organisms. Proc 23rd Eur Mar Biol Symp: Olsen and Olsen, Fredensborg, pp 379–385
Heath AG (1995) Water pollution and fish physiology. FL CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hirner A, Kritsotakis K, Tobschall H (1990) Metal organic association in sediments, I, Comparisons of unpolluted recent and ancient sediments and sediments affected by anthropogenic pollution. Appl Geochem 5:491–505
Idardare Z, Chiffoleau J-F, Moukrim A, Alla A, Ait Auger D, Lefrere L et al (2008) Metal concentrations in sediment and Nereis diversicolor in two Moroccan lagoons: Khnifiss and Oualidia. Chem Ecol 24(5):329–340
Kamaruzzaman BY, Ong MC, Rana SZ, Joseph B (2010) Levels of some heavy metal in fishes from Pahang river estuary. Malaysia J Biol Sci 10(2):157–161
Karthikeyan R, Vijayalakshmi S, Balasubramanian T (2007) Monthly variations of heavy metals and metal resistant bacteria from the Uppanar estuary (Southeast coast of India). Res J Microbiol 2(1):50–57
Kasparek M (1988) Bafasee. Natur und Geschichte in der Türkischen Ägäis. Max Kasparek Verlag, Heidelberg; p.174
Keil RG, Tsamakis E, Fuh CB, Giddings CA, Hedges J (1994) Mineralogical and textural controls on the organic composition of coastal marine sediments: hydrodynamic separation using SPLITT-fractionation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:879–893
Koç C (2008) The effects of the environment and ecology projects on lake management and water quality. Environ Monit Assess 146:397–409
Lawson EO (2011) Physico-chemical parameters and heavy metal contents of water from the mangrove swamps of Lagos lagoon. Nigeria Adv Biol Res 5(1):8–2
Linnaeus C (1758) Systema naturæ per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I. Editio decima, reformata. Laurentius Salvius, Holmiae; p. [1–4], 1–824
Lucas F, Bertru G (1997) Bacteriolysis in the gut of Nereis diversicolor and effect of diet. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 215(2):235–245
Marcovecchio JE (2004) The use of Micropogonias furnieri and Mugil liza as bioindicators of heavy metals pollution in La Plata river estuary, Argentina. Sci Total Environ 323(1–3):219–226
Momba MNB, Tyafa Z, Makala N, Brouckaert BM, Obi CL (2006) Safe drinking water still a dream in rural areas of South Africa. Case study: the Eastern Cape Province. Water SA 32(5):715–720
Moreira SM, Lima I, Ribeiro R, Guilhermino L (2006) Effects of estuarine sediment contamination on feeding and on key physiological functions on the polychaete Hediste diversicolor: laboratory and in situ assays. Aquat Toxicol 78:186–201
Mouneyrac C, Mastain O, Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Beaunier P, Jeantet AY et al (2003) Trace-metal detoxification and tolerance of the estuarine worm Hediste diversicolor chronically exposed in their environment. Mar Biol 143:731–74
Müller OF (1776) Zoologiae Danicae Prodromus seu Animalium Daniae et Norvegiae indigenarum characteres, nomina, et synonyma imprimis popularium. Hafniae, Typiis Hallageriis; p. xxii + 274
Peakall D, Burger J (2003) Methodologies for assessing exposure to metals: speciation, bioavailability of metals, and ecological host factors. Ecotox Environ Safe 56(1):110–121
Radojevic M, Bashkin VN (1999) Practical environmental analysis. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, p 466
Ruffin P, Demuynck S, Hilbert JL, Dhainaut A (1994) Stress proteins in the polychaete annelid Nereis diversicolor induced by heat shock or cadmium exposure. Biochimie 76(5):423–427
Saiz-Salinas JI, Francés-Zubillaga G (1997) Nereis diversicolor: an unreliable biomonitor of metal contamination in the ‘Ría de Bilbao’ (Spain). Mar Ecol 18(2):113–125. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0485.1997.tb00431.x
Scaps P (2002) A review of the biology, ecology and potential use of the common ragworm Hediste diversicolor (O.F. Müller) (Annelida: Polychaeta). Hydrobiologia 470:203–218
Schropp SJ, Windrom HL (1988) A guide to the interpretation of metal concentrations in estuarine sediments. In: Schropp SJ, Windom HL editors. Savannah, Georgia; p. 53
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1972) A practical hand book of seawater analysis. J Fish Res Bd Canada. Bulletin 167, Second edition, Ottawa
Taş EÇ, Ergen Z, Sunlu U (2009) 2002–2004 Yılları Arasında Homa Lagünü’nden (İzmir Körfezi) Toplanan Hediste diversicolor’da ve Yaşadığı Sedimentte Ağır Metal Düzeylerinin (Cd, Cu, Zn, Pb, Cr, Fe) Araştırılması. E.U. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 26:179–185
Thomann RV, Mahony JD, Mueller R (1995) Steady-state model of biota sediment accumulation factor for metals in two marine bivalves. Environ Toxicol Chem 14(11):1989–1998
TUIK. Turkey’s Statistical Yearbook (2010) (www.tuik.gov.tr.), 2010. p.12
TUIK. Turkey’s Statistical Yearbook (2011) (www.tuik.gov.tr.), 2011. p.12
Turkish Alimentarius Codex (2002) Microbial toxins, metal and metalloid residues. 63
UNEP (1982) Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies 14
UNEP (1984) Determination of total Cd, Zn, Pb and Cu in selected marine organisms by flameless AAS. Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies. 11
UNEP (1985) Reference methods for marine pollution studies, determination of total Hg in marine sediments and suspended solids by cold vapour AAS 26
UNEP (1985a) GESAMP, cadmium, lead and tin in the marine environment. UNEP Regional Seas Reports and Studies 56
UNEP (1985b) Determination of total Hg in marine sediments and suspended solids by cold vapour AAS. Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies 26
UNEP (1985c) Determination of total cadmium in marine sediments by flameless AAS. Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies 27
UNEP (1985d) Determination of total chromium in marine sediments by flameless AAS. Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies 31
UNEP (1985e) Determination of total lead in marine sediments by flameless AAS. Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies 34
USEPA (1999) “Volunteer lake monitoring: a methods manual,” EPA 440/4-91-002, office of water US environ-mental protection agency. USEPA, Washington DC
USEPA (2002) “Risk Assessment: Technical Background Information,”http://www.epa.gov/reg3hwmd/risk
Virgilio M, Baroncini N, Trombini C, Abbiati M (2003) Relationships between sediments and tissue contamination and allozymic patterns in Hediste diversicolor (Polychaeta Nereididae) in the Pialassa lagoons (north Adriatic Sea). Oceanol Acta 26:85–92
Volpi Ghiradini A, Cavallini L, Delaney E, Tagliapietra D, Ghetti PF, Bettiol C et al (1999) H. diversicolor, N.succinea and P.cultrifera (Polychaeta: Nereididae) as bioaccumulators of cadmium and zinc from sediments: preliminary results in the Venetian lagoon (Italy). Toxicol Environ Chem 71(3–4):457–474
Waltham NJ, Teasdale PR, Connolly RM (2011) Contaminants in water, sediment and fish from natural and artificial residential waterways in southern Moreton Bay. J Environ Monit 13:3409–3419
WHO (2004) “World Health Organization standard for Drinking Water”, Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, vol 1. Recommendation, France, p 181
Williams TP, Bubb JM, Lester JN (1994) Metal accumulation within salt marsh environments: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 28(5):277–290
World Health Organisation (WHO) (1986) Review of potentially harmful substances-Arsenic, mercury and selenium. Rep Stud 28:172
Yilgor S, Kucuksezgin F, Özel E (2012) Assessment of metal concentrations in sediments from Lake Bafa (Western Anatolia): an Inlex analysis approach. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:512–518. doi:10.1007/s00128-012-0699-3
Yilmaz AB (2009) The comparison of heavy metal concentrations (Cd, Cu, Mn, Pb and Zn) in tissues of three economically important fish (Anguilla anguilla, Mugil cephalus and Oreochromis niloticus) inhabiting Köycegiz Lake-Mugla (Turkey). Turk J Sci Tech 4(1):7–15
Yilmaz E, Koç C (2014) Research on water quality of Lake Bafa in Turkey. Environ Eng Manag J 13(1):153–162
Acknowledgments
The authors express their sincere gratitude to Dr. Melih Ertan Çınar for the identification of the polychaetes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Stuart Simpson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aydin-Onen, S., Kucuksezgin, F., Kocak, F. et al. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in Hediste diversicolor (O.F. Müller, 1776), Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758), and surface sediments of Bafa Lake (Eastern Aegean). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 8702–8718 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4047-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4047-5