Abstract
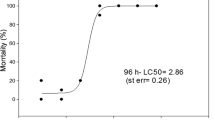
In order to clarify the suitability of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos for the detection of neurotoxic compounds, the acetylcholinesterase assay was adapted and validated with a series of priority pollutants listed as relevant for the European water policy (Aroclor 1254, 2,3-benzofuran, bisphenol A, chlorpyrifos, paraoxon-methyl, quinoline, and methyl mercury chloride) as well as acetonic extracts from three sediments of known contamination. The acute toxicities of the model substances and the sediment extracts were determined by means of the fish embryo test as specified in OECD TG 236, and concentrations as low as the effective concentration at 10 % inhibition (EC10) were used as the highest test concentration in the acetylcholinesterase test in order to avoid nonspecific systemic effects mimicking neurotoxicity. Among the model compounds, only the known acetylcholinesterase inhibitors paraoxon-methyl and chlorpyrifos produced a strong inhibition to about 20 and 33 %, respectively, of the negative controls. For the sediment extracts, a reduction of acetylcholinesterase activity to about 60 % could only be shown for the Vering Canal sediment extracts; this could be correlated to high contents of acetylcholinesterase-inhibiting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) as identified by chemical analyses. Co-incubation of the Vering Canal sediment extracts with chlorpyrifos at EC10 concentrations each did not significantly increase the inhibitory effect of chlorpyrifos, indicating that the mode of action of acetylcholinesterase inhibition by the sediment-borne PAHs is different to that of the typical acetylcholinesterase blocker chlorpyrifos. Overall, the study documents that zebrafish embryos represent a suitable model not only to reveal acetylcholinesterase inhibition, but also to investigate various modes of neurotoxic action.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arufe MI, Arellano JM, García L, Albendín G, Sarasquete C (2007) Cholinesterase activity in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) larvae: characterization and sensitivity to the organophosphate azinphosmethyl. Aquat Toxicol 84:328–336
Bachmann J (2002) Entwicklung und Erprobung eines Teratogenitäts-Screening Testes mit Embryonen des Zebrabärblings Danio rerio. Dissertation. Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades Doctor rerum naturalium Thesis, Technische Universität
Behra M, Cousin X, Bertrand C, Vonesch J-L, Biellmann D, Chatonnet A, Strähle U (2002) Acetylcholinesterase is required for neuronal and muscular development in the zebrafish embryo. Nat Neurosci 5:111–118
Behra M, Etard C, Cousin X, Strähle U (2004) The use of zebrafish mutants to identify secondary target effects of acetylcholine esterase inhibitors. Toxicol Sci 77:325–333
Bertrand C, Chatonnet A, Takke C, Yan Y-L, Postlethwait J, Toutant J-P, Cousin X (2001) Zebrafish acetylcholinesterase is encoded by a single gene localized on linkage group 7: gene structure and polymorphism; molecular forms and expression pattern during development. J Biol Chem 276:464–474
Braunbeck T (1992) Umweltcytologie—zelluläre Reaktionen zum Nachweis einer Schadstoffbelastung von Organismen. Ruperto Carola 85:61–85
Braunbeck T (1994) Entwicklung von Biotestverfahren mit Zellkulturen aus Fischen zum Nachweis letaler und subletaler Schäden von Organismen durch Umweltschadstoffe im Wasser. Veröff PAÖ 8:533–558
Braunbeck T (1998) Cytological alterations in fish hepatocytes—in vivo and in vitro biomarkers of environmental contamination. In: Braunbeck T, Hinton DE, Streit B (eds) Fish ecotoxicology. Experientia, Suppl. Ser. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 61–140
Braunbeck T, Brauns A, Keiter S, Hollert H, Schwartz P (2009) Fish populations under stress—the example of the Lower Neckar River. UWSF–Z Umweltchem Ökotox 21:197–211
Chen G, White PA (2004) The mutagenic hazards of aquatic sediments: a review. Mutat Res 567:151–225
Chen C, Wang Y, Zhao X, Wang Q, Qian Y (2014) The combined toxicity assessment of carp (Cyprinus carpio) acetylcholinesterase activity by binary mixtures of chlorpyrifos and four other insecticides. Ecotoxicology 23:221–228
De Domenico E, Mauceri A, Giordano D, Maisano M, Giannetto A, Parrino V, Natalotto A, D’Agata A, Cappello T, Fasulo S (2013) Biological responses of juvenile European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) exposed to contaminated sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 97:114–123
Dembélé K, Haubruge E, Gaspar C (2000) Concentration effects of selected insecticides on brain acetylcholinesterase in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 45:49–54
Durou C, Poirier L, Amiard JC, Budzinski H, Gnassia-Barelli M, Lemenach K, Peluhet L, Mouneyrac C, Roméo M, Amiard-Triquet C (2007) Biomonitoring in a clean and a multi-contaminated estuary based on biomarkers and chemical analyses in the endobenthic worm Nereis diversicolor. Environ Pollut 148:445–458
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
EPA U (2007) Validation of the fish short-term reproduction assay: integrated summary report. US Environmental Agency, Washington, DC. Unpublished report dated 15 December 2007
EU (2001) Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy (Water Framework Directory). Off J EU L 327/1:72 p
EU (2008) Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on environmental quality standards in the field of water policy, amending and subsequently repealing Council Directives 82/176/EEC, 83/513/EEC, 84/156/EEC, 84/491/EEC, 86/280/EEC and amending Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Off J EU L 348/84:14 p
Fan Y, Ding S, Ye X, Manyande A, He D, Zhao N, Yang H, Jin X, Liu J, Tian C, Xu S, Ying C (2013) Does preconception paternal exposure to a physiologically relevant level of bisphenol A alter spatial memory in an adult rat? Horm Behav 64:598–604
Förstner U (2008) Umweltschutztechnik. 7th edn. Springer, Heidelberg, p 475
Fukuto TR (1990) Mechanism of action of organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides. Environ Health Perspect 87:245–254
Fulton MH, Key PB (2001) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in estuarine fish and invertebrates as an indicator of organophosphorus insecticide exposure and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:37–45
Gorokhova E, Löf M, Halldórsson HP, Tjärnlund U, Lindström M, Elfwing T, Sundelin B (2010) Single and combined effects of hypoxia and contaminated sediments on the amphipod Monoporeia affinis in laboratory toxicity bioassays based on multiple biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 99:263–274
Guilhermino L, Celeste Lopes M, Carvalho AP, Soares AM (1996) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity as effect criterion in acute tests with juvenile Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 32:727–738
Hafner C, Gartiser S, Garcia-Kaeufer M, Schiwy S, Hercher C, Meyer W, Achten A, Larsson M, Engwall M, Keiter S, Hollert H (2014) Investigations on sediment toxicity of German rivers applying a standardized bioassay battery. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3894-4
Hannemann EH (1992) Diisopropylfluorophosphate inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity and disrupts somitogenesis in the zebrafish. J Exp Zool 263:41–53
Heinrich P, Diehl U, Förster F, Braunbeck T (2014) Improving the in vitro ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) assay with RTL-W1 by metabolic normalization and use of β-naphthoflavone as the reference substance. Comp Biochem Physiol 164C:27–34
Hollert H, Dürr M, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T (2000) Cytotoxicity of settling particulate matter (SPM) and sediments of the Neckar River (Germany) during a winter flood. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:528–534
Hollert H, Heise S, Keiter S, Heininger P, Förstner U (2007) Wasserrahmenrichtlinie—Fortschritte und Defizite. UWSF–Z Umweltchem Ökotox 19:58–70
Hollert H, Bluhm K, Keiter S, Böttcher M, Grund S, Seitz N, Otte J, Braunbeck T, Hecker M, Higley E, Giesy J, Takner H, Bavel B, Engwall M, Reifferscheid G, Manz W, Erdinger L, Schulze T, Luebcke-van Varel U, Brack W, Kammann U, Schöneberger R, Suter M, Strähle U (2009) Eine Weight-of-Evidence-Studie zur Bewertung der Sedimentbelastung und des Fischrückgangs in der Oberen Donau. UWSF–Z Umweltchem Ökotox 21:260–263
Humphrey C, Klumpp DW (2003) Toxicity of chlorpyrifos to the early life history stages of eastern rainbowfish Melanotaenia splendida splendida (Peters 1866) in tropical Australia. Environ Toxicol 18:418–427
Irmler I, Schmidt K, Starck JM (2004) Developmental variability during early embryonic development of zebra fish, Danio rerio. Mol Dev Evol 302B:446–457
Jett DA, Navoa RV, Lyons MA (1999) Additive inhibitory action of chlorpyrifos and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on acetylcholinesterase activity in vitro. Toxicol Lett 105:223–229
Jung JH, Hong SH, Yim UH, Ha SY, Shim WJ, Kannan N (2012) Multiple in vitro bioassay approach in sediment toxicity evaluation: Masan Bay, Korea. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:32–37
Kang JJ, Fang HW (1997) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons inhibit the activity of acetylcholinesterase purified from electric eel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 238:367–369
Keiter S, Rastall A, Kosmehl T, Wurm K, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2006) Ecotoxicological assessment of sediment, suspended matter and water samples in the upper Danube River. A pilot study in search for the causes for the decline of fish catches. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 13:308–319
Keiter S, Böttcher M, Grund S, Seitz N, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2009) Der Fischrückgang in der oberen Donau. UWSF–Z Umweltchem Ökotox 21:186–196
Keiter S, Peddinghaus S, Feiler U, von der Goltz B, Hafner C, Ho NY, Rastegar S, Otte J, Ottermanns R, Reifferscheid G, Strähle U, Braunbeck T, Hammers-Wirtz M, Hollert H (2010a) DanTox—ein BMBF-Verbundprojekt zur Ermittlung spezifischer Toxizität und molekularer Wirkungsmechanismen sedimentgebundener Umweltschadstoffe mit dem Zebrabärbling (Danio rerio). Umweltwiss Schadst Forsch 22:94–98
Keiter S, Peddinghaus S, Feiler U, von der Goltz B, Hafner C, Ho NY, Rastegar S, Otte J, Ottermanns R, Reifferscheid G, Strähle U, Braunbeck T, Hammers-Wirtz M, Hollert H (2010b) DanTox—a novel joint research project using zebrafish (Danio rerio) to identify specific toxicity and molecular modes of action of sediment-bound pollutants. J Soils Sediments 10:714–717
Kloas W, Urbatzka R, Opitz R, Würtz S, Behrends T, Hermelink B, Hofmann F, Jagnytsch O, Kroupova H, Lorenz C, Neumann N, Pietsch C, Trubiroha A, Van Ballegooy C, Wiedemann C, Lutz I (2009) Endocrine disruption in aquatic vertebrates. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1163:187–200
Kopecka-Pilarczyk J, Correia AD (2011) Effects of exposure to PAHs on brain AChE in gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata L., under laboratory conditions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:379–383
Korzh S, Pan X, Garcia-Lecea M, Lanny Winata C, Pan X, Wohland T, Korzh V, Gong Z (2008) Requirement of vasculogenesis and blood circulation in late stages of liver growth in zebrafish. BMC Dev Biol 8:84
Küster E (2005) Cholin- and carboxylesterase activities in developing zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio) and their potential use for insecticide hazard assessment. Aquat Toxicol 75:78–95
Küster E, Altenburger R (2006) Comparison of cholin- and carboxylesterase enzyme inhibition and visible effects in the zebra fish embryo bioassay under short-term paraoxon-methyl. Biomarkers 111:341–343
Küster E, Altenburger R (2007) Suborganismic and organismic effects of aldicarb and its metabolite aldicarb-sulfoxide to the zebrafish embryo (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 68:751–760
Lammer E, Carr GJ, Wendler K, Rawlings JM, Belanger SE, Braunbeck T (2009) Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp Biochem Physiol 149C:196–209
Minier C, Forget-Leray J, Bjornstad A, Camus L (2008) Multixenobiotic resistance, acetyl-choline esterase activity and total oxyradical scavenging capacity of the Arctic spider crab, Hyas araneus, following exposure to bisphenol A, tetra bromo diphenyl ether and diallyl phthalate. Mar Pollut Bull 56:1410–1415
Miyagawa K, Narita M, Narita M, Akama H, Suzuki T (2007) Memory impairment associated with a dysfunction of the hippocampal cholinergic system induced by prenatal and neonatal exposures to bisphenol-A. Neurosci Lett 418:236–241
Monteiro M, Quintaneiro C, Morgado F, Soares AM, Guilhermino L (2005) Characterization of the cholinesterases present in head tissues of the estuarine fish Pomatoschistus microps: application to biomonitoring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:341–347
Moralev SN, Rozengart EV (2001) “Substrate inhibition” is one of the aspects of substrate specificity in vertebrate and invertebrate cholinesterases. J Evol Biochem Physiol 37:469–491
Muthuvel R, Venkataraman P, Krishnamoorthy G, Gunadharini DN, Kanagaraj P, Jone Stanley A, Srinivasan N, Balasubramanian K, Aruldhas MM, Arunakaran J (2006) Antioxidant effect of ascorbic acid on PCB (Aroclor 1254) induced oxidative stress in hypothalamus of albino rats. Clin Chim Acta 365:297–303
Mwila K, Burton MH, Van Dyk JS, Pletschke BI (2013) The effect of mixtures of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides on acetylcholinesterase and application of chemometrics to identify pesticides in mixtures. Environ Monit Assess 185:2315–2327
Nagel R (2002) DarT: the embryo test with the zebrafish Danio rerio—a general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX 19:38–48
Netzband M, Stefanov WL, Redman CL (2007) Applied remote sensing for urban planning, governance and sustainability. Springer, Heidelberg
OECD (2013) OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Section 2: effects on biotic systems test no. 236: fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Oropesa AL, Perez-Lopez M, Hernandez D, Garcia JP, Fidalgo LE, Lopez-Beceiro A, Soler F (2007) Acetylcholinesterase activity in seabirds affected by the Prestige oil spill on the Galician coast (NW Spain). Sci Total Environ 372:532–538
Perez J, Domingues I, Monteiro M, Soares AM, Loureiro S (2013) Synergistic effects caused by atrazine and terbuthylazine on chlorpyrifos toxicity to early-life stages of the zebrafish Danio rerio. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:4671–4680
Perkins EJ, Schlenk D (2000) In vivo acetylcholinesterase inhibition, metabolism, and toxicokinetics of aldicarb in channel catfish: role of biotransformation in acute toxicity. Toxicol Sci 53:308–315
Rodrigues AP, Lehtonen KK, Guilhermino L, Guimarães L (2013) Exposure of Carcinus maenas to waterborne fluoranthene: accumulation and multibiomarker responses. Sci Total Environ 443:454–463
Russom CL, LaLone CA, Villeneuve DL, Ankley GT (2014) Development of an adverse outcome pathway for acetylcholinesterase inhibition leading to acute mortality. Environ Toxicol Chem. doi:10.1002/etc.2662:
Scholz S, Fischer S, Gündel U, Küster E, Luckenbach T, Voelker D (2008) The zebrafish embryo model in environmental risk assessment—applications beyond acute toxicity testing. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:394–404
Scholz S, Sela E, Blaha L, Braunbeck T, Galay-Burgos M, García-Franco M, Guinea J, Klüver N, Schirmer K, Tanneberger K, Tobor-Kapłon M, Witters H, Belanger S, Benfenati E, Creton S, Cronin MTD, Eggen RIL, Embry M, Ekman D, Gourmelon A, Halder M, Hardy B, Hartung T, Hubesch B, Jungmann D, Lampi MA, Lee L, Léonard M, Küster E, Lillicrap A, Luckenbach T, Murk AJ, Navas JM, Peijnenburg W, Repetto G, Salinas E, Schüürmann G, Spielmann H, Tollefsen KE, Walter-Rohde S, Whale G, Wheeler JR, Winter MJ (2013) A European perspective on alternatives to animal testing for environmental hazard identification and risk assessment. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 67:506–530
Schulte C, Nagel R (1994) Testing acute toxicity in the embryo of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio, as an alternative to the acute fish test—preliminary results. ATLA 22:12–19
Schvezov N, Amin O (2011) Biochemical response of amphipods (Gammarid: Paramorea) in a sediment laboratory exposure from Ushuaia Bay, Beagle Channel. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:394–402
Söffker M, Tyler CR (2012) Endocrine disrupting chemicals and sexual behaviors in fish—a critical review on effects and possible consequences. Crit Rev Toxicol 42:653–668
Steevens JA, Benson WH (1999) Toxicological interactions of chlorpyrifos and methyl mercury in the amphipod, Hyalella azteca. Toxicol Sci 52:168–177
Straus DL, Schlenk D, Chambers JE (2000) Hepatic microsomal desulfuration and dearylation of chlorpyrifos and parathion in fingerling channel catfish: lack of effect from Aroclor 1254. Aquat Toxicol 50:1141–1149
Tang J, Cao Y, Rose RL, Hodgson E (2002) In vitro metabolism of carbaryl by human cytochrome P450 and its inhibition by chlorpyrifos. Chem Biol Interact 141:229–241
Tang Y, Donnelly KC, Tiffany-Castiglioni E, Mumtaz MM (2003) Neurotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and simple chemical mixtures. J Toxicol Environ Health 66A:919–940
Tyler CR, Jobling S, Sumpter JP (1998) Endocrine disruption in wildlife: a critical review of the evidence. Crit Rev Toxicol 28:319–361
Wogram J, Sturm A, Segner H, Liess M (2001) Effects of parathion on acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase and carboxylesterase in three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus) following short-term exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1528–1531
Wölz J, Fleig M, Schulze T, Maletz S, Lübcke-von Varel U, Reifferscheid G, Kühlers D, Braunbeck T, Brack W, Hollert H (2010a) Impact of contaminants bound to suspended particulate matter in the context of flood events. J Soils Sediments 10:1174–1185
Wölz J, Schulze T, Lübcke-von Varel U, Fleig M, Reifferscheid G, Brack W, Kühlers D, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2010b) Investigation on soil contamination at recently inundated and non-inundated sites. J Soils Sediments 11:82–92
Yen J, Donerly S, Levin ED, Linney EA (2011) Differential acetylcholinesterase inhibition of chlorpyrifos, diazinon and parathion in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:735–741
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Cinta Porte
Britta Kais and Daniel Stengel contributed equally to this article and are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kais, B., Stengel, D., Batel, A. et al. Acetylcholinesterase in zebrafish embryos as a tool to identify neurotoxic effects in sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 16329–16339 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4014-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4014-1