Abstract
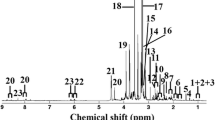
Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) is a ubiquitous contaminant in the marine environment, and relatively little is known about the toxicological mechanisms of this compound at the metabolite level. In this study, marine gastropods (abalone) were exposed to DBP at environmentally relevant concentrations (2, 10, and 50 μg/L) for 30 days. The plasma metabolite profiles were determined at the 5th, 15th, and 30th. The major metabolite changes corresponding to DBP exposure were related to osmotic regulation, energy metabolism, and environmental stress, and the effects displayed a dose-dependent pattern. The most obvious change was the increase in the levels of intracellular metabolites (betaine, dimethylglycine, homarine, glutamine, and lactate) and tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates. The results revealed that DBP may lead to abalone oxidative stress, lipid metabolism dysfunction, energy metabolism disturbance, and osmoregulation imbalance. These results would be helpful in better understanding the mechanisms of abalone response to DBP stress at the system level.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidli S, Lahbib Y, Menif NTE (2009) Effects of TBT on the imposex development, reproduction and mortality in Hexaplex trunculus (Gastropoda: muricidae). J Mar Biol Asso UK 89:139–146. doi:10.1017/S0025315408002282
Belpaire C, Goemans G (2007) Eels: contaminant cocktails pinpointing environmental contamination. ICES J Mar Sci 64:1423–1436. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsm121
Cheng Z, Nie XP, Wang HS, Wong MH (2013) Risk assessments of human exposure to bioaccessible phthalate esters through market fish consumption. Environ Int 57:75–80
Chio DW (1988) Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1:623–634. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6
Daviss B (2005) Growing pains for metabolomics. Scientist 19:25–28
Ding LN, Hao FH, Shi ZM, Wang YL, Zhang HX, Tang HR, Dai JY (2009) Systems biological responses to chronic perfluorododecanoic acid exposure by integrated metabonomic and transcriptomic studies. J Proteome Res 8:2882–2891. doi:10.1021/pr9000256
d’Yvoire M, Bremer S, Casati S, Ceridono M, Coecke S, Corvi R, Eskes C, Gribaldo L, Griesinger C, Knaut H, Linge JP, Roi A, Zuang V (2012) ECVAM and new technologies for toxicity testing. Adv Exp Med Biol 745:154–180. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-3055-1_10
Ekman DR, Teng Q, Villeneuve DL, Kahl MD, Jensen KM, Durhan EJ, Ankley GT, Collette TW (2008) Investigating compensation and recovery of fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) exposed to 17α-ethynylestradiol with metabolite profiling. Environ Sci Technol 42:4188–4194. doi:10.1021/es8000618
Fabjan E, Hulzebos E, Mennes W, Piersma AH (2006) A category approach for reproductive effects of phthalates. Crit Rev Toxicol 36(9):695–726. doi:10.1080/10408440600894914
Fairbairn EA, Bonthius J, Cherr GN (2012) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and dibutyl phthalate disrupt dorsal–ventral axis determination via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in zebrafish embryos. Aquat Toxicol 124–125:188–196. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.08.017
Fatta-Kassinos D, Kalavrouziotis IK, Koukoulakis PH, Vasquez MI (2011) The risks associated with wastewater reuse and xenobiotics in the agroecological environment. Sci Total Environ 409(19):3555–3563. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.03.036
Fedotcheva NI, Sokolov AP, Kondrashova MN (2006) Nonenzymatic formation of succinate in mitochondria under oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 41:56–64. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.02.012
Fend K (2004) Ecotoxicological effects at contaminated sites. Toxicology 205:223–240. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2004.06.060
Hall CM, Rhind SM, Wilson MJ (2009) The potential for use of gastropod molluscs as bioindicators of endocrine disrupting compounds in the terrestrial environment. J Environ Monit 11:491–497. doi:10.1039/b804320e
Harris CA, Henttu P, Parker MG, Sumpter JP (1997) The estrogenic activity of phthalate esters in vitro. Environ Health Perspect 105:802–811
Imai Y, Kondo A, Iizuka H, Maruyama T, Kurohane K (2006) Effects of phthalate esters on the sensitization phase of contact hypersensitivity induced by fluorescein isothiocyanate. Clin Exp Allergy 3:1462–1468. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02574.x
Jung Y, Lee J, Kwon J, Lee KS, Ryu do H, Hwang GS (2010) Discrimination of the geographical origin of beef by (1)H NMR-based metabolomics. J Agric Food Chem 58(19):10458–10466. doi:10.1021/jf102194t
Know YK, Jung YS, Park JC, Seo J, Chio MS, Hwang GS (2012) Characterizing the effect of heavy metal contamination on marine mussels using metabolomics. Mar Pollut Bull 64:1874–1879. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.06.012
Lin CY, Viant MR, Tjeerdema RS (2006) Metabolomics: methodologies and applications in the environmental sciences. J Pestic Sci 31:245–251. doi:10.1584/jpestics.31.245
Liu Y (2010) Acute toxicity of typical environmental estrogens to the metamorphosis development of the abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta. PhD. thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.
Mackintosh CE, Maldonado JA, Ikonomou MG, Gobas FA (2006) Sorption of phthalate esters and PCBs in a marine ecosystem. Environ Sci Technol 40:3481–3488. doi:10.1021/es0519637
Matthiessen P (2008) An assessment of endocrine disruption in mollusks and the potential for developing internationally standardized mollusk life cycle test guidelines. Integr Environ Assess Manag 4:274–284. doi:10.1897/IEAM_2008-003.1
Nicholson JK, Connelly J, Lindon JC, Holmes E (2002) Metabonomics: a platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1(2):153–161. doi:10.1038/nrd728
Oehlmann J, Schulte OU, Kloas W, Jagnytsch O, Lutz I, Kusk KO, Wollenberger L, Santos EM, Paull GC, Van Look KJ, Tyler CR (2009) A critical analysis of the biological impacts of plasticizers on wildlife. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 364:2047–2062. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0242
Parsons HM, Ludwig C, Günther UL, Viant MR (2007) Improved classification accuracy in 1- and 2-dimensional NMR metabolomics data using the variance stabilising generalised logarithm transformation. BMC Bioinformatics 8:234–239. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-8-234
Pickering AD, Pottinger TG, Christie P (1982) Recovery of the brown trout, Salmo turtta L., from acute handing stress: a time course study. J Fish Biol 20:229–244. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1982.tb03923.x
Preston RL (2005) Transport of amino acids by marine invertebrates. Comp Physiol Biochem 265:410–421. doi:10.1002/jez.1402650410
Purohit PV, Rocke DM, Viant MR, Woodruff DL (2004) Discrimination models using variance-stabilizing transformation of metabolomic NMR data. OMICS 8(2):118–130. doi:10.1089/1536231041388348
Schwarzenbach RP, Escher BI, Fenner K, Hofstetter TB, Johnson CA, von Gunten U, Wehrli B (2006) The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 313:1072–1077. doi:10.1126/science.1127291
Stentiford GD, Viant MR, Ward DG, Johnson PJ, Martin A, Wenbin W, Cooper HJ, Lyons BP, Feist SW (2005) Liver tumors in wild flatfish: a histopathological, proteomic, and metabolomic study. OMICS 9(3):281–299. doi:10.1089/omi.2005.9.281
Suggatt RH, Foote K, Christopher AB, Paul Thomas (2003). Aquatic toxicity of phthalate esters. The handbook of environmental chemistry. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg Press. V. 3Q/2002, pp. 93e104.
Viant MR, Rosenblum ES, Tieerdema RS (2003) NMR-based metabolomics: a powerful approach for characterizing the effects of environmental stressors on organism health. Environ Sci Technol 37(21):4982–4989. doi:10.1021/es034281x
Wang Y, Zhou J (2013) Endocrine disrupting chemicals in aquatic environments: a potential reason for organism extinction? Aquat Ecosys Health Manag 16(1):88–93. doi:10.1080/14634988.2013.759073
Wang Y, Bollard ME, Keun H, Antti H, Beckonert O, Ebbels TM, Lindon JC, Holmes E, Tang H, Nicholson JK (2003) Spectral editing and pattern recognition methods applied to high-resolution magic-angle spinning 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of liver tissues. Anal Biochem 323(1):26–32. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2003.07.026
Wang W, Wu FY, Huang MJ, Kang Y, Cheung KC, Wong MH (2013) Size fraction effect on phthalate esters accumulation, bioaccessibility and in vitro cytotoxicity of indoor/outdoor dust, and risk assessment of human exposure. J Hazard Mater 261:753–762. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.04.039
Wei L, Liao PQ, Wu HF, Li XJ, Pei FK, Li WS, Wu YJ (2009) Metabolic profiling studies on the toxicological effects of Realgar in rats by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Toxicol Allp Pharmacol 234:314–325. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2008.11.010
Wilson JT, Dixon DR, Dixon LR (2002) Numerical chromosomal aberrations in the early life-history stages of a marine tubeworm, Pomatoceros lamarckii (Polychaeta: Serpulidae). Aquat Toxicol 9(3–4):163–175. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(01)00249-1
Wu H, Wang WX (2010) NMR-based metabolomic studies on the toxicological effects of cadmium and copper on green mussels Perna viridis. Aquat Toxicol 100:339–345. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.08.005
Zhang L, Liu X, You L, Zhou D, Wang Q, Li F, Cong M, Li L, Zhao J, Liu D, Yu J, Wu H (2011a) Benzo(a)pyrene-induced metabolic responses in Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1HNMR) based metabolomics. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2(2):218–225. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2011.05.006
Zhang L, Liu X, You L, Zhou D, Wu H, Li L, Zhao J, Feng J, Yu J (2011b) Metabolic responses in gills of Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum exposed to copper using NMR-based metabolomics. Mar Environ Res 72(1–2):33–39. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2011.04.002
Zhang XF, Zhang LJ, Li L, Feng YN, Chen B, Ma JM, Huynh E, Shi QH, De Felici M, Shen W (2013) Diethylhexyl phthalate exposure impairs follicular development and affects oocyte maturation in the mouse. Environ Mol Mutagen 54(5):354–361. doi:10.1002/em.21776
Zhou J, Zhu XS, Cai ZH (2009) Endocrine disruptors: an overview and discussion on issues surrounding their impact on marine animals. J Mar Anim Ecol 2:7–18
Zhou J, Cai ZH, Li L, Gao YF, Hunchinson TH (2010a) A proteomics based approach to assessing the toxicity of bisphenol A and diallyl phthalate to the abalone (Haliotis diversicolor supertexta). Chemosphere 79:595–604. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.01.052
Zhou J, Cai ZH, Zhu XS (2010b) Are endocrine disruptors among the causes of the deterioration of aquatic biodiversity? Integra Environ Assess Manag 6(3):492–498. doi:10.1002/ieam.47
Zhou J, Zhu XS, Cai ZH (2010c) Tributyltin toxicity in abalone (Haliotis diversicolor supertexta) assessed by antioxidant enzyme activity, metabolic response, and histopathology. J Hazard Mater 183:428–433. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.042
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Marine Public Welfare Projects of China (201205020-9, 201305021-1), Natural Science Foundation of China (41106087, 41476092), Guangdong Province Marine and Fishery Special Funding of Science & Technology Promote Project (A201303F06), Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Coastal Ocean Dynamic and Environment (ZDSY20130402163735964),Special Fund of State Key Joint Laboratory of Environment Simulation and Pollution Control (13K10ESPCT), Fundamental Research Project of Shenzhen (JCYJ20130402145002375, JCYJ20140417115840286), and Innovation Research & Develop Project of Nanshan District of Shenzhen (KC2013JSCX003A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Jin Zhou and Baiyang Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Chen, B. & Cai, Z. Metabolomics-based approach for assessing the toxicity mechanisms of dibutyl phthalate to abalone (Haliotis diversicolor supertexta). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 5092–5099 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3859-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3859-7