Abstract
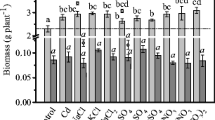
Many polluted sites are typically characterized by contamination with multiple heavy metals, drought, salinity, and nutrient deficiencies. Here, an Australian native succulent halophytic plant species, Carpobrotus rossii (Haw.) Schwantes (Aizoaceae) was investigated to assess its tolerance and phytoextraction potential of Cd, Zn, and the combination of Cd and Zn, when plants were grown in soils spiked with various concentrations of Cd (20–320 mg kg−1 Cd), Zn (150–2,400 mg kg−1 Zn) or Cd + Zn (20 + 150, 40 + 300, 80 + 600 mg kg−1). The concentration of Cd in plant parts followed the order of roots > stems > leaves, resulting in Cd translocation factor (TF, concentration ratio of shoots to roots) less than one. In contrast, the concentration of Zn was in order of leaves > stems > roots, with a Zn TF greater than one. However, the amount of Cd and Zn were distributed more in leaves than in stems or roots, which was attributed to higher biomass of leaves than stems or roots. The critical value that causes 10 % shoot biomass reduction was 115 μg g−1 for Cd and 1,300 μg g−1 for Zn. The shoot Cd uptake per plant increased with increasing Cd addition while shoot Zn uptake peaked at 600 mg kg−1 Zn addition. The combined addition of Cd and Zn reduced biomass production more than Cd or Zn alone and significantly increased Cd concentration, but did not affect Zn concentration in plant parts. The results suggest that C. rossii is able to hyperaccumulate Cd and can be a promising candidate for phytoextraction of Cd from polluted soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assuncao AGL, Bleeker P, ten Bookum WM, Vooijs R, Schat H (2008) Intraspecific variation of metal preference patterns for hyperaccumulation in Thlaspi caerulescens: evidence from binary metal exposures. Plant Soil 303:289–299
Ayoub AS, McGaw BA, Shand CA, Midwood AJ (2003) Phytoavailability of Cd and Zn in soil estimated by stable isotope exchange and chemical extraction. Plant Soil 252:291–300
Baker AJM, Reeves RD, Hajar ASM (1994) Heavy metal accumulation and tolerance in British populations of the metallophyte Thlaspi caerulescens J. & C. Presl (Brassicaceae). New Phytol 127:61–68
Broadley MR, White PJ, Hammond JP, Zelko I, Lux A (2007) Zinc in plants. New Phytol 173:677–702
Brown SL, Chaney RL, Angle JS, Baker AJM (1995) Zinc and cadmium uptake by hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens grown in nutrient solution. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59:125–133
Cataldo DA, Garland TR, Wildung RE (1983) Cadmium uptake kinetics in intact soybean plants. Plant Physiol 73:844–848
Chaney RL, Malik M, Li YM, Brown SL, Brewer EP, Angle JS, Baker AJM (1997) Phytoremediation of soil metals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:279–284
Chiang HC, Lo JC, Yeh KC (2006) Genes associated with heavy metal tolerance and accumulation in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri: a genomic survey with cDNA microarray. Environ Sci Technol 40:6792–6798
Craciun AR, Courbot M, Bourgis F, Salis P, Saumitou-Laprade P, Verbruggen N (2006) Comparative cDNA-AFLP analysis of Cd-tolerant and -sensitive genotypes derived from crosses between the Cd hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri and Arabidopsis lyrata ssp. petraea. J Exp Bot 57:2967–2983
Cunningham S, Berti W (1993) Remediation of contaminated soils with green plants: an overview. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 29:207–212
Forbes EA, Posner AM, Quirk JP (1976) Specific adsorption of divalent Cd, Co, Cu, Pb, and Zn on goethite. J Soil Sci 27:154–166
Geraghty DP, Ahuja KDK, Pittaway J, Shing C, Jacobson GA, Jager N, Jurkovic S, Narkowicz C, Saunders CI, Ball M, Pinkard A, Vennavaram RR, Adams MJ (2011) In vitro antioxidant, antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory activity of Carpobrotus rossii (pigface) extract. J Ethnopharmacol 134:97–103
Green CE, Chaney RL, Bouwkamp J (2003) Interactions between cadmium uptake and phytotoxic levels of zinc in hard red spring wheat. J Plant Nutr 26:417–430
Haghiri F (1974) Plant uptake of cadmium as influenced by cation exchange capacity, organic matter, zinc, and soil temperature. J Environ Qual 3:180–183
Hassan Z, Aarts MGM (2011) Opportunities and feasibilities for biotechnological improvement of Zn, Cd or Ni tolerance and accumulation in plants. Environ Exp Bot 72:53–63
Hawf LR, Schmid WE (1967) Uptake and translocation of zinc by intact plants. Plant Soil 27:249–260
Hogan GD, Rauser WE (1981) Role of copper-binding, absorption, and translocation in copper tolerance of Agrostis gigantea Roth. J Exp Bot 32:27–36
Honma Y, Hirata H (1978) Noticeable increase in cadmium absorption by zinc-deficient rice plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 24:295–297
Hooda PS, Alloway BJ (1993) Effects of time and temperature on the bioavailability of Cd and Pb from sludge-amended soils. J Soil Sci 44:97–110
Hu PJ, Qiu RL, Senthilkumar P, Jiang D, Chen ZW, Tang YT, Liu FJ (2009) Tolerance, accumulation and distribution of zinc and cadmium in hyperaccumulator Potentilla griffithii. Environ Exp Bot 66:317–325
Koren Š, Arčon I, Kump P, Nečemer M, Vogel-Mikuš K (2013) Influence of CdCl2 and CdSO4 supplementation on Cd distribution and ligand environment in leaves of the Cd hyperaccumulator Noccaea (Thlaspi) praecox. Plant Soil 370:125–148
Kramer U (2010) Metal hyperaccumulation in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:517–534
Kupper H, Kochian LV (2010) Transcriptional regulation of metal transport genes and mineral nutrition during acclimatization to cadmium and zinc in the Cd/Zn hyperaccumulator, Thlaspi caerulescens (Ganges population). New Phytol 185:114–129
Liu Z, He X, Chen W, Yuan F, Yan K, Tao D (2009) Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of cadmium in a potential hyperaccumulator—Lonicera japonica Thunb. J Hazard Mater 169:170–175
Lombi E, Zhao FJ, Dunham SJ, McGrath SP (2000) Cadmium accumulation in populations of Thlaspi caerulescens and Thlaspi goesingense. New Phytol 145:11–20
Long XX, Yang XE, Ni WZ, Ye ZQ, He ZL, Calvert DV, Stoffella JP (2003) Assessing zinc thresholds for phytotoxicity and potential dietary toxicity in selected vegetable crops. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 34:1421–1434
McGrath S, Sidoli C, Baker A, Reeves R (1993) The potential for the use of metal-accumulating plants for the in situ decontamination of metal-polluted soils. In: Eijsackers HJP, Hamers T (eds) Integrated Soil and Sediment Research: A Basis for Proper Prediction. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 673–676
McLaughlin MJ, Henderson R (1999) Effect of zinc and copper on cadmium uptake by Thlaspi caerulescens and Cardaminopsis halleri. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on the Bio-geochemistry of Trace Elements, Vienna. 11-15 July 1999. Int. Soc. for Trace Element Res., Vienna. pp. 886-887
McLaughlin MJ, Lambrechts RM, Smolders E, Smart MK (1998) Effects of sulfate on cadmium uptake by Swiss chard: II. Effects due to sulfate addition to soil. Plant Soil 202:217–222
Mohammad A, Moheman A (2010) The effects of cadmium and zinc interactions on the accumulation and tissue distribution of cadmium and zinc in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Arch Agron Soil Sci 56:551–561
Monsant AC, Tang C, Baker AJ (2008) The effect of nitrogen form on rhizosphere soil pH and zinc phytoextraction by Thlaspi caerulescens. Chemosphere 73:635–642
Papazoglou EG (2011) Responses of Cynara cardunculus L to single and combined cadmium and nickel treatment conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:195–202
Papoyan A, Pineros M, Kochian LV (2007) Plant Cd2+ and Zn2+ status effects on root and shoot heavy metal accumulation in Thlaspi caerulescens. New Phytol 175:51–58
Podar D, Ramsey MH, Hutchings MJ (2004) Effect of cadmium, zinc and substrate heterogeneity on yield, shoot metal concentration and metal uptake by Brassica juncea: implications for human health risk assessment and phytoremediation. New Phytol 163:313–324
Pongrac P, Vogel-Mikuš K, Vavpetič P, Tratnik J, Regvar M, Simčič J, Grlj N, Pelicon P (2010) Cd induced redistribution of elements within leaves of the Cd/Zn hyperaccumulator Thlaspi praecox as revealed by micro-PIXE. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res Sect B: Beam Interactions Mater Atoms 268:2205–2210
Qiu RL, Thangavel P, Hu PJ, Senthilkumar P, Ying RR, Tang YT (2011) Interaction of cadmium and zinc on accumulation and sub-cellular distribution in leaves of hyperaccumulator Potentilla griffithii. J Hazard Mater 186:1425–1430
Reeves RD, Brooks RR (1983) Hyperaccumulation of lead and zinc by two metallophytes from a mining area of central Europe. Environ Pollut 31:277–285
Roosens N, Verbruggen N, Meerts P, Ximenez-Embun P, Smith JAC (2003) Natural variation in cadmium tolerance and its relationship to metal hyperaccumulation for seven populations of Thlaspi caerulescens from western Europe. Plant Cell Environ 26:1657–1672
Root RA, Miller RJ, Koeppe DE (1975) Uptake of cadmium—its toxicity, and effect on the iron ratio in hydroponically grown corn. J Environ Qual 4:473–476
Salt DE, Smith RD, Raskin I (1998) Phytoremediation. Annu Rev Plant Phys 49:643–668
Sanaeiostovar A, Khoshgoftarmanesh AH, Shariatmadari H, Afyuni M, Schulin R (2012) Combined effect of zinc and cadmium levels on root antioxidative responses in three different zinc-efficient wheat genotypes. J Agron Crop Sci 198:276–285
Smilde KW, Vanluit B, Vandriel W (1992) The extraction by soil and absorption by plants of applied zinc and cadmium. Plant Soil 143:233–238
Smith GC, Brennan EG (1983) Cadium–zinc interactionship in tomato plants. Phytopathology 73:879–882
Smolders E, Lambregts RM, McLaughlin MJ, Tiller KG (1998) Effect of soil solution chloride on cadmium availability to Swiss chard. J Environ Qual 27:426–431
Tang YT, Qiu RL, Zeng XW, Ying RR, Yu FM, Zhou XY (2009a) Lead, zinc, cadmium hyperaccumulation and growth stimulation in Arabis paniculata Franch. Environ Exp Bot 66:126–134
Tang YT, Qiu RL, Zeng XW, Fang XH, Yu FM, Zhou XY, Wu YD (2009b) Zn and Cd hyperaccumulating characteristics of Picris divaricata Vant. Int J Environ Pollut 38:26–38
Turner MA (1973) Effect of cadmium treatment on cadmium and zinc uptake by selected vegetable species. J Environ Qual 2:118–119
Ueno D, Iwashita T, Zhao FJ, Ma JF (2008) Characterization of Cd translocation and identification of the Cd form in xylem sap of the Cd-hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. Plant Cell Physiol 49:540–548
White PJ, Brown PH (2010) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 105:1073–1080
Wojcik M, Vangronsveld J, Tukiendorf A (2005) Cadmium tolerance in Thlaspi caerulescens I. Growth parameters, metal accumulation and phytochelatin synthesis in response to cadmium. Environ Exp Bot 53:151–161
Yang XE, Long XX, Ye HB, He ZL, Calvert DV, Stoffella PJ (2004) Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Zn-hyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance). Plant Soil 259:181–189
Ye BH, Yang Y, He B, Long XX, Shi WY (2003) Growth response and metal accumulation of Sedum alfredii to Cd/Zn complex polluted ion levels. Acta Bot Sin 45:1030–1036
Ying RR, Qiu RL, Tang YT, Hu PJ, Qiu H, Chen HR, Shi TH, Morel JL (2010) Cadmium tolerance of carbon assimilation enzymes and chloroplast in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Picris divaricata. J Plant Physiol 167:81–87
Zha HG, Jiang RF, Zhao FJ, Vooijs R, Schat H, Barker JHA, McGrath SP (2004) Co-segregation analysis of cadmium and zinc accumulation in Thlaspi caerulescens interecotypic crosses. New Phytol 163:299–312
Zhang GP, Fukami M, Sekimoto H (2002) Influence of cadmium on mineral concentrations and yield components in wheat genotypes differing in Cd tolerance at seedling stage. Field Crop Res 77:93–98
Zhao FJ, Lombi E, Breedon T, McGrath SP (2000) Zinc hyperaccumulation and cellular distribution in Arabidopsis halleri. Plant Cell Environ 23:507–514
Zhao FJ, Jiang RF, Dunham SJ, McGrath SP (2006) Cadmium uptake, translocation and tolerance in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. New Phytol 172:646–654
Zhu QS, Liu J, Li KQ, Xu JK, Liang JS, Lu XL, Yang JC (2003) Interaction of Cd and five mineral nutrients for uptake and accumulation in different rice cultivars and genotypes. Field Crop Res 83:271–281
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Trevor Edwards for the identification of Carpobrotus rossii and Mr. Rob Evans for assistance in the experiment. We are grateful to an anonymous reviewer for constructive and detailed comments on the manuscript. This research was supported by an Australian Research Council Linkage Project (LP100100800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Sale, P.W.G., Doronila, A.I. et al. Australian native plant species Carpobrotus rossii (Haw.) Schwantes shows the potential of cadmium phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 9843–9851 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2919-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2919-3