Abstract
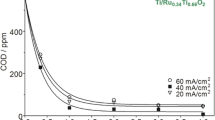
Dairy wastewater is characterized by a high content of hardly biodegradable dissolved, colloidal, and suspended organic matter. This work firstly investigates the performance of two individual electrochemical treatments, namely electrocoagulation (EC) and electro-oxidation (EO), in order to finally assess the mineralization ability of a sequential EC/EO process. EC with an Al anode was employed as a primary pretreatment for the conditioning of 800 mL of wastewater. A complete reduction of turbidity, as well as 90 and 81 % of chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total organic carbon (TOC) removal, respectively, were achieved after 120 min of EC at 9.09 mA cm−2. For EO, two kinds of dimensionally stable anodes (DSA) electrodes (Ti/IrO2-Ta2O5 and Ti/IrO2-SnO2–Sb2O5) were prepared by the Pechini method, obtaining homogeneous coatings with uniform composition and high roughness. The ·OH formed at the DSA surface from H2O oxidation were not detected by electron spin resonance. However, their indirect determination by means of H2O2 measurements revealed that Ti/IrO2-SnO2–Sb2O5 is able to produce partially physisorbed radicals. Since the characterization of the wastewater revealed the presence of indole derivatives, preliminary bulk electrolyses were done in ultrapure water containing 1 mM indole in sulfate and/or chloride media. The performance of EO with the Ti/IrO2-Ta2O5 anode was evaluated from the TOC removal and the UV/Vis absorbance decay. The mineralization was very poor in 0.05 M Na2SO4, whereas it increased considerably at a greater Cl− content, meaning that the oxidation mediated by electrogenerated species such as Cl2, HClO, and/or ClO− competes and even predominates over the ·OH-mediated oxidation. The EO treatment of EC-pretreated dairy wastewater allowed obtaining a global 98 % TOC removal, decreasing from 1,062 to <30 mg L−1.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anglada A, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I (2009) Contributions of electrochemical oxidation to waste-water treatment: fundamentals and review of applications. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:1747–1755
Anotai J, Sairiam S, Lu MC (2011) Enhancing treatment efficiency of wastewater containing aniline by electro-Fenton process. Sustain Environ Res 21:141–147
Ayhan Şengil I, Özacar M (2006) Treatment of dairy wastewaters by electrocoagulation using mild steel electrodes. J Hazard Mater 137:1197–1205
Bensadok K, El Hanafi N, Lapicque F (2011) Electrochemical treatment of dairy effluent using combined Al and Ti/Pt electrodes system. Desalination 280:244–251
Beteta A, Cañizares P, Rodrigo MA, Rodríguez L, Sáez C (2009) Treatment of door-manufacturing factories wastewaters using CDEO and other AOPs. A comparison. J Hazard Mater 168:358–363
Bezerra Rocha JH, Suely Fernandes N, Regina Souza K, da Silva DR, Quiroz MA, Martínez-Huitle CA (2011) Electrochemical decolourization process of textile dye in the presence of NaCl at boron doped diamond electrode. Sustain Environ Res 21:291–298
Bitencourt JFS, Ventieri A, Gonçalves KA, Pires EL, Mittani JC, Tamuti SH (2010) A comparison between neodymium doped alumina samples obtained by Pechini and sol–gel methods using thermo-stimulated luminescence and SEM. J NonCryst Solids 356:2956–2959
Brillas E, Sirés I, Oturan MA (2009) Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem Rev 109:6570–6631
Butrón E, Juárez ME, Solis M, Teutli M, González I, Nava JL (2007) Electrochemical incineration of indigo textile dye in filter-press-type FM01-LC electrochemical cell using BDD electrodes. Electrochim Acta 52:6888–6894
Cañizares P, Lobato J, Paz R, Rodrigo MA, Sáez C (2007) Advanced oxidation processes for the treatment of olive-oil mills wastewater. Chemosphere 67:832–838
Chaiyont R, Badoe C, Ponce de León C, Nava JL, Recio FJ, Sirés I, Herrasti P, Walsh FC (2013) Decolorization of Methyl Orange dye at IrO2-SnO2-Sb2O5 coated titanium anodes. Chem Eng Technol 36:123–129
Comisión Nacional del Agua (Conagua) (2010). Estadísticas del agua en México. http://www.conagua.gob.mx/CONAGUA07/Publicaciones/Publicaciones/SGP-1-11-EAM2011.PDF. Accessed March 2011
Comninellis C (1994) Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste water treatment. Electrochim Acta 39:1857–1862
Comninellis C, Nerini A (1995) Anodic oxidation of phenol in the presence of NaCl for wastewater treatment. J Appl Electrochem 25:23–28
Cotillas S, Llanos J, Cañizares P, Mateo S, Rodrigo MA (2013) Optimization of an integrated electrodisinfection/electrocoagulation process with Al bipolar electrodes for urban wastewater reclamation. Water Res 47:1741–1750
Dirany A, Sirés I, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2010) Electrochemical abatement of the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole from water. Chemosphere 81:594–602
Dirany A, Sirés I, Oturan N, Özcan A, Oturan MA (2012) Electrochemical treatment of the antibiotic sulfachloropyridazine: kinetics, reaction pathways, and toxicity evolution. Environ Sci Technol 46:4074–4082
El-Ghenymy A, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Cabot PL, Centellas F, Arias C, Brillas E (2013a) Degradation of sulfanilamide in acidic medium by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond anode. J Electroanal Chem 689:149–157
El-Ghenymy A, Cabot PL, Centellas F, Garrido JA, Rodríguez RM, Arias C, Brillas E (2013b) Electrochemical incineration of the antimicrobial sulfamethazine at a boron-doped diamond anode. Electrochim Acta 90:254–264
Fierro S, Kapalka A, Comninellis C (2010) Electrochemical comparison between IrO2 prepared by thermal treatment of iridium metal and IrO2 prepared by thermal decomposition of H2IrCl6 solution. Electrochem Commun 12:172–174
Flox C, Arias C, Brillas E, Savall A, Groenen-Serrano K (2009) Electrochemical incineration of cresols: a comparative study between PbO2 and boron-doped diamond anodes. Chemosphere 74:1340–1347
Flox C, Brillas E, Savall A, Groenen-Serrano K (2012) Kinetic study of the electrochemical mineralization of m-cresol on a boron-doped diamond anode. Curr Org Chem 16:1960–1966
Forti JC, Olivi P, De Andrade AR (2001) Characterisation of DSA®-type coatings with nominal composition Ti/Ru0.3Ti(0.7−x)SnxO2 prepared via a polymeric precursor. Electrochim Acta 47:913–920
Hammami S, Bellakhal N, Oturan N, Oturan MA, Dachraoui M (2008) Degradation of acid orange 7 by electrochemically generated ·OH radicals in acidic aqueous medium using a boron-doped diamond or platinum anode. A mechanistic study. Chemosphere 7:678–684
Hamza M, Abdelhedi R, Brillas E, Sirés I (2009) Comparative electrochemical degradation of the triphenylmethane dye Methyl Violet with boron-doped diamond and Pt anodes. J Electroanal Chem 627:41–50
Hoekstra AY (2010) The water footprint of animal products. In: D’Silva J, Webster J (eds) The meat crisis: developing more sustainable production and consumption. Earthscan, London, pp 22–33
Keech PG, Chartrand MMG, Bunce NJ (2002) Oxidation of simple indoles at a platinum anode. J Electroanal Chem 534:75–78
Kushwaha JP, Srivastava VC, Mall ID (2010) Organics removal from dairy wastewater by electrochemical treatment and residue disposal. Sep Purif Technol 76:198–205
Laor Y, Koziel JA, Cai L, Ravid U (2008) Chemical-sensory characterization of dairy manure odor using headspace solid-phase microextraction and multidimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry-olfactometry. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 58:1187–1197
Li B-S, Lin A, Gan F-X (2006) Preparation and electrocatalytic properties of Ti/IrO2-Ta2O5 anodes for oxygen evolution. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 16:1193–1199
Liu L, Zhao G, Wu M, Lei Y, Geng R (2009) Electrochemical degradation of chlorobenzene on boron-doped diamond and platinum electrodes. J Hazard Mater 168:179–186
Marselli B, Garcia-Gomez J, Michaud P-A, Rodrigo MA, Comninellis C (2003) Electrogeneration of hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 150:D79–D83
Martínez-Huitle CA, Brillas E (2008) Electrochemical alternatives for drinking water disinfection. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:1998–2005
Martínez-Huitle CA, Brillas E (2009) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl Catal B-Environ 87:105–145
Martínez-Huitle CA, Ferro S, De Battisti A (2004) Electrochemical incineration of oxalic acid. Role of electrode material. Electrochim Acta 49:4027–4034
Mollah MYA, Schennach R, Jose RP, David LC (2001) Electrocoagulation (EC)—science and applications. J Hazard Mater B84:29–41
Özcan A, Şahin Y, Koparal AS, Oturan MA (2008) Propham mineralization in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation using boron-doped diamond anode. Experimental parameters’ influence on degradation kinetics and mineralization efficiency. Water Res 42:2889–2898
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2004) Electrochemical oxidation as a final treatment of synthetic tannery wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 38:5470–5475
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2006) Olive mill wastewater treatment by anodic oxidation with parallel plate electrodes. Water Res 40:1179–1184
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2007) Electrocatalytic materials for the electrochemical oxidation of synthetic dyes. Appl Catal B-Environ 75:95–101
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2009) Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chem Rev 109:6541–6569
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2010) Applicability of electrochemical methods to carwash wastewaters for reuse. Part 2: Electrocoagulation and anodic oxidation integrated process. J Electroanal Chem 638:236–240
Pechini MP, Adams N (1967) Method for preparing lead and alkaline earth titanates and niobates and coating method using the same to form a capacitor. U.S. Patent 3,330,697, 11 July 1967
Polcaro AM, Mascia M, Palmas S (2004) Electrochemical degradation of diuron and dichloroaniline at BDD electrode. Electrochim Acta 49:649–656
Randazzo S, Scialdone O, Brillas E, Sirés I (2011) Comparative electrochemical treatments of two chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons. Time course of the main reaction by-products. J Hazard Mater 192:1555–1564
Ribeiro J, Purgato FLS, Kokoh KB, Léger J-M, De Andrade AR (2008) Application of Ti/RuO2-Ta2O5 electrodes in the electrooxidation of ethanol and derivants: reactivity versus electrocatalytic efficiency. Electrochim Acta 53:7845–7851
Scialdone O, Randazzo S, Galia A, Filardo G (2009) Electrochemical oxidation of organics at metal oxide electrode: the incineration of oxalic acid at IrO2-Ta2O5 (DSA-O2) anode. Electrochim Acta 54:1210–1217
Sirés I, Low CTJ, Ponce-de-León C, Walsh FC (2010) The deposition of nanostructured β-PbO2 coatings from aqueous methanesulfonic acid for the electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants. Electrochem Commun 12:70–74
Souza Duarte JP, Martínez-Huitle CA, da Silva DR (2011) Electrochemical treatment for removing petroleum polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from synthetic produced water using DSA-type anode: preliminary results. Sustain Environ Res 21:329–335
Szpyrkowicz L (2005) Hydrodynamic effects on the performance of electro-coagulation/electro-flotation for the removal of dyes from textile wastewater. Ind Eng Chem Res 44:7844–7853
Tahar NB, Savall A (1998) Mechanistics aspects of phenol electrochemical degradation by oxidation on a Ta/PbO2 anode. J Electrochem Soc 145:3427–3434
Tchamango S, Nanseu-Njiki CP, Ngmaeni E, Hadjiev D, Darchen A (2010) Treatment of dairy effluents by electrocoagulation using aluminium electrodes. Sci Total Environ 408:947–952
Vourch M, Balannec B, Chaufer B, Dorange G (2008) Treatment of dairy industry wastewater by reverse osmosis for water reuse. Desalination 219:190–202
Welcher FJ (1975) Standard methods of chemical analysis, vol. 2, 6th edn. Krieger, Huntington, p 1827, Part B
Xu L, Xin Y, Wang J (2009) A comparative study on IrO2-Ta2O5 coated titanium electrodes prepared with different methods. Electrochim Acta 54:1820–1825
Zodi S, Potier O, Lapicque F, Leclerc J-P (2010) Treatment of the industrial wastewaters by electrocoagulation: optimization of coupled electrochemical and sedimentation processes. Desalination 261:186–190
Acknowledgments
Support from CONACYT (Mexico) under program “Becas Mixtas 2012–2013 Movilidad en el extranjero”, as well as from MICINN (Spain) under project CTQ2010-16164/BQU, co-financed with FEDER funds, is acknowledged. The authors also thank the Centro de Graduados e Investigación en Química del Instituto Tecnológico de Tijuana.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) confirm that this article content has no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borbón, B., Oropeza-Guzman, M.T., Brillas, E. et al. Sequential electrochemical treatment of dairy wastewater using aluminum and DSA-type anodes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 8573–8584 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2787-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2787-x