Abstract
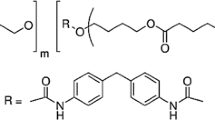
The increasing usage and the persistence of polyester polyurethane (PU) generate significant sources of environmental pollution. The effective and environmental friendly bioremediation techniques for this refractory waste are in high demand. In this study, three novel PU degrading bacteria were isolated from farm soils and activated sludge. Based upon 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequence blast, their identities were determined. Particularly robust activity was observed in Pseudomonas putida; it spent 4 days to degrade 92 % of Impranil DLNTM for supporting its growth. The optimum temperature and pH for DLN removal by P. putida were 25 °C and 8.4, respectively. The degradation and transformation of DLN investigated by Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy show the decrease in ester functional group and the emergence of amide group. The polyurethanolytic activities were both presented in the extracellular fraction and in the cytosol. Esterase activity was detected in the cell lysate. A 45-kDa protein bearing polyurethanolytic activity was also detected in the extracellular medium. This study presented high PU degrading activity of P. putida and demonstrated its responsible enzymes during the PU degradation process, which could be applied in the bioremediation and management of plastic wastes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akutsu Y, Nakajima-Kambe T, Nomura N, Nakahara T (1998) Purification and properties of a polyester polyurethane-degrading enzyme from Comamonas acidovorans TB-35. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:62–67
Allen AB, Hilliard NP, Howard GT (1999) Purification and characterization of a soluble polyurethane degrading enzyme from Comamonas acidovorans. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 43:37–41
Chang P, Tsai W-S, Tsai C-L, Tseng M-J (2004) Cloning and characterization of two thermostable xylanases from an alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319:1017–1025
ElSayed A, Mahmoud WM, Davis EM, Coughlin RW (1996) Biodegradation of polyurethane coatings by hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 37:69–79
Fortner JD, Zhang C, Spain JC, Hughes JB (2003) Soil column evaluation of factors controlling biodegradation of DNT in the vadose zone. Environ Sci Technol 37:3382–3391
Gokulakumar B, Narayanaswamy R (2008) Fourier transform-infrared spectra (FT-IR) analysis of root rot disease in sesame (Sesamum indicum). Romanian J Biophys 18:217–223
Guillén MD, Cabo N (2000) Some of the most significant changes in the Fourier transform infrared spectra of edible oils under oxidative conditions. J Sci Food Agric 80:2028–2036
Howard GT (2011) Microbial biodegradation of polyurethane. In: Fainleib A, Grigoryeva O (eds) Recent developments in polymer recycling. Kerala, India, Research Signpost, pp 215–238
Howard GT, Blake RC (1998) Growth of Pseudomonas fluorescens on a polyester-polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase-protease enzyme. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 42:213–220
Howard GT, Ruiz C, Newton NP (1999) Growth of Pseudomonas chlororaphis on a polyester-polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase-esterase enzyme. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 43:7–12
Howard GT, Crother B, Vicknair J (2001) Cloning, nucleotide sequencing and characterization of a polyurethanase gene (pueB) from Pseudomonas chlororaphis. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 47:141–149
Howard GT, Norton WN, Burks T (2012) Growth of Acinetobacter gerneri P7 on polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase enzyme. Biodegradation 23:561–573
Hudcova T, Halecky M, Kozliak E, Stiborova M, Paca J (2011) Aerobic degradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by individual bacterial strains and defined mixed population in submerged cultures. J Hazard Mater 192:605–613
Khanam N, Mikoryak C, Draper RK, Balkus KJ Jr (2007) Electrospun linear polyethyleneimine scaffolds for cell growth. Acta Biomater 3:1050–1059
Li Y, Li J, Wang C, Wang P (2010) Growth kinetics and phenol biodegradation of psychrotrophic Pseudomonas putida LY1. Bioresour Technol 101:6740–6744
Malghani S, Chatterjee N, Yu HX, Luo ZJ (2009) Isolation and identification of profenofos degrading bacteria. Braz J Microbiol 40:893–900
Mordocco A, Kuek C, Jenkins R (1999) Continuous degradation of phenol at low concentration using immobilized Pseudomonas putida. Enzyme Microb Technol 25:530–536
Mukherjee K, Tribedi P, Chowdhury A, Ray T, Joardar A, Giri S, Sil AK (2011) Isolation of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain from soil that can degrade polyurethane diol. Biodegradation 22:377–388
NakajimaKambe T, Onuma F, Akutsu Y, Nakahara T (1997) Determination of the polyester polyurethane breakdown products and distribution of the polyurethane degrading enzyme of Comamonas acidovorans strain TB-35. J Ferment Bioeng 83:456–460
Nomura N, Shigeno-Akutsu Y, Nakajima-Kambe T, Nakahara T (1998) Cloning and sequence analysis of a polyurethane esterase of Comamonas acidovorans TB-35. J Ferment Bioeng 86:339–345
Oceguera-Cervantes A, Carrillo-Garcia A, Lopez N, Bolanos-Nunez S, Cruz-Gomez MJ, Wacher C, Loza-Tavera H (2007) Characterization of the polyurethanolytic activity of two Alicycliphilus sp strains able to degrade polyurethane and N-methylpyrrolidone. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6214–6223
Rojo F (2009) Degradation of alkanes by bacteria. Environ Microbiol 11:2477–2490
Russell JR, Huang J, Anand P, Kucera K, Sandoval AG, Dantzler KW, Hickman D, Jee J, Kimovec FM, Koppstein D et al (2011) Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane by endophytic fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6076–6084
Shah Z, Hasan F, Krumholz L, Aktas DF, Shah AA (2013) Degradation of polyester polyurethane by newly isolated Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain MZA-85 and analysis of degradation products by GC-MS (vol 77, pg 114, 2013). Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 79:105–105
Sohn SB, Kim TY, Park JM, Lee SY (2010) In silico genome-scale metabolic analysis of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 for polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis, degradation of aromatics and anaerobic survival. Biotechnol J 5:739–750
Stern RV, Howard GT (2000) The polyester polyurethanase gene (pueA) from Pseudomonas chlororaphis encodes a lipase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 185:163–168
Vega RE, Main T, Howard GT (1999) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a polyurethane-degrading enzyme from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 43:49–55
Wales DS, Sagar BF (1988) Mechanistic aspects of polyurethane biodeterioration. In: Houghton DR, Smith RN, Eggins HOW (eds) Biodeterioration 7. Springer, Netherlands, pp 351–358
Wang SN, Liu Z, Tang HZ, Meng J, Xu P (2007) Characterization of environmentally friendly nicotine degradation by Pseudomonas putida biotype A strain S16. Microbiology 153:1556–1565
Wu J, Jung B-G, Kim K-S, Lee Y-C, Sung N-C (2009) Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas otitidis WL-13 and its capacity to decolorize triphenylmethane dyes. J Environ Sci 21:960–964
Zachinyaev YV, Miroshnichenko II, Zachinyaeva AV (2009) Microbial degradation of polyurethane. Russ J Appl Chem 82:1321–1323
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Bayer Material Science for offering free sample.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, YH., Shih, Yh., Lai, YC. et al. Degradation of polyurethane by bacterium isolated from soil and assessment of polyurethanolytic activity of a Pseudomonas putida strain. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 9529–9537 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2647-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2647-8