Abstract
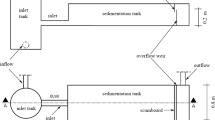
Sedimentation is a common but complex phenomenon in the urban drainage system. The settling mechanisms involved in detention basins are still not well understood. The lack of knowledge on sediment transport and settling processes in actual detention basins is still an obstacle to the optimization of the design and the management of the stormwater detention basins. In order to well understand the sedimentation processes, in this paper, a new boundary condition as an attempt to represent the sedimentation processes based on particle tracking approach is presented. The proposed boundary condition is based on the assumption that the flow turbulent kinetic energy near the bottom plays an important role on the sedimentation processes. The simulated results show that the proposed boundary condition appears as a potential capability to identify the preferential sediment zones and to predict the trapping efficiency of the basin during storm events.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamsson Ǻ, Stovin VR, Bergdahl L (2003) Bed shear stress boundary condition for storage tank sedimentation. J Environ Eng 129(7):651–657
Aiguier E, Chebbo G, Bertrand-Krajewski J-L, Hedges P, Tyack JN (1996) Methods for determining the settling velocity profiles of solids in storm sewage. Water Sci Technol 33(9):117–125
Ansys (2010) Ansys fluent theory guide. Release 13, Ansys Inc., Canonsburg, USA.
Ashley RM, Bertrand-Krajewski J-L, Hvitved-Jacobsen T, Verbanck M (2004) Solids in sewers: characteristics effects and control of sewer solids and associated pollutants. IWA Publishing, London
Bakhtyar R, Yeganeh-bakhtiary A, Barry DA, Ghaheri A (2009) Euler-Euler coupled two–phase flow modeling of sheet flow sediment motion in the nearshore. J Coast Res Spec Issue 56:467–471
Bardin JP, Barraud S (2004) Diagnostic and restructuration aid of the retention basin in Chassieu. Report for the management of the Greater Lyon. INSA Lyon. Villeurbanne, France
Benoist A, Lijklema L (1990) Distribution of sedimentation rates of suspended solids and heavy metals in combined sewer overflows. Water Sci Technol 22(10/11):61–68
Bentzen TR (2010) 3D numerical modelling of transport, deposition and resuspension of highway deposited sediments in wet detention ponds. Water Sci Technol 62(3):736–742
Bertrand-Krajewski J-L (2001) Determination of settling velocities of the particulate pollutants of urban wastewater by adjusting the numerical curve M (t) for the protocol VICTOR. Research Report, INSA Lyon, Villeurbanne, France
Bertrand-Krajewski J-L (2004) TSS concentration in sewers estimated from turbidity measurements by means of linear regression accounting for uncertainties in both variables. Water Sci Technol 50(11):81–88
Bertrand-Krajewski J-L, Barraud S, Lipeme-Kouyi G, Torres A, Lepot M (2007) Event and annual TSS and COD loads in combined sewer overflows estimated by continuous in situ turbidity measurements. 11th international conference on diffuse pollution, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 26–31 August 2007
Brown JS, Stein ED, Ackerman D, Dorsey JH, Lyon J, Carter PM (2013) Metals and bacteria partitioning to various size particles in Ballona creek storm water runoff. Environ Toxicol Chem 32(2):320–328
Chancelier FP, Chebbo G, Lucas-Aiguier E (1998) Estimation of settling velocities. Water Res 32(11):3461–3471
Chebbo G (1992) Solids in urban wet weather discharges: characterization and treatment. Thesis, ENPC
Chebbo G, Gromaire-Mertz MC, Lucas E (2003) VICAS Protocol: measure of the settling velocity of TSS in effluents. TSM. 12: 39–49. (Protocole VICAS : mesure de la vitesse de chute des MES dans les effluents urbains. TSM. 12, 39–49)
Dufresne M, Vazquez J, Terfous A (2009) Experimental investigation and CFD modelling of flow, sedimentation, and solids separation in a combined sewer detention tank. Comput Fluids 38:1042–1049
EPA (1999) Development of bench-scale settling apparatus: settling velocity data for design and operation of wet-weather flow solids-liquid separation processes. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Washington DC 20460, EPA/600/X-99/031, 42 p.
Gonzalez-Merchan C (2011) Improved knowledge of the clogging in the infiltration systems of stormwater. Ph.D thesis, INSA Lyon, Villeurbanne, France
Gromaire-Mertz MC (2004). Urban wet weather pollution in combined sewer networks: Characteristics and origins. Thesis, ENPC
Gromaire-Mertz MC, Chebbo G (2003) Measuring the fall velocity of suspended particles in effluents. VICAS protocol user's manual. CEREVE ENPC, Marne-la-Vallee
Gromaire-Mertz MC, Garnaud S, Gonzalez A, Chebbo G (1999) Characterization of urban runoff pollution in Paris. Water Sci Technol 39(2):1–8
Hribersek M, Zajdela B, Hribernik A, Zadravec M (2011) Experimental and numerical investigations of sedimentation of porous wastewater sludge flocs. Water Res 45:1729–1735
Iimura K, Nakagawa H, Higashitani K (1998) Deformation of aggregates depositing on a plate in a viscous fluid simulated by a modified discrete element method. Adv Powder Technol 9(4):345–361
Karunaratne SHP (1992) The influence of Gullly pot performance on the entry of sediment into sewers. Ph.D. South Bank University. London, UK
Krishnappan BG, Marsalek J (2002) Modelling of flocculation and transport of cohesive seiment from an on-stream stormwater setention pond. Water Res 36:3849–3859
Lee B, Shimizu Y, Matsuda T, Matsui S (2005) Characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in different size fractions in deposited road particles (DRPs) from Lake Biwa area, Japan. Environ Sci Technol 39:7402–7409
Lipeme Kouyi G, Torres A, Bertrand-Krajewski JL (2008) CFD modelling of the spatial distribution of sediment in a large detention basin. Proceedings of the international conference on measurements and hydraulics of sewers, 19–21 August 2008, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Lipeme Kouyi G, Arias L, Barraud S, Bertrand-Krajewski JL (2010) CFD modelling of flows in a large stromwater detention and settling basin. Proceedings of the 7th international conference on NOVATECH, 27 June to 1 July 2010, Lyon, France
Lu N, Anderson MT, Likos WJ, Mustoe GW (2007) A discrete element model for kaolinite aggregate formation during sedimentation. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 32(8):965–980
Morquecho R, Pitt R, Clark S (2005) Pollutant associations with particulates in stormwater. In: 2005 World water and environmental resources congress. ASCE/EWRI. Anchorage, Alaska, May 2005. ASCE/EWRI, Reston, VA. Conference CD-ROM
Morsi SA and Alexander AJ (1972). An investigation of particle trajectories in two-phase flow systems. Journal of Fluid Mechanisms 55(2):193–208
Nascimento NO, Ellis JB, Baptista MB, Deutsch JC (1999) Using detention basins: operational experience and lessons. Urban Water 1:113–124
Papanicolaou AN, Elhakeem M, Krallis G, Orakash S, Edinger J (2008) Sediment transport modeling review—current and future developments. J Hydraul Eng 134(1):1–14
Sebastian C, Barraud S (2010) Behavior of a stormwater detention and settling basin face to face the micropollutants flow and ecotoxicity releases. 4th JDHU, 16–17 November 2010, Champs sur Marne, France, 8 p
Spencer KL, Droppo IG, He C, Grapentine L, Exall K (2011) A novel tracer technique for the assessment of fine sediment dynamics in urban water management systems. Water Res 45(8):2595–2606
Stovin VR (1996) The prediction of sediment deposition in storage chambers based on laboratory observations and numerical simulation. Thesis, The University of Sheffield
Stovin VR, Saul AJ (1996) Efficiency prediction for storage chambers using computational fluid dynamics. Water Sci Technol 33(9):163–170
Stovin VR, Saul AJ (2000) Computational fluid dynamics and the design of sewage storage chambers. Water Environ Manag 14(2):103–110
Torres A (2008) Stormwater settling process within a full-scale sedimentation system: elements of reflection for monitoring and modeling. Thesis, INSA Lyon
Torres A, Bertrand-Krajewski J-L (2007a) Evaluation of uncertainties in settling velocities of particles in urban stormwater runoff. 5th SPN conference, 28–31 August, Delft, Netherlands, 8 p
Torres A, Bertrand-Krajewski J-L (2007b) Heterogeneity and variability of settling velocities of deposits in large stormwater retention and settling tanks. 5th SPN conference, 28–31 August, Delft, Netherlands, 8 p
Versteeg H, Malalasekera W (1995) An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: the finite volume method. Prentice Hall, London
Wong THF, Fletcher TD, Duncan HP, Jenkins GA (2006) Modeling urban stormwater treatment–a unified approach. Ecol Eng 27(1):58–70
Wood MG, Howes T, Keller J, Johns MR (1998) Two dimensional computational fluid dynamic models for waste stabilization ponds. Water Res 33(3):958–963
Wu W (2004) Depth-averaged two-dimensional numerical modeling of unsteady flow and nonuniform sediment transport in open channels. J Hydraul Eng 130(10):1013–1024
Wu W, Rodi W, Wenka T (2000) 3D numerical modeling of flow and sediment transport in open channels. J Hydraul Eng 126(1):4–15
Yan H, Lipeme Kouyi G, Bertrand-Krajewski J-L (2011) Modélisation numérique 3D des écoulements turbulents a surface libre charges en polluants particulaires dans un bassin de retenue - décantation des eaux pluviales. La Houille Blanche 2011(5):40–44
Zhang Z, Chen Q (2007) Comparison of the Eulerian and Lagrangian methods for predicting particle transport in enclosed spaces. Atmos Environ 41(25):5236–5248
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the OTHU (Observatoire de Terrain en Hydrologie Urbaine), Labex IMU and ANR CESA CABRRES programme for the scientific support and financing, and the Chinese Scholarship Council for funding through the Doctoral Scholarship project CSC/UT-INSA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Michael Matthies
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Lipeme Kouyi, G., Gonzalez-Merchan, C. et al. Computational fluid dynamics modelling of flow and particulate contaminants sedimentation in an urban stormwater detention and settling basin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 5347–5356 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2455-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2455-6