Abstract
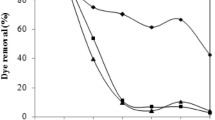
The native and physico-chemically treated fungal biomasses of Neurospora intermedia were used for adsorption of colored pollutants from distillery spent wash in batch systems. Experiments were conducted at varying color concentrations of the effluent (1,000–6,500 CU). The kinetics of effect of initial sorbate concentration, dose of biosorbent, temperature, and pH on adsorption were studied. Physical and chemical pretreatments of biomass resulted in an increase or decrease in color removal capacity. This effect was further studied by FTIR analysis of the dried fungal mycelium. The maximum color uptake on all the tested fungal biomass preparations was observed at pH 3.0 and temperature 30°C, within first 4 h. The Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption models were used for the mathematical description of the biosorption equilibrium and the data showed an optimal fit to these isotherms. Kinetic parameters indicated the dominance of Lagergren pseudo first-order kinetic model for adsorption. On the basis of maximum adsorption capacity, the color removal capacity by fungal preparations was in the order of native > heat > acid, base.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu Z, Tezer S (2000) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of biosorption of Remazol Black B by Rhizopus arrhizus in a batch system: effect of temperature. Process Biochem 36(5):431–439
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Babel S, Kurniawan TA (2003) Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: a review. J Hazard Mater B 97:219–243
Bayramoglu G, Bektas S, Arica MY (2003) Biosorption of heavy metal ions on immobilized white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor. J Hazard Mater 101:285–300
Bernardo ECR, Egashira E, Kawasaki J (1997) Decolourization of molasses' wastewater using activated carbon prepared from cane bagasse. Carbon 35(9):1217–1221
Borja R, Martin A, Luque M, Duran MM (1993) Enhancement of the anaerobic digestion of wine distillery wastewater by the removal of phenolics inhibitors. Bioresour Technol 45:99–104
Das SK, Bhowal J, Das AR, Guha AK (2006) Adsorption behavior of rhodamine B on Rhizopus oryzae biomass. Langmuir 22:7265–7272
Devi R, Singh V, Kumar A (2008) COD and BOD reduction from coffee processing wastewater using Avacado peel carbon. Bioresour Technol 99(6):1853–1860
Fu YZ, Viraraghavan T (2001) Fungal decolorization of dye wastewaters: a review. Bioresour Technol 79:251–262
Goyal SK, Seth R, Handa BK (1996) Diphasic fixed-film biomethanation of distillery spentwash. Bioresour Technol 56:239–244
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008a) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of cadmium(II) biosorption by nonliving algal biomass Oedogonium sp. from aqueous phase. J Hazard Mater 153:759–766
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008b) Biosorption of lead(II) from aqueous solutions by non-living algal biomass Oedogonium sp. and Nostoc sp.—a comparative study. Colloid Surf B 64:170–178
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008c) Sorption and desorption studies of chromium (VI) from nonviable cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum biomass. J Hazard Mater 154:347–354
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2009) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by raw and acid-treated green alga Oedogonium hatei from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 163:396–402
Gupta VK, Sharma S (2003) Removal of zinc from aqueous solutions using bagasse fly ash—a low cost adsorbent. Ind Eng Chem Res 42(25):6619–6624
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Dwivedi MK, Mohan D (1997) Process-development for the removal of zinc and cadmium from waste-water using slag—a blast-furnace waste material. Sep Sci Technol 32(17):2883–2912
Gupta VK, Srivastava SK, Tyagi R (2000) Design parameters for the treatment of phenolic wastes by carbon columns (obtained from fertilizer waste material). Water Res 34(5):1543–1550
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Gajbe V, Mittal J (2006a) Removal and recovery of the hazardous azo dye acid orange 7 through adsorption over waste materials: bottom ash and de-oiled soya. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(4):1446–1453
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Krishanan L, Mittal J (2006b) Adsorption treatment and recovery of the hazardous dye, Brilliant Blue FCF, over bottom ash and de-oiled soya. J Colloid Interface Sci 293:16–26
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Kurup L, Mittal J (2006c) Adsorption of a hazardous dye, erythrosine, over hen feathers. J Colloid Interface Sci 304:52–57
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saini VK (2007a) Defluoridation of wastewaters using waste carbon slurry. Water Res 41:3307–3316
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saini VK (2007b) Adsorption studies on the removal of Vertigo Blue 49 and Orange DNA13 from aqueous solutions using carbon slurry developed from a waste material. J Colloid Interface Sci 315(1):87–93
Gupta VK, Jain R, Mittal A, Mathur M, Sikarwar S (2007c) Photochemical degradation of the hazardous dye Safranin-T using TiO2 catalyst. J Colloid Interface Sci 309:464–469
Gupta VK, Jain R, Varshney S (2007d) Electrochemical removal of the hazardous dye Reactofix Red 3 BFN from industrial effluents. J Colloid Interface Sci 312(2):292–296
Gupta VK, Jain R, Varshney S (2007e) Removal of Reactofix golden yellow 3 RFN from aqueous solution using wheat husk—an agricultural waste. J Hazard Mater 142:443–448
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Nayak A (2010) Adsorption studies on the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using a low cost fertilizer industry waste material. J Colloid Interface Sci 342:135–141
Gupta VK, Ali I, Saleh TA, Nayak A, Agarwal S (2012) Chemical treatment technologies for waste-water recycling—an overview. RSC Adv. doi:10.1039/C2RA20340E
Hall KR, Eagleton LC, Acrivos A, Vermeulen T (1966) Pore and solid diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant pattern conditions. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 5:212–223
Hamdaoui O, Naffrechoux E (2007) Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chlorophenols onto granular activated carbon Part I. Two-parameter models and equations allowing determination of thermodynamic parameters. J Hazard Mater 147(1–2):381–394
Ho YS, Mckay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption process. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Hu TL (1992) Sorption of dye reactive dyes by Aeromonas biomass. Water Sci Technol 26:357–366
Jain AK, Gupta VK, Jain S, Suhas (2004) Removal of chlorophenols using industrial wastes. Environ Sci Technol 38(4):1195–1200
Kaushik G, Thakur IS (2009) Isolation of fungi and optimization of process parameters for decolorization of distillery mill effluent. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:955–964
Kaushik G, Gopal M, Thakur IS (2010) Evaluation of performance and community dynamics of microorganisms during treatment of distillery spent wash in sequential bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 101:4296–4305
Mahony TO, Guibal E, Tobin JM (2002) Reactive dye biosorption by Rhizopus arrhizus biomass. Enzyme Microb Technol 31:456–463
Maurya NS, Mittal AK, Cornel P, Rother E (2006) Biosorption of dyes using dead macro fungi: effect of dye structure, ionic strength and pH. Bioresour Technol 97:512–521
Miranda PM, Benito GG, Cristobal NS, Nieto CH (1996) Colour elimination from molasses wastewater by Aspergillus niger. Bioresour Technol 57:229–235
Mittal A (2006) Removal of the dye, Amaranth from waste water using hen feathers as potential adsorbent. Electron J Environ Agric Food Chem 5(2):1296–1305
Mittal A, Gupta VK (2010) Adsorptive removal and recovery of the azo dye Eriochrome Black T. Toxicol Environ Chem 92:1813–1823
Mittal A, Kurup L, Gupta VK (2005) Use of waste materials—bottom ash and de-oiled soya, as potential adsorbents for the removal of Amaranth from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 117:171–178
Mittal A, Mittal J, Kurup L (2007) Utilization of hen feathers for the adsorption of indigo carmine from simulated effluents. J Environ Prot Sci 1:92–100
Mittal A, Kaur D, Mittal J (2009a) Batch and bulk removal of a triarylmethane dye, Fast Green FCF, from wastewater by adsorption over waste materials. J Hazard Mater 163:568–577
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Gupta VK (2009b) Adsorptive removal of hazardous anionic dye “Congo red” from wastewater using waste materials and recovery by desorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 340:16–26
Mittal A, Jain R, Mittal J, Varshney S, Sikarwar S (2010a) Removal of Yellow ME 7 GL from industrial effluent using electrochemical and adsorption techniques. Int J Environ Pollut 43(4):308–323
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Gupta VK (2010b) Removal and recovery of Chrysoidine Y from aqueous solutions by waste materials. J Colloid Interface Sci 344:497–507
Mittal A, Mittal J, Malviya A, Kaur D, Gupta VK (2010c) Decoloration treatment of a hazardous triarylmethane dye, light green SF (Yellowish) by waste material adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 342:518–527
Mittal A, Thakur V, Gajbe V (2012a) Adsorptive removal of toxic azo dye Amido Black 10B by hen feather. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0843-y
Mittal A, Thakur V, Gajbe V (2012b) Evaluation of adsorption characteristics of an anionic azo dye Brilliant Yellow onto hen feathers in aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0756-9
Nandy T, Shastry S, Kaul SN (2002) Wastewater management in cane molasses distillery involving bioresource recovery. J Environ Manag 65:25–38
Ozer A, Akkaya G, Turabik M (2005) Biosorption of acid red 274 (AR 274) on Enteromorpha prolifera in a batch system. J Hazard Mater 126:119–127
Saha NK, Balakrishnan M, Batra VS (2005) Improving industrial water use: case study for an Indian distillery. Resour Conserv Recycl 43:163–174
Saleh TA, Gupta VK (2012) Column with CNT/magnesium oxide composite for lead(II) removal from water. Environ Sci Pollut Res doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0670-6
Singh DB, Prasad D, Rupainwar DC, Singh VN (1989) As(III) removal from aqueous solution by adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut 42:376–386
Sirianuntapiboon S, Sihanonth P, Somchai P, Atthasampunna P, Hayashida S (1995) An adsorption mechanism for melanoidin decolourization by Rhizoctonia sp. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:1185–1189
Sirivastava S, Thakur IS (2007) Evaluation of biosorption potency of Acinetobacter sp. for removal of hexavalent chromium from tannery effluent. Biodegradation 18:637–646
Srivastava SK, Gupta VK, Yadav IS, Mohan D (1995) Removal of 2,4, dinitrophenol using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste material. Fresenius Environ Bull 4:550–557
Tsezos M, Bell JP (1989) Comparison of the biosorption and desorption of hazardous organic pollutants by live and dead biomass. Water Res 23:561–568
Vandevivere PC, Bianchi R, Verstraete W (1998) Treatment and reuse of wastewater from the textile wet-processing industry: review of emerging technologies. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 72:289–302
Wedzicha BL, Kaputo MT (1992) Melanoidins from glucose and glycine: composition, characteristics and reactivity towards sulphite ion. Food Chem 43:359–367
Yesilada O, Asma D, Cing S (2003) Decolorization of textile dyes by fungal pellets. Process Biochem 38:933–938
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Modi distilleries, Modinagar, Uttar Pradesh, India for providing effluent and sludge/sediments during the course of investigation. Thanks are also to Dr. Manish Kaushik for his excellent technical assistance in preparing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vinod Kumar Gupta
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaushik, G., Thakur, I.S. Adsorption of colored pollutants from distillery spent wash by native and treated fungus: Neurospora intermedia . Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 1070–1078 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0957-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0957-2