Abstract
Background, aim, and scope
Biowaste contains compounds of agricultural value such as organic carbon, nutrients, and trace elements and can partially replace mineral fertilizer (MIN) and improve the physical properties of the soil. However, the obvious benefits of land spreading need to be carefully evaluated against potential adverse effects on the environment and human health. Environmental contamination resulting from biowaste application is one of the key variables when assessing cost/benefits. This study provides data on the resulting concentration of polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (DL-PCBs) in the soil column as a result of the different types of fertilizers.
Materials and methods
In a long-term field experiment established in 1962, we investigated the influence of the application of biowaste-derived fertilizers such as sewage sludge (SSL), compost (COM), and farmyard manure (FYM) to a luvisol derived from loess on the contents of PCDD/Fs and DL-PCBs. Control plots amended only with MIN served as a basis to compare the biowaste-amended soils with soils affected only by atmospheric deposition, thus experimentally separating the two pathways of soil contamination. Samples of the soil column down to a depth of 90 cm were taken in 2001 and analyzed for PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs according to US-EPA methods 1613 and 1668, respectively.
Results
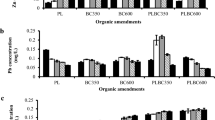
Thirty-nine years of experimental SSL and COM applications exceeding four times the maximal amount as laid down in German legislation resulted in a doubling of the international toxicity equivalent (I-TEQ) budget for PCDD/Fs and a threefold increase for DL-PCBs as compared to test plots amended with MIN only. As compared to MIN, the application of FYM had no effect on the PCDD/F and PCB content in soil. The average contribution of the DL-PCBs to the WHO-TEQ was 19% in the MIN and FYM plots and somewhat higher in the COM (23%) and in the SSL (27%) plots.
Discussion
Although the test plots received four times the maximum application of SSL as laid down in the German SSL ordinance and the investigated region represents the upper end of the topsoil concentrations typically found in Germany, the soils treated with SSL and COM were still a factor of 4 below the German guideline value of PCDD/Fs for arable land. No enhancement of translocation of PCDD/Fs and PCBs into the corresponding subsoils due to the presence of dissolved humic matter or other surfactants potentially present in the biowaste was observed. The similarity of congener patterns in all soils, irrespective of the type of fertilizer applied, points towards atmospheric deposition of PCDD/Fs and DL-PCBs as the main intake route in the soils. The higher levels in the SSL- and COM-amended soils can be explained by the fact that both biowastes are subject to atmospheric deposition occurring at their origin. In the case of COM, it is accumulation in the foliage, while in the case of SSL, atmospheric particulate from wet and dry deposition is collected in the wastewater treatment system via urban runoff.
Conclusions
It appears that the common practice of SSL applications in Germany does not pose a current threat to the agro-environment with regard to PCDD/Fs and DL-PCBs. However, time trend data on PCDD/Fs in SSL-amended soils will be needed to obtain a prognosis about the long-term effect of biowaste applications on soil quality.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Except for DL-PCBs in the compost plots, where one outlier (x) was not included in the average and for PCDD/Fs in manure, where the PCDD/F fraction of one of the topsoil samples was misplaced during sample purification.
References
Abad E, Saulo J, Caixach J, Rivera J (2000) Evaluation of a new automated cleanup system for the analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in environmental samples. J Chromatogr A 893(6):838–391
BGB1 (1992) Sewage sludge ordinance (Klärschlammverordnung (AbfKlärV)), of 15.4.1992, Federal Law Gazette, BGBl I of 28.4.1992, p. 912, modified by the ordinance of 6.3.1997, BGBl p.446 and § 11 Abs. 2V of 26.11.2003 I 2373
BGB1 (1998) Ordinance on the utilisation of biowastes on land used for agricultural, silvicultural and horticultural purposes. Federal Law Gazette BGBl. I. p 2955
Bright DA, Healey N (2003) Contaminant risk from bio solids land application: contemporary organic contaminant levels in digested sewage sludge from five treatment plants in Greater Vancouver, British Columbia. Environ Pollut 126:39–49
Chambers B, Nicholson F (2001) Beneficial effects of biosolids on soil quality and fertility. ADAS report for the UK Water Industry Research Ltd.
Council (1986) Council Directive 86/278/EEC of 12 June 1986 on the protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture as amended by Council Directive 91/692/EEC (further amended by Council Regulation 1882/2003/EC), and Council Regulation 807/2003/EC
Council (1991) Council Directive 91/676/EEC of 12 December 1991 concerning the protection of waters against pollution caused by nitrates from agricultural sources
Eljarrat E, Caixach J, Rivera J (1997) Effects of sewage sludge contaminated with polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls on agricultural soils. Environ Sci Technol 31:2765–2771
Eljarrat E, Caixach J, Rivera J (1999) Decline in PCDD and PCDF levels in sewage sludges from Catalonia (Spain). Environ Sci Technol 33(15):2493–2498
Eljarrat E, Caixach J, Rivera J (2003) A comparison of TEQ contributions from PCDDs, PCDFs and dioxin-like PCBs in sewage sludges from Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere 51:595–601
European Commission (2005) Proposal for a directive of the European Parliament and of the Council on waste, presented by the Commission. COM(2005)667
Federal Environmental Agency (1993) Government/Laender working group on DIOXINS. 2nd Report including recommendation values and action levels for PCDD/F in soil. Ministry of the Environment of the Federal Republic of Germany. UBA, Berlin
Federal Environmental Agency (2002) Government/Laender working group on DIOXINS. Data from Germany. Data on environmental pollution by dioxins 3rd report of the Government/Laender working group on DIOXINS. Ministry of the Environment of the Federal Republic of Germany. UBA, Berlin
Jackson AP, Eduljee G (1994) An assessment of the risks associated with PCDDs and PCDFs following the application of sewage sludge to agricultural land in the UK. Chemosphere 29(12):2523–2543
Kim Y, Lee D (2002) Solubility enhancement of PCDD/F in the presence of dissolved humic matter. J Hazard Mater B91:113–127
Lee D, Kim Y, Ohsako, M (2000) In: Hanashima (ed) Modern landfill technology and management. JSWME, pp 369–376
McLachlan MS, Reissinger M (1990) The influence of sewage sludge fertilization on the PCDD/F concentration in soil. An example from northeastern Bavaria. Organohalogen Compd 1:577–582
McLachlan MS, Sewart AP, Bacon R, Jones KC (1996) Persistence of PCDD/F in a sludge-amended soil. Environ Sci Technol 30:2567–2571
Molina L, Diaz-Ferrero J, Coll M, Marti R, Broto-Puig F, Comellas L, Rodriguez-Larena MC (2000) Study of evolution of PCDD/Fs in sewage sludge-amended soils for land restoration purposes. Chemosphere 40:1173–1178
Payá-Pérez AB, Rahman MS, Skejø-Andresen H, Larsen BR (1996) Surfactant solubilization of hydrophobic compounds in soil and water. II. The role of dodecyl sulphate–soil interactions for hexachlorobenzene. Environ Sci Pollut Res 4:183–188
Rappe C, Oberg L, Nilsson C, Hakansson H (1999) Biosolids in land application—a study on the dioxin situation. United States Conference of Mayors Urban Water Council, Washington, DC
Rideout K, Teschke K (2004) Potential for increased human foodborne exposure when recycling sewage sludge on agricultural land. Environ Health Perspect 112(9):959–969
Rideout K, Teschke K, Varughese S (2002) Guidance document: potential for exposure to polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans when recycling sewage biosolids on agricultural land. Environment Canada, BC Ministry of Water, Land and Air Protection, Mat 13
Schramm KW, Wu WZ, Henkelmann B, Merk M, Xu Y, Zhang YY, Kettrup A (1995) Influence of linear alkyl benzene sulfonate (LAS) as organic cosolvent on leaching behaviour of PCDD/Fs from fly ash and soil. Chemosphere 31(6):3445–3453
Smith LM, Stalling DL, Johnson L (1984) Determination of part per trillion levels of polychlorinated dibenzofurans and -dioxins in environmental samples. Anal Chem 56:1830–1842
Sommelier L, Morell JL, Morel C, Wiart J (1996) La valeur phosphatée des boues résiduaires des stations d’épuration urbaines. ADEME Éditions, Angers
Stevens JL, Jones K (2003) Quantification of PCDD/F concentrations in animal manure and comparison to the effects of the application of cattle manure and sewage sludge to agricultural land on human exposure to PCDD/Fs. Chemosphere 50:1183–1191
UMK-AG (2000) Arbeitsgruppe der Umweltministerkonferenz “Ursachen der Klärschlammbelastung mit gefährlichen Stoffen, Massnahmenplan”. Abschlussbericht
Umlauf G, Christoph EH, Savolainen R, Skejo H, Clemens J, Goldbach H, Scherer H (2004) PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in soil after 42 years of bio waste application. Organohalogen Compd 66:1363–1366
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum L, Bosveld ATC, Brunström B, Cook P, Feeley M, Giesy JP, Hanberg A, Hasegawa R, Kennedy SW, Kubiak T, Larsen JC, van Leeuwen RFX, Djien Liem AK, Nolt C, Peterson RE, Poellinger L, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tillitt D, Tysklind M, Younes M, Wærn F, Zacharewski T (1998) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Perspect 106:775–792
Vives I, Mueller A, Umlauf G, Christoph EH, Mariani G, Skejo H, Cenci RM, Sena F, Beone GM (2008) Levels of PCDD/Fs and trace elements in superficial soils of Pavia Province (Italy). Environ Int 34:994–1000
Welsch-Pausch K, McLachlan M (1998) Fate of airborne polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in an agricultural system. Environ Pollut 83:357–369
Werner W, Warnusz J (1997) Ecological evaluation of long-term application of sewage sludges according to the legislative permissions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 43:1047–1049
Wilson SC, Alcock RE, Sewart AP, Jones KC (1997) Persistence of organic contaminants in sewage sludge-amended soil: a field experiment. J Environ Qual 26:1467–1477
Acknowledgement
We are grateful to Ingrid Vives Rubio for helpful discussions on the manuscript and Sara Comero for the statistics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ake Bergman
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umlauf, G., Christoph, E.H., Lanzini, L. et al. PCDD/F and dioxin-like PCB profiles in soils amended with sewage sludge, compost, farmyard manure, and mineral fertilizer since 1962. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18, 461–470 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0389-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0389-9