Abstract
Background, aim, and scope
The main pathway for human exposure to the highly toxic polychlorinated-p-dioxins and polychlorinated furans [polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs)] is via dietary intake. Other exposure pathways may, however, be important in close proximity to point sources, such as wood preservation sites, where PCDD/F contaminated chlorophenols (CP) were previously used. In this study, a heavily PCDD/F contaminated CP saw mill site in Sweden was investigated. Human exposure through a broad spectrum of exposure pathways was assessed. Such studies are in demand since the question whether contaminated sites represent a current or future risk can only be answered by detailed site-specific risk assessments.
Materials and methods
Sampling of exposure media (soil, air, groundwater, raspberries, carrots, potatoes, grass, milk, eggs, and chicken fodder) was made. Exposure media concentrations and congener distribution patterns were used to investigate the mobilization of PCDD/Fs from soil to the environment and to calculate exposure levels for adults. Blood serum levels from site-exposed and control individuals were also analyzed.
Results
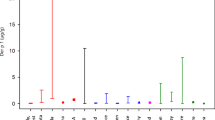
Congener distribution patterns at the site were generally dominated by a specific marker congener (1234678-HpCDF), which is highly abundant in the polluted soil. The dioxin toxic equivalents (TEQ) concentrations were notably elevated as compared to national reference samples for most exposure media, and the marker congener was a major contributor to increased TEQ levels. There were also indications of soil-to-air volatilization of tetra- and penta-CDD/Fs. People who participated in the restoration of a contaminated building showed higher levels of 1234678-HpCDF compared to controls, and calculated exposure levels suggest that several site-specific exposure routes may be of importance for the daily intake of PCDD/F.
Conclusions, recommendations, and perspectives
Despite low mobility of higher chlorinated PCDD/Fs, these contaminants were transferred from the polluted soil to the surroundings and into human tissue. The extent of increased exposure from contaminated sites depends on the PCDD/F source strength of the soil, composition of the pollution, human activities, and dietary patterns of the residents. Impact from the contaminated soil on other exposure media was seen also for areas with low to moderate soil contamination. In the future, not only the levels of PCDD/F soil pollution but also the composition must be considered in risk assessments of contaminated sites.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åberg A, MacLeod M, Wiberg K (2008) Physical-chemical property data for dibenzo-p-dioxin (DD), dibenzofuran (DF), and chlorinated DD/Fs: a critical review and recommended values. J Phys Chem Ref Data 37(4):1997–2008
Air V, Pless-Mulloli T, Schilling B, Paepke O (2003) Environmental non-feed contributors to PCDD/PCDF in free-range allotment poultry eggs: many questions and some answers. Organohalog Compd 63:126–129
Alcock RE, Sweetman AJ, Anderson DR, Fisher R, Jennings RA, Jones KC (2002) Using PCDD/F congener patterns to determine the source of elevated TEQ concentrations in cow’s milk: a case study. Chemosphere 46(3):383–391
Bidleman TF, Leone AD, Wong F, van Vliet L, Szeto S, Ripley BD (2006) Emission of legacy chlorinated pesticides from agricultural and orchard soils in British Columbia, Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 25(3):1448–1457
Budinsky RA, Rowlands JC, Casteel S, Fent G, Cushing CA, Newsted J, Giesy JP, Ruby MV M, Aylward LL (2008) A pilot study of oral bioavailability of dioxins and furans from contaminated soils: impact of differential hepatic enzyme activity and species differences. Chemosphere 70(10):1774–1786
Chen HL, Lee CC, Liao PC, Guo YL, Chen CH, Su HJ (2003) Associations between dietary intake and serum polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran (PCDD/F) levels in Taiwanese. Environ Res 91(3):172–178
Collins JJ, Bodner K, Burns CJ, Budinsky RA, Lamparski LL, Wilken M, Martin GD, Carson ML (2007) Body mass index and serum chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran levels. Chemosphere 66(6):1079–1085
Costera A, Feidt C, Marchand P, Le Bizec B, Rychen G (2006) PCDD/F and PCB transfer to milk in goats exposed to a long-term intake of contaminated hay. Chemosphere 64(4):650–657
Dahlgren J, Warshaw R, Horsak RD, Parker FM, Takhar H (2003) Exposure assessment of residents living near a wood treatment plant. Environ Res 92(2):99–109
Danielsson C, Wiberg K, Korytar P, Bergek S, Brinkman UAT, Haglund P (2005) Trace analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and WHO polychlorinated biphenyls in food using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with electron-capture detection. J Chromatogr A 1086(1–2):61–70
Diliberto JJ, Jackson JA, Birnbaum LS (1996) Comparison of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) disposition following pulmonary, oral, dermal, and parenteral exposures to rats. Toxicol Appl Pharm 138(1):158–168
Engwall M, Hjelm K (2000) Uptake of dioxin-like compounds from sewage sludge into various plant species—assessment of levels using a sensitive bioassay. Chemosphere 40(9–11):1189–1195
European Commission (1999) Compilation of EU dioxin exposure and health data. AEAT/EEQC/0016
European Commission (2001a) Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on the risk assessment of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs in food. CS/CNTM/DIOXIN/20 final
European Commission (2001b) Community strategy for dioxins, furans and polychlorinated biphenyls. No 2001/C 322/02
European Commission (2003) Commission directive amending directive 2002/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on undesirable substances in animal feed. No 2003/57/EC
European Commission (2006) Commission regulation setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. EC No 1881/2006
Harnly ME, Petreas MX, Flattery J et al (2000) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and polychlorinated dibenzofuran contamination in soil and home-produced chicken eggs near pentachlorophenol sources. Environ Sci Technol 34:1143–1149
Huwe JK, Smith DJ (2005) Laboratory and on-farm studies on the bioaccumulation and elimination of dioxins from a contaminated mineral supplement fed to dairy cows. J Agr Food Chem 53(6):2362–2370
Hülster A, Marschner H (1993) Transfer of PCDD/PCDF from contaminated soils to food and crop plants. Chemosphere 27(1–3):439–446
Karouna-Renier NK, Rao KR, Lanza JJ, Davis DA, Wilson PA (2007) Serum profiles of PCDDs and PCDFs, in individuals near the Escambia Wood Treating Company Superfund Site in Pensacola, FL. Chemosphere 69(8):1312–1319
Kemakta (2007). Kramfors Community: Mariebergs f.d. sågverk, Huvudstudie om markföroreningar m.m. Huvudstudierapport: Miljöteknisk del.2007-10-12, Kemakta AR 2007-08 (in Swedish)
Lake IR, Foxall CD, Lovett AA, Fernandes A, Dowding A, White S, Rose M (2005) Effects of river flooding on PCDD/F and PCB levels in cow’s milk, soil and grass. Environ Sci Technol 39(23):9033–9038
Lindström G, Henriksson S, Hagberg J, Björnfoth H, van Bavel B (2005) Uptake of PCDDs, PCDFs and non-ortho PCBs in sheep from PCP contaminated sawmill soil. Organohalog Compd 67:1387–1389
Matscheko N, Tysklind M, de Wit C, Bergek S, Andersson R, Sellström U (2002) Application of sewage sludge to arable land-soil concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls, and their accumulation in earthworms. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(12):2515–2525
Müller JF, Hülster A, Päpke O, Ball M, Marschner H (1994) Transfer of PCDD/PCDF from contaminated soils into carrots, lettuce and peas. Chemosphere 29(9–11):2175–2181
Oehme M, Haugen JE, Schlabach M (1996) Seasonal changes and relations between levels of organochlorines in arctic ambient air: first results of an all-year-round monitoring program at Ny-Alesund, Svalbard, Norway. Environ Sci Technol 30(7):2294–2304
Persson Y, Lundstedt S, Öberg L, Tysklind M (2007) Levels of chlorinated compounds (CPs, PCPPs, PCDEs, PCDFs and PCDDs) in soils at contaminated sawmill sites in Sweden. Chemosphere 66(2):234–242
Persson Y, Hernström K, Öberg L, Tysklind M, Enell A (2008a) Use of a column leaching test to study the mobility of chlorinated HOCs from a contaminated soil and the distribution of compounds between soluble and colloid phases. Chemosphere 71(6):1035–1042
Persson Y, Shchukarev A, Öberg L, Tysklind M (2008b) Dioxins, chlorophenols and other chlorinated organic pollutants in colloidal and water fractions of groundwater from a contaminated sawmill site. Environ Sci Poll R 15(6):463–471
Pirard C, Focant J-F, Massart A-C, De Pauw E (2003) Measurable impact of an old MSWI on the level of dioxins in free-range chickens and eggs grown in its vicinity. Organohalog Compd 64:158–161
Pirard C, Eppe G, Massart A-C, Fierens S, De Pauw E, Focant JF (2005) Environmental and human impact of an old timer incinerator in terms of dioxin and PCB level: a case study. Environ Sci Technol 39(13):4721–4728
Riss A, Hagenmaier H, Weberruss U, Schlatter C, Wacker R (1990) Comparison of PCDD/PCDF levels in soil, grass, cow’s milk, human blood and spruce needles in an area of PCDD/PCDF contamination through emissions from a metal reclamation plant. Chemosphere 21(12):1451–1456
Ruby MV, Fehling KA, Paustenbach DJ, Landenberger BD, Holsapple MP (2002) Oral bioaccessibility of dioxins/furans at low concentrations (50–350 ppt toxicity equivalent) in soil. Environ Sci Technol 36(12):4905–4911
Rylander L, Hagmar L, Wallin E, Kitti Sjöström A, Tysklind M (2009) Intra-individual variations and temporal trends in dioxin levels in human blood 1987 to 2000. Chemosphere. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.05.036
Sagunski H, Forschner S, Kappos AD (1989) Indoor air pollution by dioxins in day-nurseries. Risk assessment and management. Chemosphere 18(1–6):1139–1142
Salo S, Verta M, Malve O, Korhonen M, Lehtoranta J, Kiviranta H, Isosaari P, Ruokojarvi P, Koistinen J, Vartiainen T (2008) Contamination of River Kymijoki sediments with polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and mercury and their transport to the Gulf of Finland in the Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 73(10):1675–1683
Schmid P, Gujer E, Zennegg M, Studer C (2003) Temporal and local trends of PCDD/F levels in cow’s milk in Switzerland. Chemosphere 53(2):129–136
Schroll R, Schneuert I (1993) Uptake pathways of octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin from soil by carrot. Chemosphere 26(9):1631–1640
Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Garreta J (2004) Pollutants emitted by a cement plant: health risks for the population living in the neighborhood. Environ Res 95(2):198–206
Schuler F, Schmid P, Schlatter C (1997) The transfer of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from soil into eggs of foraging chicken. Chemosphere 34(4):711–718
Sellström U, Egebäck A-L, McLachlan MS (2009) Identifying source regions for the atmospheric input of PCDD/Fs to the Baltic Sea. Atmos Environ 43(10):1730–1736
Shih TS, Chen HL, Wu YL, Lin YC, Lee CC (2006) Exposure assessment of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) in temporary municipal-waste-incinerator maintenance workers before and after annual maintenance. Chemosphere 64(9):1444–1449
Stephens RD, Petreas MX, Hayward DG (1995) Biotransfer and bioaccumulation of dioxins and furans from soil: chicken as a model for foraging animals. Sci Total Environ 175(3):253–273
SWECO VIAK (2005) Kramfors Community: Mariebergs f.d. sågverk, fördjupad förstudie, Sundsvall 2005-11-25, rev 051129 (in Swedish)
Swedish Environmental Research Institute (2006) Dioxins in the Swedish Atmosphere: results from monitoring activities in 2004 and 2005. U 1969
Swedish National Food Administration (2002) Riksmaten 1997–1998. Kostvanor och Näringsintag i Sverige (in Swedish)
Swedish National Food Administration (2005) Intagsberäkningar för dioxin (PCDD/DF), dioxin-lika PCBer och metylkvicksilver via livsmedel. Report no. 25
Swedish National Food Administration (2007) Risk assessment of persistent chlorinated and brominated environmental pollutants in food. Report no. 9 (in English)
Thomas GO, Jones JL, Jones KC (2002) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and furan (PCDD/F) uptake by pasture. Environ Sci Technol 36(11):2372–2378
Trapp S, Matthies M (1997) Modeling volatilization of PCDD/F from soil and uptake into vegetation. Environ Sci Technol 31(1):71–74
Tsukino H, Hanaoka T, Sasaki H, Motoyama H, Hiroshima M, Tanaka T, Kabuto M, Turner W, Patterson DG, Needham L, Tsugane S (2006) Fish intake and serum levels of organochlorines among Japanese women. Sci Total Environ 359(1–3):90–100
Turrio-Baldassarri L, Abate V, Alivernini S, Battistelli CL, Carasi S, Casella M, Iacovella N, Iamiceli AL, Indelicato A, Scarcella C, La Rocca C (2007) A study on PCB, PCDD/PCDF industrial contamination in a mixed urban-agricultural area significantly affecting the food chain and the human exposure. Part I: soil and feed. Chemosphere 67(9):1822–1830
Tysklind M, Fängmark I, Marklund S, Lindskog A, Thaning L, Rappe C (1993) Atmospheric transport and transformation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Environ Sci Technol 27(10):2190–2197
Tysklind M, Persson Y, Frankki S, Andersson R, Öberg L, Skyllberg U (2006) Chlorophenol sites in Sweden—a major dioxin reservoir with complex contamination pattern. Organohalog Compd 68:895–898
University of Michigan (2006) Measuring people’s exposure to dioxin contamination along the Tittabawassee River and surrounding areas. Findings from the University of Michigan Dioxin Exposure Study. August 2006
US Environmental Protection Agency (1996) Exposure factors handbook. Volume I of III—General factors. Update to Exposure Factors Handbook EPA/600/8-89/043, May 1989. Office of Research and Development, National Center for Environmental Assessment, US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA/600/P-95/002Ba. SAB Review Draft
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum L, Bosveld TC, Brunström B, Cook P, Feeley M, Giesy JP, Hanberg A, Hasegawa R, Kennedy SW, Kubiak T, Larsen JC, van Leeuwen FXR, Liem AKD, Nolt C, Peterson RE, Poellinger L, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tillitt D, Tysklind M, Younes M, Waern F, Zacharewski T (1998) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Persp 106:775–792
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum LS, Denison M, De Vito M, Farland W, Feeley M, Fiedler H, Håkansson H, Hanberg A, Haws L, Rose M, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tohyama C, Tritscher A, Tuomisto J, Tysklind M, Walker N, Peterson RE (2006) The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 93(2):223–241
Verta M, Kiviranta H, Salo S, Malve O, Korhonen M, Verkasalo PK, Ruokojarvi P, Rossi E, Hanski A, Paatalo K, Vartiainen T (2009) A decision framework for possible remediation of contaminated sediments in the River Kymijoki, Finland. Environ Sci Poll R 16(1):95–105
Weber R, Gaus C, Tysklind M (2008a) Dioxin—contemporary and future challenges of historical legacies. Environ Sci Poll R 15(2):96–100
Weber R, Gaus C, Tysklind M, Johnston P, Forter M, Hollert H, Heinisch E, Holoubek I, Lloyd-Smith M, Masunaga S, Moccarelli P, Santillo D, Seike N, Symons R, Torres JPM, Verta M, Varbelow G, Vijgen J, Watson A, Costner P, Woelz J, Wycisk P, Zennegg M (2008b) Dioxin- and POP-contaminated sites-contemporary and future relevance and challenges. Environ Sci Poll R 15(5):363–393
Welsch-Pausch K, McLachlan MS (1998) Fate of airborne polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in an agricultural ecosystem. Environ Poll 102(1):129S–137S
Welsch-Pausch K, McLachlan M, Umlauf G (1995) Determination of the principal pathways of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans to Lolium multiflorum (Welsh ray grass). Environ Sci Technol 29(4):1090–1098
Wiberg K, Andersson PL, Berg H, Olsson P-E, Haglund P (2006) The fate of chiral organochlorine compounds and selected metabolites in intraperitoneally exposed Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus). Environ Toxicol Chem 25(6):1465–1473
Wiberg K, Åberg A, McKone TE, Tysklind M, Hanberg A, MacLeod M (2007a) Model selection and evaluation for risk assessment of dioxin contaminated sites. AMBIO 36(6):458–466
Wiberg K, Sporring S, Haglund P, Björklund E (2007b) Selective pressurized liquid extraction of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls from food and feed samples. J Chromatogr A 1138(1–2):55–64
Zohair A, Salim A-B, Soyibo AA, Beek AJ (2006) Residues of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and organochlorine pesticides in organically-farmed vegetables. Chemosphere 63(4):541–553
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank residents of the study site who gave us permission to establish a garden plot on private land, allowed sampling at private land, and assisted in exposure media sampling. Kramfors community and contracted environmental consultant agencies are acknowledged for guidance of the area and data sharing. Katarina Stenman and Viktor Sjöblom (Umeå University) are acknowledged for plant identification and for grass and soil sampling, respectively. We also wish to thank Jaruslav Jurenka (ALS Czech Republic), who provided details about the blood serum analyses. This work was a part of a project financed by the Swedish Environmental Protection Agency; contract numbers E-92-05 and E-5-06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Peter Luthardt
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM Table 1
(PDF 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Åberg, A., Tysklind, M., Nilsson, T. et al. Exposure assessment at a PCDD/F contaminated site in Sweden—field measurements of exposure media and blood serum analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17, 26–39 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-009-0223-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-009-0223-4