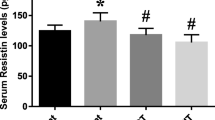
Abstract
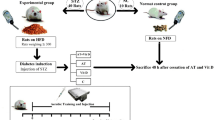
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of exercise training, caloric restriction and combination of caloric restriction with exercise training on plasma concentrations of adiponectin, insulin, and blood glucose in diabetic female rats. Forty, 8-week-old female Wistar rats (189 ± 10 g) were randomly assigned to two group of healthy (n = 8) as control and diabetic candidates (n = 32). Then after induction of diabetes, diabetic group were split up into four groups of Ex, CR and Ex+CR as experimental groups and DC as diabetic control group (n = 8). Then 20 % negative energy balance were administered through caloric restriction, exercise training and in combination for 8 weeks. The intensity was constant (28 m/min) but its time was flexible to adjust negative energy balance (equal to 20 % of their energy intake). Two bout of 35 min was for Ex and two of 40 min for Ex+CR. The finding showed that glucose level of CR and Ex+CR was significantly lower than DC. Also Ex+CR showed a significant increase in plasma total adiponectin comparing to DC. It is concluded that exercise training via caloric restriction has more beneficial effects on fasting glucose and plasma total adiponectin in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giannopoulou I et al (2005) Effects of diet and/or exercise on the adipocytokine and inflammatory cytokine levels of postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 54(7):866–875
Scherer PE (2006) Adipose tissue from lipid storage compartment to endocrine organ. Diabetes 55(6):1537–1545
Garekani ET et al (2011) Exercise training intensity/volume affects plasma and tissue adiponectin concentrations in the male rat. Peptides 32(5):1008–1012
Karbowska J, Kochan Z (2006) Role of adiponectin in the regulation of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. J Physiol Pharmacol 57:103
Mason C et al (2011) Dietary weight loss and exercise effects on insulin resistance in postmenopausal women. Am J Prev Med 41(4):366–375
Ma K et al (2002) Increased β-oxidation but no insulin resistance or glucose intolerance in mice lacking adiponectin. J Biol Chem 277(38):34658–34661
Hotta K et al (2000) Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(6):1595–1599
Gavrila A et al (2003) Diurnal and ultradian dynamics of serum adiponectin in healthy men: comparison with leptin, circulating soluble leptin receptor, and cortisol patterns. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(6):2838–2843
Speakman JR, Mitchell SE (2011) Caloric restriction. Mol Aspects Med 32(3):159–221
Zhu M et al (2005) Caloric restriction modulates insulin receptor signaling in liver and skeletal muscle of rat. Nutrition 21(3):378–388
Esposito K et al (2003) Effect of weight loss and lifestyle changes on vascular inflammatory markers in obese women. J Am Med Assoc 289(14):1799–1804
Koh EH et al (2010) eNOS plays a major role in adiponectin synthesis in adipocytes. Am J Physiol-Endocrinol Metab 298(4):E846–E853
Kraemer RR, Castracane VD (2007) Exercise and humoral mediators of peripheral energy balance: ghrelin and adiponectin. Expe biol med 232(2):184–194
Yatagai T et al (2003) Relationship between exercise training-induced increase in insulin sensitivity and adiponectinemia in healthy men. Endocr J-Tokyo- 50(2):233–238
Boudou P et al (2003) Absence of exercise-induced variations in adiponectin levels despite decreased abdominal adiposity and improved insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic men. Eur J Endocrinol 149(5):421–424
Hulver MW et al (2002) Adiponectin is not altered with exercise training despite enhanced insulin action. Am J Physiol-Endocrinol Metab 283(4):E861–E865
Marcell TJ et al (2005) Exercise training is not associated with improved levels of C-reactive protein or adiponectin. Metabolism 54(4):533–541
Ryan A et al (2003) Adiponectin levels do not change with moderate dietary induced weight loss and exercise in obese postmenopausal women. Int J Obes 27(9):1066–1071
Yokoyama H et al (2004) Effect of aerobic exercise on plasma adiponectin levels and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27(7):1756–1758
Baratta R et al (2004) Adiponectin relationship with lipid metabolism is independent of body fat mass: evidence from both cross-sectional and intervention studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(6):2665–2671
Yip I et al (2001) Insulin-leptin-visceral fat relation during weight loss. Pancreas 23(2):197–203
Xydakis AM et al (2004) Adiponectin, inflammation, and the expression of the metabolic syndrome in obese individuals: the impact of rapid weight loss through caloric restriction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(6):2697–2703
Yamauchi T et al (2002) Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med 8(11):1288–1295
Sutherland LN et al (2009) Exercise and adrenaline increase PGC-1α mRNA expression in rat adipose tissue. J physiol 587(7):1607–1617
Bueno AA et al (2008) Effects of different fatty acids and dietary lipids on adiponectin gene expression in 3T3-L1 cells and C57BL/6 J mice adipose tissue. Pflügers Archiv-Eur J Physiol 455(4):701–709
Koh EH et al (2007) Essential role of mitochondrial function in adiponectin synthesis in adipocytes. Diabetes 56(12):2973–2981
Guo Z et al (2007) Cardiac expression of adiponectin and its receptors in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Metabolism 56(10):1363–1371
Shepherd R, Gollnick P (1976) Oxygen uptake of rats at different work intensities. Pfluegers Arch 362(3):219–222
Christiansen T et al (2010) Diet-induced weight loss and exercise alone and in combination enhance the expression of adiponectin receptors in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle, but only diet-induced weight loss enhanced circulating adiponectin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(2):911–919
Blüher M et al (2006) Circulating adiponectin and expression of adiponectin receptors in human skeletal muscle: associations with metabolic parameters and insulin resistance and regulation by physical training. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(6):2310–2316
O’Leary VB et al (2006) Exercise-induced reversal of insulin resistance in obese elderly is associated with reduced visceral fat. J Appl Physiol 100(5):1584–1589
Han SH et al (2007) Adiponectin and Cardiovascular Disease Response to Therapeutic Interventions. J Am Coll Cardiol 49(5):531–538
Acknowledgments
The research was funded by Jahrom University Medical Science. Especial thanks to Saeedeh Erfanian for her precious aids.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jashni, H.K., Mohebbi, H., Delpasand, A. et al. Caloric restriction and exercise training, combined, not solely improve total plasma adiponectin and glucose homeostasis in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Sport Sci Health 11, 81–86 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-014-0212-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-014-0212-y