Abstract
Purpose
To assess how expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty (ESP) impacts blood pressure (BP) and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in hypertensive patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Methods
Patients were separated into two groups based upon whether or not they adhered to antihypertensive drug regimens. Patients underwent 24-h ambulatory BP monitoring before and at 6 months post-ESP, while clinical BP measurements and HRQOL questionnaires (SF-36) were conducted over the course of 24 months post-surgery.
Results
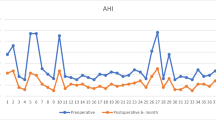
We enrolled 62 patients, with 25 and 37 in the medicated and non-medicated groups, respectively. Mean 24-h BP differed significantly, with systolic and diastolic BP (SBP and DBP) decreases of 5.3 mmHg and 2.5 mmHg, respectively (P <0.01). Mean 24-h SBP and DBP decreases in the medicated group were 10.2 mmHg and 4.6 mmHg, respectively (P < 0.001), with significant decreases during the daytime of 8.6 mmHg, 3.0 mmHg, and nighttime of 12.3 mmHg, 7.7 mmHg (P <0.001). In the non-medicated treatment group, 24-h SBP and DBP decreases were 1.9 mmHg and 1.1 mmHg (P < 0.005) with significant decreases in mean nighttime BP values of 3.2 mmHg and 1.9 mmHg (P < 0.001). While pre- and postoperative SF-36 results differed significantly, no differences were observed between the two groups.
Conclusion
ESP decreases BP and improves HRQOL in OSA patients with hypertension, particularly in combination with antihypertensive drugs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gottlieb DJ, Yenokyan G, Newman AB, O'Connor GT, Punjabi NM, Quan SF, Redline S, Resnick HE, Tong EK, Diener-West M, Shahar E (2010) Prospective study of obstructive sleep apnea and incident coronary heart disease and heart failure: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Circulation. 122(4):352–360. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.901801
Gami AS, Pressman G, Caples SM, Kanagala R, Gard JJ, Davison DE, Malouf JF, Ammash NM, Friedman PA, Somers VK (2004) Association of atrial fibrillation and obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation. 110(4):364–367. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000136587.68725.8E
Bauters F, Rietzschel ER, Hertegonne KBC, Chirinos JA (2016) The link between obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease. Curr Atheroscler Rep 18(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-015-0556-z
Sanchez de la Torre M, Campos-Rodriguez F, Barbe F (2013) Obstructive sleep apnoea and cardiovascular disease. Lancet Respir Med 1(1):61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(12)70051-6
Baldwin CM, Griffith KA, Nieto FJ, O’Connor GT, Walsleben JA, Redline S (2001) The association of sleep-disordered breathing and sleep symptoms with quality of life in the Sleep Heart Health Study. Sleep. 24(1):96–105. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/24.1.96
Lindberg E, Carter N, Gislason T, Janson C (2001) Role of snoring and daytime sleepiness in occupational accidents. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164(11):2031–2035. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.164.11.2102028
Fava C, Dorigoni S, Dalle Vedove F, Danese E, Montagnana M, Guidi GC, Narkiewicz K, Minuz P (2014) Effect of CPAP on blood pressure in patients with OSA/hypopnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest. 145(4):762–771. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.13-1115
Muxfeldt ES, Margallo V, Costa LMS, Guimarães G, Cavalcante AH, Azevedo JCM, de Souza F, Cardoso CRL, Salles GF (2015) Effects of continuous positive airway pressure treatment on clinic and ambulatory blood pressures in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and resistant hypertension: a randomized controlled trial. Hypertension. 65(4):736–742. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04852
Casitas R, Martinez-Ceron E, Galera R et al (2017) The effect of treatment for sleep apnoea on determinants of blood pressure control. Eur Respir J 50(5):1701261. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01261-2017
Hoffstein V (2007) Review of oral appliances for treatment of sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Breath 11(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-006-0084-8
Iftikhar IH, Hays ER, Iverson M-A, Magalang UJ, Maas AK (2013) Effect of oral appliances on blood pressure in obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Sleep Med 9(2):165–174. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.2420
Pengo MF, Soranna D, Giontella A, Perger E, Mattaliano P, Schwarz EI, Lombardi C, Bilo G, Zambon A, Steier J, Parati G, Minuz P, Fava C (2020) Obstructive sleep apnoea treatment and blood pressure: which phenotypes predict a response? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 55(5):1901945. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01945-2019
Picard F, Panagiotidou P, Weinig L, Steffen M, Tammen AB, Klein RM (2020) Effect of CPAP therapy on nocturnal blood pressure fluctuations, nocturnal blood pressure, and arterial stiffness in patients with coexisting cardiovascular diseases and obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-020-02075-4
Wolkove N, Baltzan M, Kamel H, Dabrusin R, Palayew M (2008) Long-term compliance with continuous positive airway pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Can Respir J 15(7):365–369. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/534372
Riachy M, Najem S, Iskandar M, Choucair J, Ibrahim I, Juvelikian G (2017) Factors predicting CPAP adherence in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 21(2):295–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-016-1408-y
Tan KB, Toh ST, Guilleminault C, Holty JC (2015) A cost-effectiveness analysis of surgery for middle-aged men with severe obstructive sleep apnea intolerant of CPAP. J Clin Sleep Med 11(5):525–535. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.4696
Caples SM, Rowley JA, Prinsell JR et al (2010) Surgical modifications of the upper airway for obstructive sleep apnea in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep 33(10):1396–1407. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/33.10.1396
Pang KP, Woodson BT (2007) Expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty: a new technique for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137(1):110–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2007.03.014
Pang KP, Pang EB, Win MT, Pang KA, Woodson BT (2016) Expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty for the treatment of OSA: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(9):2329–2333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3831-2
Hong SN, Kim HG, Han SY, Ji JY, Kim MK, Han DH, Won TB, Kim DY, Kim HJ (2019) Indications for and outcomes of expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty to treat lateral pharyngeal collapse in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 145(5):405–412. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2019.0006
Berry RB, Budhiraja R, Gottlieb DJ, Gozal D, Iber C, Kapur VK, Marcus CL, Mehra R, Parthasarathy S, Quan SF, Redline S, Strohl KP, Ward SLD, Tangredi MM (2012) Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: update of the 2007 AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events. Deliberations of the Sleep Apnea Defifinitions Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J Clin Sleep Med 8(5):597–619. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.2172
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 14(6):540–545. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/14.6.540
Jenkinson C, Stradling J, Petersen S (1997) Comparison of three measures of quality of life outcome in the evaluation of continuous positive airways pressure therapy for sleep apnoea. J Sleep Res 6(3):199–204. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2869.1997.00043.x
Schellenberg JB, Maislin G, Schwab RJ (2000) Physical findings and the risk for obstructive sleep apnea: the importance of oropharyngeal structures. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162(2 Pt 1):740–748. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.162.2.9908123
Genta PR, Sands SA, Butler JP, Loring SH, Katz ES, Demko BG, Kezirian EJ, White DP, Wellman A (2017) Airflow shape is associated with the pharyngeal structure causing OSA. Chest 152(3):537–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2017.06.017
Fehrm J, Friberg D, Bring J, Browaldh N (2017) Blood pressure after modifified uvulopalatopharyngoplasty: results from the SKUP3 randomized controlled trial. Sleep Med 34:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2017.02.030
Tsai MH, Lin PW, Lin HC, Friedman M, Salapatas AM, Lu YH, Su MC, Lin MC (2020) Alternations of blood pressure before and after OSA surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Jun 2:194599820926137–194599820926848. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599820926137
Navarro-Soriano C, Martínez-García MA, Torres G, Barbé F, Caballero-Eraso C, Lloberes P, Diaz Cambriles T, Somoza M, Masa JF, González M, Mañas E, de la Peña M, García-Río F, Montserrat JM, Muriel A, Oscullo G, Feced Olmos L, García-Ortega A, Calhoun D, Campos-Rodriguez F, on behalf the Spanish Sleep Network (2019) Effect of continuous positive airway pressure in patients with true refractory hypertension and sleep apnea: a post-hoc intention-to-treat analysis of the HIPARCO randomized clinical trial. J Hypertens 37(6):1269–1275. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000002053
Logan AG, Perlikowski SM, Mente A, Tisler A, Tkacova R, Niroumand M, Leung RST, Bradley TD (2001) High prevalence of unrecognized sleep apnoea in drug-resistant hypertension. J Hypertens 19(12):2271–2277. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004872-200112000-00022
Thunstrom E, Manhem K, Rosengren A, Peker Y (2016) Blood pressure response to losartan and continuous positive airway pressure in hypertension and obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 193(3):310–320. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201505-0998OC
Hedna K, Hakkarainen KM, Gyllensten H, Jönsson AK, Andersson Sundell K, Petzold M, Hägg S (2015) Adherence to antihypertensive therapy and elevated blood pressure: should we consider the use of multiple medications? PLoS One 10(9):e0137451. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137451
McEvoy RD, Antic NA, Heeley E et al (2016) CPAP for prevention of cardiovascular events in obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med 375(10):919–931. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1606599
Zhao YY, Wang R, Gleason KJ et al (2017) Effect of continuous positive airway pressure treatment on health-related quality of life and sleepiness in high cardiovascular risk individuals with sleep apnea: Best Apnea Interventions for Research (BestAIR) Trial. Sleep 40(4):zsx040. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsx040
Zhang XQ, Zhao X, Hong PW, Zhou J, Zeng P, Liu C, Li XY, Zhao Y, Jiang LQ (2020) Change in quality of life of OSAHS patients with minimally invasive surgery or CPAP therapy: a 2-year retrospective, single-center parallel-group study. Curr Mol Med 20(3):231–239. https://doi.org/10.2174/1566524019666191009150734
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dong Wang: study design, data collection and analysis, and manuscript draft. Si-Fan Gao, Jun Chen, Hong-Ting Hua, and Yun-Xia Ma: data collection and analysis. Ye-Hai Liu: study design and manuscript review. Chao-Bing Gao: study design, manuscript review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Gao, SF., Chen, J. et al. The long-term impact of expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty treatment on blood pressure control and health-related quality of life in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and hypertension. Sleep Breath 25, 2155–2162 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-021-02314-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-021-02314-2