Abstract
Purpose
Several studies have used the cardiopulmonary exercise test to assess patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). However, no report has investigated the use of the 6-min walk test (6MWT) in this group of patients.
Methods
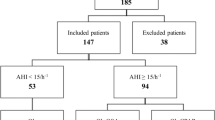
We studied consecutive, newly diagnosed, OSA patients (aged >18 years). The control group was composed of matched healthy subjects with no clinical history indicative of sleep breathing disorders. The study population was divided into three groups: an OSA group, a control obese group, and a control lean group. The obese controls were gender-, age- (±2 years), height- (±5 cm), and weight- (±2 kg) matched to the OSA patients, while the lean controls were matched in gender, age, and height, but not weight. All patients underwent sleep study at our Sleep Disorders Center. Each subject underwent a single 6MWT within 1 week of the sleep study.
Results
A total of 55 patients were recruited to the OSA group (age 36.7 ± 7.9 years, body mass index 38.7 ± 8.6 kg/m2, and apnea hypopnea index 66.6 ± 34.8/h), 32 subjects to the control obese group, and 30 to the control lean group. There was no difference in distance walked (6-min walk distance (6MWD)) between the OSA group (389 ± 70 m) and the obese group (408 ± 66 m). In the OSA group, the 6MWD results did not correlate with patient age, apnea hypopnea index, or other polysomnographic variables. At the end of the test, heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and dyspnea perception were significantly increased in the OSA group compared with healthy subjects.
Conclusions
The 6MWT is easy to perform and well tolerated by patients with OSA. There were no correlations between the 6MWD and the severity of OSA or other polysomnographic parameters. However, patients with OSA exhibited abnormal hemodynamic responses to submaximal exercise.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones NL, Killian KJ (2000) Exercise limitation in health and disease. N Engl J Med 343(9):632–641
Yang EH, Hla KM, McHorney CA, Havighurst T, Badr MS, Weber S (2000) Sleep apnea and quality of life. Sleep 23(4):535–541
Aguillard RN, Riedel BW, Lichstein KL, Grieve FG, Johnson CT, Noe SL (1998) Daytime functioning in obstructive sleep apnea patients: exercise tolerance, subjective fatigue, and sleepiness. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 23(4):207–217
Kaleth AS, Chittenden TW, Hawkins BJ, Hargens TA, Guill SG, Zedalis D et al (2007) Unique cardiopulmonary exercise test responses in overweight middle-aged adults with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med 8(2):160–168
Alonso-Fernandez A, Garcia-Rio F, Arias MA, Mediano O, Pino JM, Martinez I et al (2006) Obstructive sleep apnoea-hypoapnoea syndrome reversibly depresses cardiac response to exercise. Eur Heart J 27(2):207–215
Vanuxem D, Badier M, Guillot C, Delpierre S, Jahjah F, Vanuxem P (1997) Impairment of muscle energy metabolism in patients with sleep apnoea syndrome. Respir Med 91(9):551–557
Cahalin LP, Mathier MA, Semigran MJ, Dec GW, DiSalvo TG (1996) The six-minute walk test predicts peak oxygen uptake and survival in patients with advanced heart failure. Chest 110(2):325–332
Kadikar A, Maurer J, Kesten S (1997) The six-minute walk test: a guide to assessment for lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 16(3):313–319
Roul G, Germain P, Bareiss P (1998) Does the 6-minute walk test predict the prognosis in patients with NYHA class II or III chronic heart failure? Am Heart J 136(3):449–457
Hoeper MM, Schwarze M, Ehlerding S, Adler-Schuermeyer A, Spiekerkoetter E, Niedermeyer J et al (2000) Long-term treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension with aerosolized iloprost, a prostacyclin analogue. N Engl J Med 342(25):1866–1870
Flaherty KR, Andrei AC, Murray S, Fraley C, Colby TV, Travis WD et al (2006) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prognostic value of changes in physiology and six minute hallwalk. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174(7):803–809
Alameri H, Al-Majed S, Al-Howaikan A (2009) Six-min walk test in a healthy adult Arab population. Respir Med 103(7):1041–1046
Netzer NC, Stoohs RA, Netzer CM, Clark K, Strohl KP (1999) Using the Berlin Questionnaire to identify patients at risk for the sleep apnea syndrome. Ann Intern Med 131(7):485–491
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A (eds) (1968) A manual of standardized terminology techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. NIH Publication number 204, US Government Printing Office, Washington
American Sleep Disorders Association, Atlas task Force (1992) EEG arousals: scoring rules and examples. Sleep 15:174–184
International Classification of Sleep Disorders (2005) Diagnostic & coding manual, 2nd edn. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Westchester (IL)
American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force (1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. Sleep 22:667–689
American Thoracic Society (1995) Standardization of spirometry, 1994 update. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:1107–1136
American Thoracic Society (2002) ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166(1):111–117
Edward Shifflett D, Walker EW, Gregg JM, Zedalis D, Herbert WG (2001) Effects of short-term PAP treatment on endurance exercise performance in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep Med 2(2):145–151
Grote L, Hedner J, Peter JH (2004) The heart rate response to exercise is blunted in patients with sleep-related breathing disorder. Cardiology 102(2):93–99
Lin CC, Lin CK, Wu KM, Chou CS (2004) Effect of treatment by nasal CPAP on cardiopulmonary exercise test in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Lung 182(4):199–212
Lin CC, Hsieh WY, Chou CS, Liaw SF (2006) Cardiopulmonary exercise testing in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 150(1):27–34
Tryfon S, Stanopoulos I, Dascalopoulou E, Argyropoulou P, Bouros D, Mavrofridis E (2004) Sleep apnea syndrome and diastolic blood pressure elevation during exercise. Respiration 71(5):499–504
Narkiewicz K, van de Borne PJ, Cooley RL, Dyken ME, Somers VK (1998) Sympathetic activity in obese subjects with and without obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 98(8):772–776
Somers VK, Dyken ME, Mark AL, Abboud FM (1993) Sympathetic-nerve activity during sleep in normal subjects. N Engl J Med 328(5):303–307
Hargens TA, Guill SG, Zedalis D, Gregg JM, Nickols-Richardson SM, Herbert WG (2008) Attenuated heart rate recovery following exercise testing in overweight young men with untreated obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 31(1):104–110
Maeder MT, Munzer T, Rickli H, Schoch OD, Korte W, Hurny C et al (2008) Association between heart rate recovery and severity of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Med 9(7):753–761
Vanhecke TE, Franklin BA, Zalesin KC, Sangal RB, deJong AT, Agrawal V et al (2008) Cardiorespiratory fitness and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in morbidly obese patients. Chest 134(3):539–545
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alameri, H., Al-Kabab, Y. & BaHammam, A. Submaximal exercise in patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 14, 145–151 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-009-0300-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-009-0300-4