Abstract
Purpose
We measure the whole-body distribution of IV injected [11C]Flumazenil (FMZ) as a function of time in adult subjects and determine the absorbed radiation doses.
Procedures
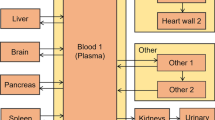
After injection with 770 MBq of [11C]FMZ (nominal), each of six subjects underwent nine consecutive whole body PET scans. Twelve source organs were identified using PET attenuation and emission images. Activity within each organ as a function of time was determined from the sequence of the nine PET scans. Source organ time activity curves were integrated and normalized by the injected dose to yield source organ residence times for the no voiding situation. Separate bladder residence-time calculations were performed for the cases of a 1- and a 2-h voiding interval. Using the source organ residence times as input, the program OLINDA/EXM (Stabin et al. in J Nucl Med. 46:1023-1027, 2005) was used to perform dosimetry calculations for the various body organs and for the whole body.
Results
For the no voiding situation, the average whole-body radiation equivalent dose was 3.02 × 10−3 mSv/MBq of injected [11C]FMZ. The average effective dose and effective dose equivalent was 7.57 × 10−3 and 1.12 × 10−2 mSv MBq−1, respectively. The organ receiving the highest equivalent dose was the urinary bladder wall with an average of 6.32 × 10−2 mSv MBq−1.
Conclusion
On average, the administration of less than 790 MBq (21 mCi) of [11C]FMZ yields (no voiding model) an organ equivalent dose of under 50 mSv [the single dose limit for research studies under US regulations (21CFR361.1) to body organs other than blood forming organs, gonads or the lens of the eye] to all organs. Equivalent dose to the blood forming organs and gonads from a 790 MBq administered FMZ dose is well under the 30 mSv limit provided under 21CFR361.1. Additionally, administration of less than 1320 MBq (35.7 mCi) yields an effective dose [International Commission on Radiation Protection (ICRP) 60 tissue weighting scheme] of under 10 mSv, which is the ICRP IIb (minor to intermediate) risk category limit.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E (2005) OLINDA/EXM: The second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med 46:1023–1027
Persson A, Ehrin E, Eriksson L, Farde L, Hedstrom CG, Litton JE et al (1985) Imaging of [11 C]-labelled Ro 15–1788 binding to benzodiazepine receptors in the human brain by positron emission tomography. J Psychiatr Res 19:609–622
Pappata S, Samson Y, Chavoix C, Prenant C, Maziere M, Baron JC (1988) Regional specific binding of [11 C]RO 15 1788 to central type benzodiazepine receptors in human brain: quantitative evaluation by PET. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:304–313
Shinotoh H, Iyo M, Yamada T, Inoue O, Suzuki K, Itoh T et al (1989) Detection of benzodiazepine receptor occupancy in the human brain by positron emission tomography. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 99:202–207
Koeppe RA, Holthoff VA, Frey KA, Kilbourn MR, Kuhl DE (1991) Compartmental analysis of [11 C]flumazenil kinetics for the estimation of ligand transport rate and receptor distribution using positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:735–744
Abadie P, Baron JC, Bisserbe JC, Boulenger JP, Rioux P, Travere JM et al (1992) Central Benzodiazepine Receptors in Human Brain - Estimation of Regional B(Max) and K(D) Values with Positron Emission Tomography. Eur J Pharmacol 213:107–115
Price JC, Mayberg HS, Dannals RF, Wilson AA, Ravert HT, Sadzot B et al (1993) Measurement of benzodiazepine receptor number and affinity in humans using tracer kinetic modeling, positron emission tomography, and [11 C]flumazenil. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13:656–667
Delforge J, Pappata S, Millet P, Samson Y, Bendriem B, Jobert A et al (1995) Quantification of benzodiazepine receptors in human brain using pet, [C-11] Flumazenil, and a single-experiment protocol. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15:284–300
Lassen NA, Bartenstein PA, Lammertsma AA, Prevett MC, Turton DR, Luthra SK et al (1995) Benzodiazepine receptor quantification in-vivo in humans using [C-11] flumazenil and pet - application of the steady-state principle. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15:152–165
Salmi E, Aalto S, Hirvonen J, Langsjo JW, Maksimow AT, Oikonen V et al (2008) Measurement of GABA(A) receptor binding in vivo with [C-11] flumazenil: A test-retest study in healthy subjects. Neuroimage 41:260–269
Frankle WG, Cho RY, Narendran R, Mason NS, Vora S, Litschge M et al (2009) Tiagabine Increases [C-11] flumazenil binding in cortical brain regions in healthy control subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:624–633
Odano I, Halldin C, Karlsson P, Varrone A, Airaksinen AJ, Krasikova RN et al (2009) [F-18]Flumazenil binding to central benzodiazepine receptor studies by PET - Quantitative analysis and comparisons with [C-11]flumazenil. Neuroimage 45:891–902
Savic I, Persson A, Roland P, Pauli S, Sedvall G, Widen L (1988) In-vivo demonstration of reduced benzodiazepine receptor binding in human epileptic foci. Lancet 2:863–866
Henry TR, Frey KA, Sackellares JC, Gilman S, Koeppe RA, Brunberg JA et al (1993) In vivo cerebral metabolism and central benzodiazepine-receptor binding in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 43:1998–2006
Prevett MC, Lammertsma AA, Brooks DJ, Bartenstein PA, Patsalos PN, Fish DR et al (1995) Benzodiazepine-Gaba(a) receptors in idiopathic generalized epilepsy measured with [C-11] flumazenil and positron emission tomography. Epilepsia 36:113–121
Savic I, Thorell JO, Roland P (1995) [C-11] Flumazenil positron emission tomography visualizes frontal epileptogenic regions. Epilepsia 36:1225–1232
Richardson MP, Koepp MJ, Brooks DJ, Fish DR, Duncan JS (1996) Benzodiazepine receptors in focal epilepsy with cortical dysgenesis: An C-11-flumazenil PET study. Ann Neurol 40:188–198
Szelies B, Weber-Luxenburger G, Pawlik G, Kessler J, Holthoff V, Mielke R et al (1996) MRI-guided flumazenil- and FDG-PET in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage 3:109–118
Koepp MJ, Richardson MP, Brooks DJ, Cunningham VJ, Duncan JS (1997) Central benzodiazepine/gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: An [C-11]flumazenil positron emission tomography study. Epilepsia 38:1089–1097
Juhasz C, Asano E, Shah A, Chugani DC, Batista CEA, Muzik O et al (2009) Focal decreases of cortical GABA(A) receptor binding remote from the primary seizure focus: What do they indicate ? Epilepsia 50:240–250
Juhasz C, Nagy F, Watson C, da Silva EA, Muzik O, Chugani DC et al (1999) Glucose and [C-11]flumazenil positron emission tomography abnormalities of thalamic nuclei in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 53:2037–2045
Szelies B, Sobesky J, Pawlik G, Mielke R, Bauer B, Herholz K et al (2002) Impaired benzodiazepine receptor binding in peri-lesional cortex of patients with symptomatic epilepsies studied by [C-11]-flumazenil PET. Eur J Neurol 9:137–142
Padma MV, Simkins R, White P, Satter M, Christian BT, Dunigan K et al (2004) Clinical utility of 11 C-flumazenil positron emission tomography in intractable temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurol India 52:457–462
Bouvard S, Costes N, Bonnefoi F, Lavenne F, Mauguiere F, Delforge J et al (2005) Seizure-related short-term plasticity of benzodiazepine receptors in partial epilepsy: a [C-11]flumazenil-PET study. Brain 128:1330–1343
Heiss WD, Kracht L, Grond M, Rudolf J, Bauer B, Wienhard K et al (2000) Early [C-11]flumazenil/H2O positron emission tomography predicts irreversible ischemic cortical damage in stroke patients receiving acute thrombolytic therapy. Stroke 31:366–369
Heiss WD, Sobesky J, Smekal U, Kracht LW, Lehnhardt FG, Thiel A et al (2004) Probability of cortical infarction predicted by flumazenil binding and diffusion-weighted imaging signal intensity: a comparative positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging study in early ischemic stroke. Stroke 35:1892–1898
Guadagno JV, Jones PS, Aigbirhio FI, Wang D, Fryer TD, Day DJ et al (2008) Selective neuronal loss in rescued penumbra relates to initial hypoperfusion. Brain 131:2666–2678
Suzuki Y, Horie C, Kiyosawa M, Nariai T, Mochizuki M, Oda K et al (2008) Measurement of the C-11-flumazenil binding in the visual cortex predicts the prognosis of hemianopia. J Neurol Sci 268:102–107
Chavoix C, Samson Y, Pappata S, Prenant C, Maziere M, Seck A et al (1990) Positron emission tomography study of brain benzodiazepine receptors in Friedreich’s ataxia. Can J Neurol Sci 17:404–409
Holthoff VA, Koeppe RA, Frey KA, Penney JB, Markel DS, Kuhl DE et al (1993) Positron Emission Tomography Measures of Benzodiazepine Receptors in Huntingtons-Disease. Ann Neurol 34:76–81
Gilman S, Koeppe RA, Junck L, Kluin KJ, Lohman M, St Laurent RT (1995) Benzodiazepine receptor binding in cerebellar degenerations studied with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 38:176–185
Meyer M, Koeppe RA, Frey KA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE (1995) Positron emission tomography measures of benzodiazepine binding in Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Neurol 52:314–317
Klumpers UMH, Veltman DJ, Drent ML, Boellaard R, Comans EFI, Meynen G et al (2010) Reduced parahippocampal and lateral temporal GABA(A)-[C-11]flumazenil binding in major depression: preliminary results. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:565–574
Ihara M, Tomimoto H, Ishizu K, Yoshida H, Sawamoto N, Hashikawa K et al (2007) Association of vascular parkinsonism with impaired neuronal integrity in the striatum. J Neural Transm 114:577–584
Geuze E, van Berckel BNM, Lammertsma AA, Boellaard R, de Kloet CS, Vermetten E et al (2008) Reduced GABA(A) benzodiazepine receptor binding in veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder. Mol Psychiatry 13:74–83
Pearl PL, Gibson KM, Quezado Z, Dustin I, Taylor J, Trzcinski S et al (2009) Decreased GABA-A binding on FMZ-PET in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Neurology 73:423–429
Litton JE, Neiman J, Pauli S, Farde L, Hindmarsh T, Halldin C et al (1993) Pet analysis of [C-11] flumazenil binding to benzodiazepine receptors in chronic alcohol-dependent men and healthy controls. Psychiatry Research Neuroimaging 50:1–13
Lingford-Hughes AR, Wilson SJ, Cunningham VJ, Feeney A, Stevenson B, Brooks DJ et al (2005) GABA-benzodiazepine receptor function in alcohol dependence: a combined C-11-flumazenil PET and pharmacodynamic study. Psychopharmacology 180:595–606
Yamauchi H, Kudoh T, Kishibe Y, Iwasaki J, Kagawa S (2005) Selective neuronal damage and borderzone infarction in carotid artery occlusive disease: A C-11-flumazenil PET study. J Nucl Med 46:1973–1979
Turner MR, Hammers A, Al-Chalabi A, Shaw CE, Andersen PM, Brooks DJ et al (2005) Distinct cerebral lesions in sporadic and ‘D90A’ SOD1 ALS: studies with [C-11]flumazenil PET. Brain 128:1323–1329
Wicks P, Turner MR, Abrahams S, Hammers A, Brooks DJ, Leigh PN et al (2008) Neuronal loss associated with cognitive performance in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An (C-11)-flumazenil PET study. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 9:43–49
Capaday C, Richardson MP, Rothwell JC, Brooks DJ (2000) Long-term changes of GABAergic function in the sensorimotor cortex of amputees - A combined magnetic stimulation and C-11-flumazenil PET study. Exp Brain Res 133:552–556
Salmi E, Kaisti KK, Metsahonkala L, Oikonen V, Aalto S, Nagren K et al (2004) Sevoflurane and propofol increase C-11-flumazenil binding to gamma-aminobutyric Acid(A) receptors in humans. Anesth Analg 99:1420–1426
Halldin C, Stone-Elander S, Thorell J-O, Persson A, Sedvall G (1988) 11 C-labelling of Ro 15–1788 in two different positions, and also 11 C-labelling of its main metabolite Ro 15–3890, for PET studies of benzodiazepine receptors. Int J Radiat Appl Instrum A Appl Radiat Isot 39:993–997
Slifstein M, Hwang DR, Martinez D, Ekelund J, Huang YY, Hackett E et al (2006) Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the dopamine D-2 ligand C-11-raclopride determined from human whole-body PET. J Nucl Med 47:313–319
Cristy M, Eckerman KF (1987) Specific absorbed fractions of energy at various ages from internal photon sources. I. Methods. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge
Stabin MG, Watson EE, Cristy M, Ryman JC, Eckerman KF, Davis JL et al (1995) Mathematical models and specific absorbed fractions of photon energy in the nonpregnant adult female and at the end of each trimester of pregnancy. National Laboratory, Oak Ridge
Stabin MG, Siegel JA (2003) Physical models and dose factors for use in internal dose assessment. Health Phys 85:294–310
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) (1979) Limits for intakes of radionuclides by workers. ICRP Publication 30. Pergamon, New York
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) (1991) 1990 Recommendations of the international commission on radiological protection. ICRP Publication 60. Pergamon, New York
ICRP (2007) P103: The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Ann ICRP 37:1–332
Nugent AC, Neumeister A, Devets WC, Eckelman WC, Channing P, Herscovitch P (2004) Human biodistribution and dosimetry of the PET benzodiazepine receptor radioligand [11 C]Flumazenil. J Nucl Med 45(Supplement):434P
Laymon CM, Narendran R, Mason NS, Carney JP, Lopresti BJ, Mountz JM et al (2009) Human dosimetry of the PET radioligand [C-11]Flumazenil (FMZ). J Nucl Med 50(Supplement):387P
Stabin MG (1996) MIRDOSE: Personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med 37:538–546
Laymon CM, Mason NS, Frankle WG, Carney JP, Lopresti BJ, Litschge MY et al (2009) Human biodistribution and dosimetry of the D2/3 agonist 11 C-N-propylnorapomorphine (11 C-NPA) determined from PET. J Nucl Med 50:814–817. doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.058131
Wrixon AD (2008) New ICRP recommendations. J Radiol Prot 28:161–168. doi:10.1088/0952-4746/28/2/r02
Verbruggen A, Coenen HH, Deverre JR, Guilloteau D, Langstrom B, Salvadori PA et al (2008) Guideline to regulations for radiopharmaceuticals in early phase clinical trials in the EU. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35:2144–2151. doi:10.1007/s00259-008-0853-7
Acknowledgment
We are grateful to the research subjects who participated in this study. The authors thank members of the PET Facility staff who carried out the acquisition of PET data and care of all subjects during PET procedures. These data were generated with the support of career development award 5K08 MH069697-02 (PI: Frankle) granted by the United States National Institutes of Health. Infrastructure support was provided through NIH grant P50 MH084053.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laymon, C.M., Narendran, R., Mason, N.S. et al. Human Biodistribution and Dosimetry of the PET Radioligand [11C]Flumazenil (FMZ). Mol Imaging Biol 14, 115–122 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-011-0478-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-011-0478-2