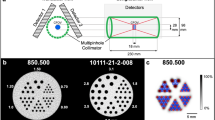
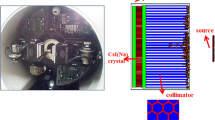
Abstract
Purpose
In this work, we developed and validated a Monte Carlo simulation (MCS) tool for investigation and evaluation of multi-pinhole (MPH) SPECT imaging.
Procedures
This tool was based on a combination of the SimSET and MCNP codes. Photon attenuation and scatter in the object, as well as penetration and scatter through the collimator detector, are modeled in this tool. It allows accurate and efficient simulation of MPH SPECT with focused pinhole apertures and user-specified photon energy, aperture material, and imaging geometry. The MCS method was validated by comparing the point response function (PRF), detection efficiency (DE), and image profiles obtained from point sources and phantom experiments. A prototype single-pinhole collimator and focused four- and five-pinhole collimators fitted on a small animal imager were used for the experimental validations. We have also compared computational speed among various simulation tools for MPH SPECT, including SimSET-MCNP, MCNP, SimSET-GATE, and GATE for simulating projections of a hot sphere phantom.
Results
We found good agreement between the MCS and experimental results for PRF, DE, and image profiles, indicating the validity of the simulation method. The relative computational speeds for SimSET-MCNP, MCNP, SimSET-GATE, and GATE are 1: 2.73: 3.54: 7.34, respectively, for 120-view simulations. We also demonstrated the application of this MCS tool in small animal imaging by generating a set of low-noise MPH projection data of a 3D digital mouse whole body phantom.
Conclusions
The new method is useful for studying MPH collimator designs, data acquisition protocols, image reconstructions, and compensation techniques. It also has great potential to be applied for modeling the collimator-detector response with penetration and scatter effects for MPH in the quantitative reconstruction method.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meikle SR, Kench P, Kassiou M, Banati RB (2005) Small animal SPECT and its place in the matrix of molecular imaging technologies, Phys Med Biol 50:R45–R61
Schramm N, Wirrwar A, Sonnenberg F, Halling H (2000) Compact high resolution detector for small animal SPECT. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 47:1163–1167
Jaszczak RJ, Li JY, Wang HL, Zalutsky MR, Coleman RE (1994) Pinhole collimation for ultra-high-resolution, small-field-of-view spect. Phys Med Biol 39:425–437
Weber DA, Ivanovic M, Franceschi D, Strand SE, Erlandsson K, Franceschi M, Atkins HL, Coderre JA, Susskind H, Button T, Ljunggren K (1994) Pinhole spect - an approach to in-vivo high-resolution spect imaging in small laboratory-animals. J Nucl Med 35:342–348
Erlandsson K, Ivanovic M, Strand SE, Sjogren K, Weber DA (1993) High-resolution pinhole spect for small animal imaging. J Nucl Med 34:P9–P9
Levin CS (2005) Small animal PET and SPECT: instrumentation, performance, and applications. Med Phys 32:2096–2096
Vogel RA, Kirch DL, Lefree MT, Rainwater JO, Jensen DP, Steele PP (1979) Tl-201 myocardial perfusion scintigraphy - results of standard and multi-pinhole Tomographic techniques. Am J Cardiol 43:787–793
Lefree MT, Vogel RA, Kirch DL, Steele PP (1981) 7-pinhole Tomography - a technical description. J Nucl Med 22:48–54
Vogel RA, Kirch DL, Lefree MT, Steele PP (1979) Gated blood pool Tomography using the 7 Pinhole anger camera technique. Circulation 60:136–136
Beekman FJ, van der Have F, Vastenhouw B, van der Linden AJA, van Rijk PP, Burbach JPH, Smidt MP (2005) U-SPECT-I: A novel system for submillimeter-resolution tomography with radiolabeled molecules in mice. J Nucl Med 46:1194–1200
Funk T, Despres P, Barber WC, Shah KS, Hasegawa BH (2006) A multipinhole small animal SPECT system with submillimeter spatial resolution, Med Phys 33:1259–1268
Ishizu K, Mukai T, Yonekura Y, Pagani M, Fujita T, Magata Y, Nishizawa S, Tamaki N, Shibasaki H, Konishi J (1995) Ultra-high-resolution spect system using 4 Pinhole collimators for small animal studies. J Nucl Med 36:2282–2287
Schramm NU, Engeland U, Ebel G, Schurrat T, Behe M, Behr TM (2002) Multi-pinhole SPECT for small animal research. J Nucl Med 43:223–223
Buvat I, Castiglion I (2002) Monte Carlo simulations in SPET and PET. Q J Nucl Med 46:48–61
Song TY, Choi Y, Chung YH, Jung JH, Choe YS, Lee KH, Kim SE, Kim BT (2003) Optimization of pinhole collimator for small animal SPECT using Monte Carlo simulation. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 50:327–332
Beekman FJ, Kamphuis C, Frey EC (1997) Scatter compensation methods in 3D iterative SPECT reconstruction: A simulation study, Phys Med Biol 42:1619–1632
Kaplan MS, Harrison RL, Vannoy SD (1998) Coherent scatter implementation for SimSET. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 45:3064–3068
Harrison RL, Haynor DR, Gillispie SB, Vannoy SD, Kaplan MS, Lewellen TK (1993) A public-domain simulation system for emission tomography - photon tracking through heterogeneous attenuation using importance sampling. J Nucl Med 34:P60–P60
Metz CE (1980) The geometric transfer function component for scintillation camera collimators with straight parallel holes. Phys Med Biol 25:1059–1070
Tsui BMW, Gullberg GT (1990) The geometric transfer-function for cone and fan beam collimators. Phys Med Biol 35:81–93
Frey EC, Tsui BMW, Gullberg GT (1998) Improved estimation of the detector response function for converging beam collimators. Phys Med Biol 43:941–950
Forster RA, Godfrey TNK (1985) Mcnp - a general Monte-Carlo code for neutron and photon transport. Lect Notes Phys 240:33–55
Santin G, Strul D, Lazaro D, Simon L, Krieguer M, Martins MV, Breton V, Morel C (2003) GATE: A Geant4-based simulation platform for PET and SPECT integrating movement and time management, IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 50:1516–1521
Chen CL, Wang YC, Lee JJS, Tsui BMW (2008) Integration of SimSET photon history generator in GATE for efficient Monte Carlo simulations of pinhole SPECT. Med Phys 35:3278–3284
He X, Frey EC, Links JM, Gilland KL, Segars WP, Tsui BMW (2004) A mathematical observer study for the evaluation and optimization of compensation methods for myocardial SPECT using a phantom population that realistically models patient variability, IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 51:218–224
Farncombe TH, Gifford HC, Narayanan MV, Pretorius PH, Bruyant P, Gennert M, King MA (2002) An optimization of reconstruction parameters and investigation into the impact of photon scatter in Ga-67 SPECT. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 49:2148–2154
Sankaran S, Frey EC, Gilland KL, Tsui BMW (2002) Optimum compensation method and filter cutoff frequency in myocardial SPECT: a human observer study. J Nucl Med 43:432–438
Du Y, Frey EC, Wang WT, Tocharoenchai C, Baird WH, Tsui BMW (2002) Combination of MCNP and SimSET for Monte Carlo simulation of SPECT with medium- and high-energy photons. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 49:668–674
Qi YJ, Tsui BM, Frey EC, Yoder B (2002) Performance evaluation of compact detectors based on new pixellated NaI(Tl) crystal arrays for high-resolution small animal imaging. J Nucl Med 43:59p–59p
Segars WP, Tsui BMW, Frey EC, Johnson GA, Berr SS (2004) Development of a 4-D digital mouse phantom for molecular imaging research, Mol Imag Biol 6:149–159
Wang YC, Tsui BMW (2007) Pinhole SPECT with different data acquisition geometries: Usefulness of unified projection operators in homogeneous coordinates. IEEE Trans Med Imag 26:298–308
Metz CE, Tsui MW, Beck RN (1974) Theoretical prediction of geometric transfer function for focused collimators. J Nucl Med 15:1078–1083
Metzler SD, Bowsher JE, Greer KL, Jaszczak RJ (2002) Analytic determination of the pinhole collimator’s point-spread function and RMS resolution with penetration, IEEE Trans Med Imag 21:878–887
Assie K, Breton V, Buvat I, Comtat C, Jan S, Krieguer M, Lazaro D, Morel C, Rey M, Santin G, Simon L, Staelens S, Strul D, Vieira JM, de Walle RV (2004) Monte Carlo simulation in PET and SPECT instrumentation using GATE, Nucl Instrum Methods phys Res, Sect A, Accel Spectrom Detect Assoc Equip 527:180–189
Rannou FR, Kohli V, Prout DL, Chatziioannou AF (2004) Investigation of OPET performance using GATE, a Geant4-based simulation software, IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 51:2713–2717
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank Mr. Si Chen from Division of Medical Imaging Physics at the Johns Hopkins University, and Dr. Chia-Lin Chen from Chung Shan Medical University for their help on the GATE and SimSET-GATE simulations. This work was supported by the US Public Health Service Grant EB001558.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mok, G.S.P., Du, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Development and Validation of a Monte Carlo Simulation Tool for Multi-Pinhole SPECT. Mol Imaging Biol 12, 295–304 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0263-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0263-7