Abstract
Introduction
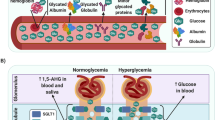
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a significant risk factor for the development of critical limb ischemia (CLI), the most advanced stage of peripheral arterial disease. The concurrent existence of T2DM and CLI often leads to adverse outcomes, namely limb amputation.
Objective
To identify biomarkers for improving the screening of CLI in high-risk people with T2DM.
Methods
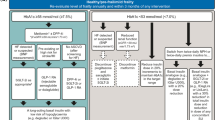
We investigated metabolome profiles in serum samples of 113 T2DM people with CLI (n = 23, G2) and without CLI (n = 45, G0: no lower limb stenosis (LLS) and n = 45, G1: LLS < 50%), using hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) approach. Principle component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) were used to analyze 1H NMR data.
Results
Twenty potential metabolites that could discriminate people with T2DM and CLI (G2) from non-CLI patients without LLS (G0) were determined in serum samples. The correct percent of classification for the PLS-DA model for the test set samples was 85% (n = 20) and 100% (n = 5) for G0 and G2 groups, respectively. Non-CLI patients with LLS < 50% (G1) were projected on the PCA abstract space built using 20 discriminatory metabolites. Eleven people with T2DM and LLS < 50% were prospectively followed, and their ankle-brachial index (ABI) was measured after 4 years. A promising agreement existed between the PCA model's predictions and those obtained by ABI values.
Conclusion
The findings suggest that confirmation of blood potential metabolic biomarkers as a complement to ABI for screening of CLI in a large group of high-risk people with T2DM is needed.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Aboyans, V., Criqui, M. H., Abraham, P., Allison, M. A., Creager, M. A., Diehm, C., Fowkes, F. G. R., Hiatt, W. R., Jönsson, B., & Lacroix, P. (2012). Measurement and interpretation of the ankle-brachial index: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 126, 2890–2909.
Association, A. D. (2003). Peripheral arterial disease in people with diabetes. Diabetes Care, 26, 3333–3341.
Azab, S. M., Zamzam, A., Syed, M. H., Abdin, R., Qadura, M., & Britz-McKibbin, P. (2020). Serum metabolic signatures of chronic limb-threatening ischemia in patients with peripheral artery disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9, 1877.
Babaei, M. R., Malek, M., Rostami, F. T., Emami, Z., Madani, N. H., & Khamseh, M. E. (2020). Non-invasive vascular assessment in people with type 2 diabetes: Diagnostic performance of Plethysmographic-and-Doppler derived ankle brachial index, toe brachial index, and pulse volume wave analysis for detection of peripheral arterial disease. Primary Care Diabetes, 14, 282–289.
Beckman, J. A., Creager, M. A., & Libby, P. (2002). Diabetes and atherosclerosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA, 287, 2570–2581.
Brown, F. F., Campbell, I. D., & Kuchel, P. W. (1977). Human erythrocyte metabolism studies by 1H spin echo NMR. FEBS Letters, 82, 12–16.
Chapman, M. J., Redfern, J. S., McGovern, M. E., & Giral, P. (2011). Optimal pharmacotherapy to combat the atherogenic lipid triad. Current Opinion in Cardiology, 26, 403–411.
Chashmniam, S., Madani, N. H., Ghoochani, B. F. N. M., Safari-Alighiarloo, N., & Khamseh, M. E. (2020). The metabolome profiling of obese and non-obese individuals: Metabolically healthy obese and unhealthy non-obese paradox. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 23, 186.
Chen, Y., Jia, H., Qian, X., Wang, J., Yu, M., Gong, Q., An, Y., Li, H., Li, S., & Shi, N. (2022). Circulating palmitoyl sphingomyelin is associated with cardiovascular disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes: Findings from the China Da Qing diabetes study. Diabetes Care, 45, 666–673.
Cronenwett, J. L., Warner, K. G., Zelenock, G. B., Whitehouse, W. M., Graham, L. M., Lindenauer, S. M., & Stanley, J. C. (1984). Intermittent claudication: Current results of nonoperative management. Archives of Surgery, 119, 430–436.
Dieterle, F., Ross, A., Schlotterbeck, G., & Senn, H. (2006). Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4281–4290.
Ding, N., Kwak, L., Ballew, S. H., Jaar, B., Hoogeveen, R. C., Ballantyne, C. M., Sharrett, A. R., Folsom, A. R., Heiss, G., & Salameh, M. (2018). Traditional and nontraditional glycemic markers and risk of peripheral artery disease: The atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Atherosclerosis, 274, 86–93.
Drake, K. J., Sidorov, V. Y., McGuinness, O. P., Wasserman, D. H., & Wikswo, J. P. (2012). Amino acids as metabolic substrates during cardiac ischemia. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 237, 1369–1378.
England, J. D., Ferguson, M. A., Hiatt, W. R., & Regensteiner, J. G. (1995). Progression of neuropathy in peripheral arterial disease. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, 18, 380–387.
Finegold, D., Lattimer, S. A., Nolle, S., Bernstein, M., & Greene, D. A. (1983). Polyol pathway activity and myo-inositol metabolism: A suggested relationship in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes, 32, 988–992.
Fitridge, R., Pena, G., & Mills, J. L. (2020). The patient presenting with chronic limb-threatening ischaemia. Does diabetes influence presentation, limb outcomes and survival? Diabetes/metabolism Research and Reviews, 36, e3242.
Guerranti, R., Pagani, R., Neri, S., Errico, S., Leoncini, R., & Marinello, E. (2001). Inhibition and regulation of rat liver L-threonine dehydrogenase by different fatty acids and their derivatives. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 1568, 45–52.
Huang, C. C., McDermott, M. M., Liu, K., Kuo, C. H., Wang, S. Y., Tao, H., & Tseng, Y. J. (2013). Plasma metabolomic profiles predict near-term death among individuals with lower extremity peripheral arterial disease. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 58(989–996), e1.
Ismaeel, A., Franco, M. E., Lavado, R., Papoutsi, E., Casale, G. P., Fuglestad, M., Mietus, C. J., Haynatzki, G. R., Smith, R. S., & Bohannon, W. T. (2019). Altered metabolomic profile in patients with peripheral artery disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8, 1463.
Jiang, Y., Tang, J., Xie, M., Wen, Z., Qiao, S., & Hou, S. (2017). Threonine supplementation reduces dietary protein and improves lipid metabolism in Pekin ducks. British Poultry Science, 58, 687–693.
Julia, P. L., Kofsky, E. R., Buckberg, G. D., Young, H. H., & Bugyi, H. I. (1990). Studies of myocardial protection in the immature heart: I. Enhanced tolerance of immature versus adult myocardium to global ischemia with reference to metabolic differences. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 100, 879–887.
Koutakis, P., Ismaeel, A., Farmer, P., Purcell, S., Smith, R. S., Eidson, J. L., & Bohannon, W. T. (2018). Oxidative stress and antioxidant treatment in patients with peripheral artery disease. Physiological Reports, 6, e13650.
Kuhn, M. (2008). Building predictive models in R using the caret package. Journal of Statistical Software, 28, 1–26.
Kumakura, H., Kanai, H., Araki, Y., Hojo, Y., Kasama, S., Sumino, H., Iwasaki, T., Takayama, Y., Ichikawa, S., & Fujita, K. (2013). Differences in brain natriuretic peptide and other factors between Japanese peripheral arterial disease patients with critical limb ischemia and intermittent claudication. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis, 20, 18929.
Kurano, M., Tsukamoto, K., Sakai, E., & Yatomi, Y. (2022). Differences in the distribution of ceramides and sphingosine among lipoprotein and lipoprotein-depleted fractions in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis, 29, 63249.
Mani-Varnosfaderani, A., Kanginejad, A., Gilany, K., & Valadkhani, A. (2016). Estimating complicated baselines in analytical signals using the iterative training of Bayesian regularized artificial neural networks. Analytica Chimica Acta, 940, 56–64.
Mudge, G., Mills, R., Taegtmeyer, H., Gorlin, R., & Lesch, M. (1976). Alterations of myocardial amino acid metabolism in chronic ischemic heart disease. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 58, 1185–1192.
Murabito, J. M., Evans, J. C., Nieto, K., Larson, M. G., Levy, D., & Wilson, P. W. (2002). Prevalence and clinical correlates of peripheral arterial disease in the Framingham offspring study. American Heart Journal, 143, 961–965.
Nehler, M. R., Duval, S., Diao, L., Annex, B. H., Hiatt, W. R., Rogers, K., Zakharyan, A., & Hirsch, A. T. (2014). Epidemiology of peripheral arterial disease and critical limb ischemia in an insured national population. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 60, 686-695.e2.
Omori, K., Katakami, N., Arakawa, S., Yamamoto, Y., Ninomiya, H., Takahara, M., Matsuoka, T. A., Tsugawa, H., Furuno, M., & Bamba, T. (2020). Identification of plasma inositol and Indoxyl sulfate as novel biomarker candidates for atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes—findings from Metabolome analysis using GC/MS. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis, 2020, 52506.
Ottosson, F., Smith, E., Melander, O., & Fernandez, C. (2018). Altered asparagine and glutamate homeostasis precede coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 103, 3060–3069.
Peterson, J. W., Boldogh, I., Popov, V. L., Saini, S. S., & Chopra, A. K. (1998). Anti-inflammatory and antisecretory potential of histidine in Salmonella-challenged mouse small intestine. Laboratory Investigation: A Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology, 78, 523–534.
Pfeifer, M. A., & Schumer, M. P. (1995). Clinical trials of diabetic neuropathy: Past, present, and future. Diabetes, 44, 1355–1361.
Premalatha, G., Ravikumar, R., Sanjay, R., Deepa, R., & Mohan, V. (2002). Comparison of colour duplex ultrasound and ankle-brachial pressure index measurements in peripheral vascular disease in type 2 diabetic patients with foot infections. The Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 50, 1240–1244.
Reddivari, L., Sapkota, B. R., Rudraraju, A., Liang, Y., Aston, C., Sidorov, E., Vanamala, J. K., & Sanghera, D. K. (2017). Metabolite signatures of diabetes with cardiovascular disease: A pilot investigation. Metabolomics, 13, 1–13.
Saigusa, D., Matsukawa, N., Hishinuma, E., & Koshiba, S. (2021). Identification of biomarkers to diagnose diseases and find adverse drug reactions by metabolomics. Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 37, 100373.
Saoi, M., Percival, M., Nemr, C., Li, A., Gibala, M., & Britz-McKibbin, P. (2019). Characterization of the human skeletal muscle metabolome for elucidating the mechanisms of bicarbonate ingestion on strenuous interval exercise. Analytical Chemistry, 91, 4709–4718.
Schwartz, R. G., Barrett, E. J., Francis, C. K., Jacob, R., & Zaret, B. L. (1985). Regulation of myocardial amino acid balance in the conscious dog. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 75, 1204–1211.
Servo, C. (1977). Accumulation of myoinositol in plasma and red cells of diabetic patients. Acta Medica Scandinavica, 201, 59–62.
Sidawy, A. P., & Perler, B. A. (2022). Rutherford’s vascular surgery and endovascular therapy, 2-volume, set E-book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Tabas, I. (1999). Nonoxidative modifications of lipoproteins in atherogenesis. Annual Review of Nutrition, 19, 123–139.
Takahara, M., Iida, O., Soga, Y., Kodama, A., & Azuma, N. (2015). Absence of preceding intermittent claudication and its associated clinical freatures in patients with critical limb ischemia. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis, 22, 28217.
Tomasi, G., Van Den Berg, F., & Andersson, C. (2004). Correlation optimized warping and dynamic time warping as preprocessing methods for chromatographic data. Journal of Chemometrics: A Journal of the Chemometrics Society, 18, 231–241.
Wallimann, T., Tokarska-Schlattner, M., & Schlattner, U. (2011). The creatine kinase system and pleiotropic effects of creatine. Amino Acids, 40, 1271–1296.
Wang, F. H., Liu, J., Deng, Q. J., Qi, Y., Wang, M., Wang, Y., Zhang, X. G., & Zhao, D. (2019). Association between plasma essential amino acids and atherogenic lipid profile in a Chinese population: A cross-sectional study. Atherosclerosis, 286, 7–13.
Ying, A. F., Tang, T. Y., Jin, A., Chong, T. T., Hausenloy, D. J., & Koh, W. P. (2022). Diabetes and other vascular risk factors in association with the risk of lower extremity amputation in chronic limb-threatening ischemia: A prospective cohort study. Cardiovascular Diabetology, 21, 1–9.
Funding
This work was supported by the Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (Grant Number 12323).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NSA, NHM, and MEK conceived and designed the research. NHM, MRB, and SMT conducted experiments. AMV and NSA analyzed data and interpreted results. AMV and NSA wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki 1964, and the study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee (IR.IUMS.REC.1397.738) at Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Informed consent
All participants in this study signed informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Safari-Alighiarloo, N., Mani-Varnosfaderani, A., Madani, N.H. et al. Potential metabolic biomarkers of critical limb ischemia in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolomics 19, 66 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-02029-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-02029-3