Abstract
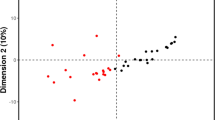
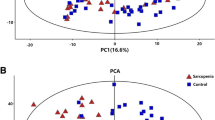
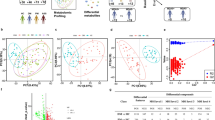
Sarcoidosis is a systemic granulomatous disease of unknown etiology. Granulomatous inflammation in sarcoidosis may affect multiple organs, including the lungs, skin, CNS, and the eyes, leading to severe morbidity and mortality. The underlying mechanisms for sustained inflammation in sarcoidosis are unknown. We hypothesized that metabolic changes play a critical role in perpetuation of inflammation in sarcoidosis. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based untargeted metabolomic analysis was used to identify circulating molecules in serum to discriminate sarcoidosis patients from healthy controls. Principal component analyses (PCA) were performed to identify different metabolic markers and explore the changes of associated biochemical pathways. Using Chenomx 7.6 NMR Suite software, we identified and quantified metabolites responsible for such separation in the PCA models. Quantitative analysis showed that the levels of metabolites, such as 3-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, carnitine, cystine, homocysteine, pyruvate, and trimethylamine N-oxide were significantly increased in sarcoidosis patients. Interestingly, succinate, a major intermediate metabolite involved in the tricyclic acid cycle was significantly decreased in sarcoidosis patients. Application of integrative pathway analyses identified deregulation of butanoate, ketone bodies, citric cycle metabolisms, and transmethylation. This may be used for development of new drugs or nutritional modification.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASCT2:
-
Amino acid transporter 2
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CD4+ :
-
Cluster of differentiation 4
- D2O:
-
Deuterium oxide
- DSS:
-
Disodium-2,2-dimethyl 2-silapentane-5-sulphonate
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- NOESY:
-
Nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy
- PC:
-
Principal component
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PLS-DA:
-
Partial least square discriminant analysis
- SIMCA:
-
Soft independent modeling of class analogy
- TCA:
-
Tricarboxylic acid cycle
- Th1:
-
T-helper type 1
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- TMA:
-
Trimethylamine
- TMAO:
-
Trimethylamine N-oxide
- VIP:
-
Variable importance in the projection
References
Altermann, E., & Klaenhammer, T. R. (2005). PathwayVoyager: Pathway mapping using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database. BMC Genomics, 6, 60.
Barallobre-Barreiro, J., Chung, Y. L., & Mayr, M. (2013). Proteomics and metabolomics for mechanistic insights and biomarker discovery in cardiovascular disease. Revista Española de Cardiología (English Edition), 66, 657–661.
Bhuiyan, A. K., Jackson, S., Turnbull, D. M., Aynsley-Green, A., Leonard, J. V., & Bartlett, K. (1992). The measurement of carnitine and acyl-carnitines: application to the investigation of patients with suspected inherited disorders of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Clinica Chimica Acta, 207, 185–204.
Chen, G., Li, D., Jin, Y., Zhang, W., Teng, L., Bunt, C., & Wen, J. (2014). Deformable liposomes by reverse-phase evaporation method for an enhanced skin delivery of (+)-catechin. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 40, 260–265.
Dawson, H., Collins, G., Pyle, R., Deep-Dixit, V., & Taub, D. D. (2004). The immunoregulatory effects of homocysteine and its intermediates on T-lymphocyte function. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, 125, 107–110.
Defeo, E. M., Wu, C. L., McDougal, W. S., & Cheng, L. L. (2011). A decade in prostate cancer: from NMR to metabolomics. Nature Reviews Urology, 8, 301–311.
De-Souza, D. A., & Greene, L. J. (2005). Intestinal permeability and systemic infections in critically ill patients: effect of glutamine. Critical Care Medicine, 33, 1125–1135.
Donohoe, D. R., Collins, L. B., Wali, A., Bigler, R., Sun, W., & Bultman, S. J. (2012). The Warburg effect dictates the mechanism of butyrate-mediated histone acetylation and cell proliferation. Molecular Cell, 48, 612–626.
Duncan, S. H., Holtrop, G., Lobley, G. E., Calder, A. G., Stewart, C. S., & Flint, H. J. (2004). Contribution of acetate to butyrate formation by human faecal bacteria. British Journal of Nutrition, 91, 915–923.
Furusawa, Y., Obata, Y., Fukuda, S., Endo, T. A., Nakato, G., Takahashi, D., et al. (2013). Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature, 504, 446–450.
Gregory, J. F., I. I. I., Park, Y., Lamers, Y., Bandyopadhyay, N., Chi, Y. Y., Lee, K., et al. (2013). Metabolomic analysis reveals extended metabolic consequences of marginal vitamin B-6 deficiency in healthy human subjects. PLoS ONE, 8, e63544.
Hunninghake, G. W., Costabel, U., Ando, M., Baughman, R., Cordier, J. F., du Bois, R., et al. (1999). ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/World Association of Sarcoidosis and other Granulomatous Disorders. Sarcoidosis, Vasculitis, and Diffuse Lung Diseases, 16, 149–173.
Iannuzzi, M. C., Rybicki, B. A., & Teirstein, A. S. (2007). Sarcoidosis. New England Journal of Medicine, 357, 2153–2165.
Ivanisevic, J., Kotur-Stevuljevic, J., Stefanovic, A., Jelic-Ivanovic, Z., Spasic, S., Videnovic-Ivanov, J., et al. (2012). Dyslipidemia and oxidative stress in sarcoidosis patients. Clinical Biochemistry, 45, 677–682.
Jayavelu, N. D., & Bar, N. S. (2014). Metabolomic studies of human gastric cancer: Review. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 20, 8092–8101.
Koeth, R. A., Wang, Z., Levison, B. S., Buffa, J. A., Org, E., Sheehy, B. T., et al. (2013). Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nature Medicine, 19, 576–585.
Louis, P., Duncan, S. H., McCrae, S. I., Millar, J., Jackson, M. S., & Flint, H. J. (2004). Restricted distribution of the butyrate kinase pathway among butyrate-producing bacteria from the human colon. Journal of Bacteriology, 186, 2099–2106.
Lower, E. E., Malhotra, A., Sudurlescu, V., & Baughman, R. P. (2013). Sarcoidosis, fatigue, and sleep apnea. Chest, 144, 1976–1977.
Lu, J., Xie, G., Jia, W., & Jia, W. (2013). Metabolomics in human type 2 diabetes research. Frontiers of Medicine, 7, 4–13.
McClelland, G. B. (2004). Fat to the fire: The regulation of lipid oxidation with exercise and environmental stress. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 139, 443–460.
Nakaya, M., Xiao, Y., Zhou, X., Chang, J. H., Chang, M., Cheng, X., et al. (2014). Inflammatory T cell responses rely on amino acid transporter ASCT2 facilitation of glutamine uptake and mTORC1 kinase activation. Immunity, 40, 692–705.
Nelson, D. L., & Cox, M. M. (2012). Lehninger principles of biochemistry. New York: W.H. Freeman.
Ni, Y., Su, M., Lin, J., Wang, X., Qiu, Y., Zhao, A., et al. (2008). Metabolic profiling reveals disorder of amino acid metabolism in four brain regions from a rat model of chronic unpredictable mild stress. FEBS Letters, 582, 2627–2636.
Noga, M. J., Dane, A., Shi, S., Attali, A., van Aken, H., Suidgeest, E., et al. (2012). Metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid reveals changes in the central nervous system metabolism in a rat model of multiple sclerosis. Metabolomics, 8, 253–263.
O’Neill, L. A., & Hardie, D. G. (2013). Metabolism of inflammation limited by AMPK and pseudo-starvation. Nature, 493, 346–355.
O’Sullivan, D., van der Windt, G. J., Huang, S. C., Curtis, J. D., Chang, C. H., Buck, M. D., et al. (2014). Memory CD8(+) T cells use cell-intrinsic lipolysis to support the metabolic programming necessary for development. Immunity, 41, 75–88.
Pearce, E. L., Poffenberger, M. C., Chang, C. H., & Jones, R. G. (2013). Fueling immunity: Insights into metabolism and lymphocyte function. Science, 342, 1242454.
Rastogi, R., Du, W., Ju, D., Pirockinaite, G., Liu, Y., Nunez, G., & Samavati, L. (2011). Dysregulation of p38 and MKP-1 in response to NOD1/TLR4 stimulation in sarcoid bronchoalveolar cells. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 183, 500–510.
Redlich, C. A., Tarlo, S. M., Hankinson, J. L., Townsend, M. C., Eschenbacher, W. L., von Essen, S. G., et al. (2014). Official American Thoracic Society technical standards: Spirometry in the occupational setting. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 189, 983–993.
Sinclair, L. V., Rolf, J., Emslie, E., Shi, Y. B., Taylor, P. M., & Cantrell, D. A. (2013). Control of amino-acid transport by antigen receptors coordinates the metabolic reprogramming essential for T cell differentiation. Nature Immunology, 14, 500–508.
Singleton, K. D., Beckey, V. E., & Wischmeyer, P. E. (2005a). Glutamine prevents activation of NF-kappaB and stress kinase pathways, attenuates inflammatory cytokine release, and prevents acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) following sepsis. Shock, 24, 583–589.
Singleton, K. D., Serkova, N., Banerjee, A., Meng, X., Gamboni-Robertson, F., & Wischmeyer, P. E. (2005b). Glutamine attenuates endotoxin-induced lung metabolic dysfunction: Potential role of enhanced heat shock protein 70. Nutrition, 21, 214–223.
Steuer, R., Kurths, J., Fiehn, O., & Weckwerth, W. (2003). Interpreting correlations in metabolomic networks. Biochemical Society Transactions, 31, 1476–1478.
Tannahill, G. M., Curtis, A. M., Adamik, J., Palsson-Mcdermott, E. M., McGettrick, A. F., Goel, G., et al. (2013). Succinate is an inflammatory signal that induces IL-1beta through HIF-1alpha. Nature, 496, 238–242.
Trujillo, E., Davis, C., & Milner, J. (2006). Nutrigenomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and the practice of dietetics. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 106, 403–413.
Ubhi, B. K., Riley, J. H., Shaw, P. A., Lomas, D. A., Tal-Singer, R., Macnee, W., et al. (2012). Metabolic profiling detects biomarkers of protein degradation in COPD patients. European Respiratory Journal, 40, 345–355.
Urbanczyk-Wochniak, E., Luedemann, A., Kopka, J., Selbig, J., Roessner-Tunali, U., Willmitzer, L., & Fernie, A. R. (2003). Parallel analysis of transcript and metabolic profiles: A new approach in systems biology. EMBO Reports, 4, 989–993.
Vekic, J., Zeljkovic, A., Jelic-Ivanovic, Z., Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V., Spasic, S., Videnovic-Ivanov, J., et al. (2013). Distribution of low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein subclasses in patients with sarcoidosis. Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, 137, 1780–1787.
Wang, R., Dillon, C. P., Shi, L. Z., Milasta, S., Carter, R., Finkelstein, D., et al. (2011a). The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity, 35, 871–882.
Wang, Z., Klipfell, E., Bennett, B. J., Koeth, R., Levison, B. S., Dugar, B., et al. (2011b). Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature, 472, 57–63.
Wang, H., Tso, V. K., Slupsky, C. M., & Fedorak, R. N. (2010). Metabolomics and detection of colorectal cancer in humans: A systematic review. Future Oncology, 6, 1395–1406.
Weinberg, S. E., & Chandel, N. S. (2014). Futility sustains memory T cells. Immunity, 41, 1–3.
Wellen, K. E., Hatzivassiliou, G., Sachdeva, U. M., Bui, T. V., Cross, J. R., & Thompson, C. B. (2009). ATP-citrate lyase links cellular metabolism to histone acetylation. Science, 324, 1076–1080.
Wen, H., Yang, H. J., An, Y. J., Kim, J. M., Lee, D. H., Jin, X., et al. (2013). Enhanced phase II detoxification contributes to beneficial effects of dietary restriction as revealed by multi-platform metabolomics studies. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 12, 575–586.
Wischmeyer, P. E., Jayakar, D., Williams, U., Singleton, K. D., Riehm, J., Bacha, E. A., et al. (2003). Single dose of glutamine enhances myocardial tissue metabolism, glutathione content, and improves myocardial function after ischemia-reperfusion injury. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 27, 396–403.
Xia, J., & Wishart, D. S. (2011a). Metabolomic data processing, analysis, and interpretation using MetaboAnalyst. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, Chapter 14, Unit 14 10.
Xia, J., & Wishart, D. S. (2011b). Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nature Protocols, 6, 743–760.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Medicine and the Center for Molecular Medicine and Genetics, Wayne State University School of Medicine (LS) and National Institute of Health R01HL113508 (LS).
Author contribution
AG contributed to the study design, participated in sample collection, conducted the analysis, interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. SVG provided access and contributed to multivariate data analysis, as well as assisted with the preparation of the manuscript. CB participated in data interpretation and preparation of the manuscript. LS designed the study, and participated in all areas of the research, data analysis and writing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
AG, SVG, CB, and LS declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geamanu, A., Gupta, S.V., Bauerfeld, C. et al. Metabolomics connects aberrant bioenergetic, transmethylation, and gut microbiota in sarcoidosis. Metabolomics 12, 35 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0932-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0932-2