Abstract
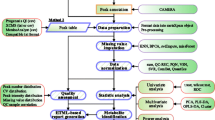
MetaboNexus is an interactive metabolomics data analysis platform that integrates pre-processing of raw peak data with in-depth statistical analysis and metabolite identity search. It is designed to work as a desktop application hence uploading large files to web servers is not required. This could speed up the data analysis process because server queries or queues are avoided, while ensuring security of confidential clinical data on a local computer. With MetaboNexus, users can progressively start from data pre-processing, multi- and univariate analysis to metabolite identity search of significant molecular features, thereby seamlessly integrating critical steps for metabolite biomarker discovery. Data exploration can be first performed using principal components analysis, while prediction and variable importance can be calculated using partial least squares-discriminant analysis and Random Forest. After identifying putative features from multi- and univariate analyses (e.g. t test, ANOVA, Mann–Whitney U test and Kruskal–Wallis test), users can seamlessly determine the molecular identity of these putative features. To assist users in data interpretation, MetaboNexus also automatically generates graphical outputs, such as score plots, diagnostic plots, boxplots, receiver operating characteristic plots and heatmaps. The metabolite search function will match the mass spectrometric peak data to three major metabolite repositories, namely HMDB, MassBank and METLIN, using a comprehensive range of molecular adducts. Biological pathways can also be searched within MetaboNexus. MetaboNexus is available with installation guide and tutorial at http://www.sph.nus.edu.sg/index.php/research-services/research-centres/ceohr/metabonexus, and is meant for the Windows Operating System, XP and onwards (preferably on 64-bit). In summary, MetaboNexus is a desktop-based platform that seamlessly integrates the entire data analytical workflow and further provides the putative identities of mass spectrometric data peaks by matching them to databases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, S. G. (2003). The central role of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves in evaluating tests for the early detection of cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 95, 511–515.
Breiman, L. E. O. (2002). Random forests. R News, 2(3), 5–32.
Chen, F., Koufaty, D. A. & Zhang, X. (2009) Understanding intrinsic characteristics and system implications of flash memory based solid state drives. Proceedings of the eleventh international joint conference on Measurement and modeling of computer systems, 181–192.
Cortes, C., & Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 20, 273–297.
Dr Hochmuth Scientific Consulting, http://massfinder.com/wiki/MassFinder_4. Accessed 26 Feb 2014.
Frolkis, A., et al. (2010). SMPDB: The Small Molecule Pathway Database. Nucleic Acids Research, 38, D480–D487.
Horai, H., et al. (2010). MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 45, 703–714.
Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., & Tanabe, M. (2012). KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, D109–D114.
Katajamaa, M., Miettinen, J., & Orešič, M. (2006). MZmine: Toolbox for processing and visualization of mass spectrometry based molecular profile data. Bioinformatics, 22, 634–636.
Kessler, N., et al. (2013). MeltDB 2.0—advances of the metabolomics software system. Bioinformatics, 29, 2452–2459.
Liaw, A., & Wiener, M. (2002). Classification and regression by randomForest. R News, 2, 18–22.
Luedemann, A., Strassburg, K., Erban, A., & Kopka, J. (2008). TagFinder for the quantitative analysis of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS)-based metabolite profiling experiments. Bioinformatics, 24, 732–737.
Patti, G. J., Tautenhahn, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2012). Meta-analysis of untargeted metabolomic data from multiple profiling experiments. Nature Protocols, 7, 508–516.
Saghatelian, A., Trauger, S. A., Want, E. J., Hawkins, E. G., Siuzdak, G., & Cravatt, B. F. (2004) Assignment of endogenous substrates to enzymes by global metabolite profiling. Biochemistry, 43, 14332–14339.
Tautenhahn, R., Böttcher, C., & Neumann, S. (2008). Highly sensitive feature detection for high resolution LC/MS. BMC Bioinformatics, 9, 504.
Tautenhahn, R., Patti, G. J., Rinehart, D., & Siuzdak, G. (2012a). XCMS Online: A web-based platform to process untargeted metabolomic data. Analytical Chemistry, 84, 5035–5039.
Tautenhahn, R., et al. (2012b). An accelerated workflow for untargeted metabolomics using the METLIN database. Nature Biotechnology, 30, 826–828.
Team, R. D. C. (2005). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Found Statistics Computing.
Tomita, M., Kawakami, M., Soga, T., Robert, M., & Sugimoto, M. (2012). Bioinformatics tools for mass spectroscopy-based metabolomic data processing and analysis. Current Bioinformatics, 7, 96–108.
Wishart, D. S., et al. (2009). HMDB: A knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, D603–D610.
Wold, S., Esbensen, K., & Geladi, P. (1987). Principal component analysis. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2, 37–52.
Wold, S., & Sjostrom, M. (2001). PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 58, 109–130.
Xia, J., Mandal, R., Sinelnikov, I. V., Broadhurst, D., & Wishart, D. S. (2012). MetaboAnalyst 2.0—a comprehensive server for metabolomic data analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, W127–W133.
Acknowledgments
SM Huang was supported by an NUS Research Scholarship. We thank the Singapore National Medical Research Council (NMRC 1242/2009 WBS R-608-000-034-213) and the NUS Environmental Research Institute (NERI) for the support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, SM., Toh, W., Benke, P.I. et al. MetaboNexus: an interactive platform for integrated metabolomics analysis. Metabolomics 10, 1084–1093 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0648-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0648-8