Abstract
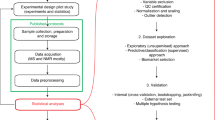
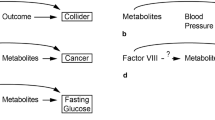
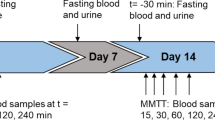
The key goal of metabolomic studies is to identify relevant individual biomarkers or composite metabolic patterns associated with particular disease status or patho-physiological conditions. There are currently very few approaches to evaluate the variability of metabolomic data in terms of characteristics of individuals or aspects pertaining to technical processing. To address this issue, a method was developed to identify and quantify the contribution of relevant sources of variation in metabolomic data prior to investigation of etiological hypotheses. The Principal Component Partial R-square (PC-PR2) method combines features of principal component and of multivariable linear regression analyses. Within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and nutrition (EPIC), metabolic profiles were determined by 1H NMR analysis on 807 serum samples originating from a nested liver cancer case–control study. PC-PR2 was used to quantify the variability of metabolomic profiles in terms of study subjects age, sex, body mass index, country of origin, smoking status, diabetes and fasting status, as well as factors related to sample processing. PC-PR2 enables the evaluation of important sources of variations in metabolomic studies within large-scale epidemiological investigations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athersuch, T. J. (2012). The role of metabolomics in characterizing the human exposome. Bioanalysis, 4, 2207–2212.
Beckonert, O., Keun, H. C., Ebbels, T. M. D., Bundy, J. G., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., et al. (2007). Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nature Protocols, 2, 2692–2703.
Bernini, P., Bertini, I., Luchinat, C., Nincheri, P., Staderini, S., & Turano, P. (2011). Standard operating procedures for pre-analytical handling of blood and urine for metabolomic studies and biobanks. Journal of Biomolecular NMR, 49, 231–243.
Blaise, B. J., Giacomotto, J., Elena, B., Dumas, M. E., Toullhoat, P., Segalat, L., et al. (2007). Metabotyping of Caenorhabditis elegans reveals latent phenotypes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 19808–19812.
Bollard, M. E., Stanley, E. G., Lindon, J. C., Nicholson, J. K., & Holmes, E. (2005). NMR-based metabonomic approaches for evaluating physiological influences on biofluid composition. NMR in Biomedicine, 18, 143–162.
de Haan, J. R., Wehrens, R., Bauerschmidt, S., Piek, E., van Schaik, R. C., & Buydens, L. M. (2007). Interpretation of ANOVA models for microarray data using PCA. Bioinformatics, 23, 184–190.
Dumas, M. E., Maibaum, E. C., Teague, C., Ueshima, H., Zhou, B. F., Lindon, J. C., et al. (2006). Assessment of analytical reproducibility of H-1 NMR spectroscopy based metabonomics for large-scale epidemiological research: the INTERMAP study. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 2199–2208.
Ebbels, T. M. D., Keun, H. C., Beckonert, O. P., Bollard, M. E., Lindon, J. C., Holmes, E., et al. (2007). Prediction and classification of drug toxicity using probabilistic modeling of temporal metabolic data: The consortium on metabonomic toxicology screening approach. Journal of Proteome Research, 6, 4407–4422.
Ellis, J. K., Athersuch, T. J., Thomas, L. D., Teichert, F., Perez-Trujillo, M., Svendsen, C., et al. (2012). Metabolic profiling detects early effects of environmental and lifestyle exposure to cadmium in a human population. BMC Medicine, 10, 61.
Eriksson, L., Antti, H., Gottfries, J., Holmes, E., Johansson, E., Lindgren, F., et al. (2004). Using chemometrics for navigating in the large data sets of genomics, proteomics, and metabonomics (gpm). Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 380, 419–429.
Fages, A., Pontoizeau, C., Jobard, E., Lévy, P., Bartosch, B., & Elena-Herrmann, B. (2013). Batch profiling calibration for robust NMR metabolomic data analysis. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 405, 8819–8827.
Fallani, M., Young, D., Scott, J., Norin, E., Amarri, S., Adam, R., et al. (2010). Intestinal microbiota of 6-week-old infants across Europe: geographic influence beyond delivery mode, breast-feeding, and antibiotics. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 51, 77–84.
Floegel, A., Stefan, N., Yu, Z., Muhlenbruch, K., Drogan, D., Joost, H. G., et al. (2012). Identification of serum metabolites associated with risk of type 2 diabetes using a targeted metabolomic approach. Diabetes, 62, 639–648.
Fonville, J. M., Richards, S. E., Barton, R. H., Boulange, C. L., Ebbels, T. M. D., Nicholson, J. K., et al. (2010). The evolution of partial least squares models and related chemometric approaches in metabonomics and metabolic phenotyping. Journal of Chemometrics, 24, 636–649.
Goldstein, H. (1995). Multilevel statistical models (2nd ed.). Kendall’s Library of Statistics, 3. Edward Arnold: London.
Griffin, J. L., Williams, H. J., Sang, E., Clarke, K., Rae, C., & Nicholson, J. K. (2001). Metabolic profiling of genetic disorders: A multitissue H-1 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic and pattern recognition study into dystrophic tissue. Analytical Biochemistry, 293, 16–21.
Holmes, E., Loo, R. L., Stamler, J., Bictash, M., Yap, I. K. S., Chan, Q., et al. (2008). Human metabolic phenotype diversity and its association with diet and blood pressure. Nature, 453, 396-U50.
Holmes, E., Nicholson, J. K., Nicholls, A. W., Lindon, J. C., Connor, S. C., Polley, S., et al. (1998). The identification of novel biomarkers of renal toxicity using automatic data reduction techniques and PCA of proton NMR spectra of urine. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 44, 245–255.
Kleinbaum, D., Kupper, L., & Muller, K. (1988). Applied regression analysis and other multivariable method. Belmont, CA: Duxbury Press.
Kochhar, S., Jacobs, D. M., Ramadan, Z., Berruex, F., Fuerhoz, A., & Fay, L. B. (2006). Probing gender-specific metabolism differences in humans by nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomics. Analytical Biochemistry, 352, 274–281.
Krzanowski, W. J. (2000). Principles of multivariate analysis: A user’s perpective (2nd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Lawton, K. A., Berger, A., Mitchell, M., Milgram, K. E., Evans, A. M., Guo, L. N., et al. (2008). Analysis of the adult human plasma metabolome. Pharmacogenomics, 9, 383–397.
Li, J., Bushel, P. R., Chu, T. M., & Wolfinger, R. D. (2009). Principal variance components analysis: Estimating batch effects in microarray gene expression data. In A. Scherer (Ed.), Batch effects and noise in microarray experiments: Sources and solutions. Chichester: Wiley.
Li, M., Wang, B. H., Zhang, M. H., Rantalainen, M., Wang, S. Y., Zhou, H. K., et al. (2008). Symbiotic gut microbes modulate human metabolic phenotypes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 2117–2122.
Lindon, J. C., Holmes, E., & Nicholson, J. K. (2001). Pattern recognition methods and applications in biomedical magnetic resonance. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, 39, 1–40.
Mitchell, B. L., Yasui, Y., Li, C. I., Fitzpatrick, A. L., & Lampe, P. D. (2005). Impact of freeze-thaw cycles and storage time on plasma samples used in mass spectrometry based biomarker discovery projects. Cancer Informatics, 1, 98–104.
Mueller, S., Saunier, K., Hanisch, C., Norin, E., Alm, L., Midtvedt, T., et al. (2006). Differences in fecal microbiota in different European study populations in relation to age, gender, and country: A cross-sectional study. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 1027–1033.
Nicholson, J. K., Holmes, E., & Elliott, P. (2008). The metabolome-wide association study: A new look at human disease risk factors. Journal of Proteome Research, 7, 3637–3638.
Nicholson, J. K., Holmes, E., & Wilson, I. D. (2005). Gut microorganisms, mammalian metabolism and personalized health care. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 3, 431–438.
Nicholson, G., Rantalainen, M., Maher, A. D., Li, J. V., Malmodin, D., Ahmadi, K. R., et al. (2011). Human metabolic profiles are stably controlled by genetic and environmental variation. Molecular Systems Biology, 7, 525.
Paltiel, L., Ronningen, K. S., Meltzer, H. M., Baker, S. V., & Hoppin, J. A. (2008). Evaluation of freeze-thaw cycles on stored plasma in the biobank of the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study. Cell Preservation Technology, 6, 223–229.
Psihogios, N. G., Gazi, I. F., Elisaf, M. S., Seferiadis, K. I., & Bairaktari, E. T. (2008). Gender-related and age-related urinalysis of healthy subjects by NMR-based metabonomics. NMR in Biomedicine, 21, 195–207.
R Development Core Team. (2005). R: A language and environment for statistical computing, reference index version 2.2.1. Vienna: R Development Core Team.
Riboli, E., Hunt, K. J., Slimani, N., Ferrari, P., Norat, T., Fahey, M., et al. (2002). European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC): study populations and data collection. Public Health Nutrition, 5, 1113–1124.
Sabeti, P. C., Varilly, P., Fry, B., Lohmueller, J., Hostetter, E., Cotsapas, C., et al. (2007). Genome-wide detection and characterization of positive selection in human populations. Nature, 449, 913-U12.
Sampson, J. N., Boca, S. M., Shu, X. O., Stolzenberg-Solomon, R. Z., Matthews, C. E., Hsing, A. W., et al. (2013). Metabolomics in epidemiology: sources of variability in metabolite measurements and implications. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention, 22, 631–640.
Slupsky, C. M., Rankin, K. N., Wagner, J., Fu, H., Chang, D., Weljie, A. M., et al. (2007). Investigations of the effects of gender, diurnal variation, and age in human urinary metabolomic profiles. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 6995–7004.
Smilde, A. K., Jansen, J. J., Hoefsloot, H. C., Lamers, R. J., van der Greef, J., & Timmerman, M. E. (2005). ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis (ASCA): A new tool for analyzing designed metabolomics data. Bioinformatics, 21, 3043–3048.
Spratlin, J. L., Serkova, N. J., & Eckhardt, S. G. (2009). Clinical applications of metabolomics in oncology: A review. Clinical Cancer Research, 15, 431–440.
Sreekumar, A., Poisson, L. M., Rajendiran, T. M., Khan, A. P., Cao, Q., Yu, J. D., et al. (2009). Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature, 457, 910–914.
Teahan, O., Gamble, S., Holmes, E., Waxman, J., Nicholson, J. K., Bevan, C., et al. (2006). Impact of analytical bias in metabonomic studies of human blood serum and plasma. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4307–4318.
Trichopoulos, D., Bamia, C., Lagiou, P., Fedirko, V., Trepo, E., Jenab, M., et al. (2011). Hepatocellular carcinoma risk factors and disease burden in a European cohort: A Nested Case-Control Study. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 103, 1686–1695.
Tuck, M. K., Chan, D. W., Chia, D., Godwin, A. K., Grizzle, W. E., Krueger, K. E., et al. (2009). Standard operating procedures for serum and plasma collection: Early detection research network consensus statement standard operating procedure integration working group. Journal of Proteome Research, 8, 113–117.
van den Berg, R. A., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Westerhuis, J. A., Smilde, A. K., & van der Werf, M. J. (2006). Centering, scaling, and transformations: improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genomics, 7, 142.
Verbeke, G., & Lesaffre, E. (1997). The effect of misspecifying the random-effects distribution in linear mixed models for longitudinal data. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 23, 541–556.
Yu, Z., Zhai, G., Singmann, P., He, Y., Xu, T., Prehn, C., et al. (2012). Human serum metabolic profiles are age dependent. Aging Cell, 11, 960–967.
Zerzucha, P., Boguszewska, D., Zagdanska, B., & Walczak, B. (2012). Non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance in the proteomic response of potato to drought stress. Analytica Chimica Acta, 719, 1–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Jianying Li (National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, Research Triangle Park, USA) and Dr. Martyn Plummer (IARC, Lyon, France) for helpful discussions on PVCA analysis. We thank Dr. Augustin Scalbert and Pr. Lyndon Emsley for fruitful comments to the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Anne Fages and Pietro Ferrari contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fages, A., Ferrari, P., Monni, S. et al. Investigating sources of variability in metabolomic data in the EPIC study: the Principal Component Partial R-square (PC-PR2) method. Metabolomics 10, 1074–1083 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0647-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0647-9