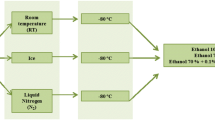
Abstract
Many metabolites in plant are highly polar and ionic. Their analysis using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry can be problematic. Therefore a capillary electrophoresis–mass spectrometry (CE–MS) method with charge-driven separation characteristic was developed to investigate polar metabolites in tobacco. To obtain as many features as possible, extraction of polar metabolites was optimized by the design of experiments and evaluated by univariate statistics. Method validation was carried out to evaluate the analytical characteristics including calibration curve, precision, sample stability and extraction reproducibility. The developed method was successfully applied in studying 30 tobacco leaves obtained from Yunnan and Guizhou provinces in China. A total of 154 polar metabolites were identified based on available database. Multivariate pattern recognition clearly revealed the metabolic differences between the two geographic areas and 43 significantly different metabolites were defined by the non-parametric hypothesis test (Mann–Whitney U test) and false discovery rate. Some key metabolites involved in photosynthesis such as ribulose 1,5-disphosphate, fructose 1,6-diphosphate, glycine, betaine, GABA and serine were found to be susceptible to environmental conditions. This study shows that the metabolic profiling based on CE–MS can clearly discriminate tobacco leaves of different geographical origins and understand the relationship between plant metabolites and their geographical origins.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alan, M. K., & Frank, J. T. (2000). Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and plant responses to stress. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 19(6), 479–509.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300.
Benjamini, Y., & Yekutieli, D. (2001). The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. The Annals of Statistics, 29(4), 1165–1188.
Bligh, E. G., & Dyer, W. J. (1959). A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology, 37(8), 911–917.
Bouché, N., & Fromm, H. (2004). GABA in plants: Just a metabolite? Trends in Plant Science, 9(3), 110–115.
Cazier, J. B., Kaisaki, P. J., Argoud, K., Blaise, B. J., Veselkov, K., Ebbels, T. M., et al. (2011). Untargeted metabolome quantitative trait locus mapping associates variation in urine glycerate to mutant glycerate kinase. Journal of Proteome Research, 11(2), 631–642.
Cruz, J. A., Emery, C., Wüst, M., Kramer, D. M., & Lange, B. M. (2008). Metabolite profiling of Calvin cycle intermediates by HPLC-MS using mixed-mode stationary phases. The Plant Journal: For Cell and Molecular Biology, 55(6), 1047–1060.
De Vos, R. C., Moco, S., Lommen, A., Keurentjes, J. J., Bino, R. J., & Hall, R. D. (2007). Untargeted large-scale plant metabolomics using liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols, 2(4), 778–791.
Decaestecker, T. N., Lambert, W. E., Van Peteghem, C. H., Deforce, D., & Van Bocxlaer, J. F. (2004). Optimization of solid-phase extraction for a liquid chromatographic–tandem mass spectrometric general unknown screening procedure by means of computational techniques. Journal of Chromatography A, 1056(1–2), 57–65.
Ferreira, S. L., Bruns, R. E., da Silva, E. G., Dos Santos, W. N., Quintella, C. M., David, J. M., et al. (2007). Statistical designs and response surface techniques for the optimization of chromatographic systems. Journal of Chromatography A, 1158(1–2), 2–14.
Fiehn, O., Kopka, J., Trethewey, R. N., & Willmitzer, L. (2000a). Identification of uncommon plant metabolites based on calculation of elemental compositions using gas chromatography and quadrupole mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 72(15), 3573–3580.
Fiehn, O., Kopka, J., Dörmann, P., Altmann, T., Trethewey, R. N., & Willmitzer, L. (2000b). Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nature Biotechnology, 18(11), 1157–1161.
Foyer, C. H., Parry, M., & Noctor, G. (2003). Markers and signals associated with nitrogen assimilation in higher plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 54(382), 585–593.
Fraser, K., Harrison, S. J., Lane, G. A., Otte, D. E., Hemar, Y., Quek, S. Y., et al. (2012). Non-targeted analysis of tea by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and high resolution mass spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 134(3), 1616–1623.
Gao, W., Yang, H., Qi, L. W., Liu, E. H., Ren, M. T., Yan, Y. T., et al. (2012). Unbiased metabolite profiling by liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multivariate data analysis for herbal authentication: Classification of seven Lonicera species flower buds. Journal of Chromatography A, 1245, 109–116.
Garcia, L. M. Z., de Oliveira, T. F., Soares, P. K., Bruns, R. E., & Scarminio, I. S. (2010). Statistical mixture design—principal component determination of synergic solvent interactions for natural product extractions. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 103(1), 1–7.
Gullberg, J., Jonsson, P., Nordström, A., Sjöström, M., & Moritz, T. (2004). Design of experiments: An efficient strategy to identify factors influencing extraction and derivatization of Arabidopsis thaliana samples in metabolomic studies with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anaytical Biochemistry, 331(2), 283–295.
Hasunuma, T., Harada, K., Miyazawa, S., Kondo, A., Fukusaki, E., & Miyake, C. (2010). Metabolic turnover analysis by a combination of in vivo 13C-labelling from 13CO2 and metabolic profiling with CE–MS/MS reveals rate-limiting steps of the C3 photosynthetic pathway in Nicotiana tabacum leaves. Journal of Experimental Botany, 61(4), 1041–1051.
Hirayama, A., Kami, K., Suqimoto, M., Suqawara, M., Toki, N., Onozuka, H., et al. (2009). Quantitative metabolome profiling of colon and stomach cancer microenvironment by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Cancer Research, 69(11), 4918–4925.
Holmström, K. O., Somersalo, S., Mandal, A., Palva, T. E., & Welin, B. (2000). Improved tolerance to salinity and low temperature in transgenic tobacco producing glycine betaine. Journal of Experimental Botany, 51(343), 177–185.
Krapp, A., Quick, W. P., & Stitt, M. (1991). Ribulose—1,5-bisphosphate carbo xylase-oxygenase, other Calvin-cycle enzymes, and chlorophyll decrease when glucose is supplied to mature spinach leaves via the transpiration stream. Planta, 186(1), 58–69.
Leffingwell, J. C. (1999). Leaf chemistry: Basic chemical constituents of tobacco leaf and differences among tobacco type. In D. L. Davis & M. T. Nielsen (Eds.), Tobacco: Production, chemistry and technology (pp. 304–312). Oxford: Blackwell Science.
Levandi, T., Leon, C., Kaljurand, M., Garcia-Cañas, V., & Cifuentes, A. (2008). Capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry for comparative metabolomics of transgenic versus conventional maize. Analytical Chemistry, 80(16), 6329–6335.
Li, X., Xu, Z., Lu, X., Yang, X., Yin, P., Kong, H., et al. (2009). Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry for metabonomics: Biomarker discovery for diabetes mellitus. Analytica Chimica Acta, 633(2), 257–262.
Li, Y., Pang, T., Li, Y., Wang, X., Li, Q., Lu, X., et al. (2011). Gas chromatography-mass spectrometric method for metabolic profiling of tobacco leaves. Journal of Separation Science, 34(12), 1447–1454.
Masson, P., Alves, A. C., Ebbels, T. M., Nicholson, J. K., & Want, E. J. (2010). Optimization and evaluation of metabolite extraction protocols for untargeted metabolic profiling of liver samples by UPLC-MS. Analytical Chemistry, 82(18), 7779–7786.
Pang, T., Bai, C., Xu, Y., Xu, G., Yuan, Z., Su, Y., et al. (2006). Determination of sugars in tobacco leaf by HPLC with evaporative light scattering detection. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies, 29(9), 1281–1289.
Ramautar, R., Somsen, G. W., & de Jong, G. J. (2009). CE–MS in metabolomics. Electrophoresis, 30(1), 276–291.
Ramautar, R., Somsen, G. W., & de Jong, G. J. (2013). CE–MS for metabolomics: Developments and applications in the period 2010–2012. Electrophoresis, 34(1), 86–98.
Riedelsheimer, C., Lisec, J., Czedik-Eysenberg, A., Sulpice, R., Flis, A., Grieder, C., et al. (2012). Genome-wide association mapping of leaf metabolic profiles for dissecting complex traits in maize. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(23), 8872–8877.
Rodgers, J. L., & Nicewander, W. A. (1988). Thirteen ways to look at the correlation coefficient. The American Statistician, 42(1), 59–66.
Rodríguez, R., Mañes, J., & Picó, Y. (2003). Off-Line solid-phase microextraction and capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry to determine acidic pesticides in fruits. Analytical Chemistry, 75(3), 452–459.
Saric, J., Want, E. J., Duthaler, U., Lewis, M., Keiser, J., Shockcor, J. P., et al. (2012). Systematic evaluation of extraction methods for multiplatform-based metabotyping: application to the fasciola hepatica metabolome. Analytical Chemistry, 84(16), 6963–6972.
Sato, S., Soga, T., Nishioka, T., & Tomita, M. (2004). Simultaneous determination of the main metabolites in rice leaves using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry and capillary electrophoresis diode array detection. The Plant Jounal, 40(1), 151–163.
Scherling, C., Roscher, C., Giavalisco, P., Schulze, E.-D., & Weckwerth, W. (2010). Metabolomics unravel contrasting effects of biodiversity on the performance of individual plant species. PLoS ONE,. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012569.
Shulaev, V., Cortes, D., Miller, G., & Mittler, R. (2008). Metabolomics for plant stress response. Physiologia Plantarum, 132(2), 199–208.
Soga, T. (2000). Amino acid analysis by capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 72(6), 1236–1241.
Soga, T., Ueno, Y., Naraoka, H., Ohashi, Y., Tomita, M., & Nishioka, T. (2002). Simultaneous determination of anionic intermediates for metabolic pathways by capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 74(10), 2233–2239.
Soga, T., Ishikawa, T., Igarashi, S., Sugawara, K., Kakazu, Y., & Tomita, M. (2007). Analysis of nucleotides by pressure-assisted capillary electrophoresis–mass spectrometry using silanol mask technique. Journal of Chromatography A, 1159(1–2), 125–133.
Soga, T., Igarashi, K., Ito, C., Mizobuchi, K., Zimmermann, H. P., & Tomita, M. (2009). Metabolomic profiling of anionic metabolites by capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 81(15), 6165–6174.
Spagou, K., Wilson, I. D., Masson, P., Theodoridis, G., Raikos, N., Coen, M., et al. (2010). HILIC-UPLC-MS for exploratory urinary metabolic profiling in toxicological studies. Analytical Chemistry, 83(1), 382–390.
Stedman, R. L. (1968). Chemical composition of tobacco and tobacco smoke. Chemical Reviews, 68(2), 153–207.
Steuer, R., Morgenthal, K., Weckwerth, W., & Selbig, J. (2007). A gentle guide to the analysis of metabolomic data. In W. Weckwerth (Ed.), Metabolomics: Methods and protocols (pp. 105–126). New York: Springer.
Tawaraya, K., Horie, R., Saito, A., Shinano, T., Wagatsuma, T., Saito, K., et al. (2013). Metabolite profiling of shoot extracts, root extracts, and root exudates of rice plant under phosphorus deficiency. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 36(7), 1138–1159.
Tikunov, Y., Lommen, A., de Vos, C. H., Verhoeven, H. A., Bino, R. J., Hall, R. D., et al. (2005). A novel approach for nontargeted data analysis for metabolomics. Large-scale profiling of tomato fruit volatiles. Plant Physiology, 139(3), 1125–1137.
Vuckovic, D., Risticevic, S., & Pawliszyn, J. (2011). In vivo solid-phase microextraction in metabolomics: Opportunities for the direct investigation of biological systems. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 50(25), 5618–5628.
Xiang, G., Yang, H., Yang, L., Zhang, X., Cao, Q., & Miao, M. (2010). Multivariate statistical analysis of tobacco of different origin, grade and variety according to polyphenols and organic acids. Microchemical Journal, 95(2), 198–206.
Yuliana, N. D., Khatib, A., Verpoorte, R., & Choi, Y. H. (2011). Comprehensive extraction method integrated with NMR metabolomics: A new bioactivity screening method for plants, adenosine A1 receptor binding compounds in orthosiphon stamineus benth. Analytical Chemistry, 83(17), 6902–6906.
Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Du, Y., Chen, S., & Tang, H. (2011). Dynamic metabonomic responses of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants to salt stress. Journal of Proteome Research, 10(4), 1904–1914.
Zhang, L., Wang, X., Guo, J., Xia, Q., Zhao, G., Zhou, H., et al. (2013). Metabolic profiling of Chinese tobacco leaf of different geographical origins by GC-MS. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(11), 2597–2605.
Zhou, T., Xiao, X., & Li, G. (2012). Hybrid field-assisted solid–liquid–solid dispersive extraction for the determination of organochlorine pesticides in tobacco with gas chromatography. Analytical Chemistry, 84(1), 420–427.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Hu, C., Zeng, J. et al. Study of polar metabolites in tobacco from different geographical origins by using capillary electrophoresis–mass spectrometry. Metabolomics 10, 805–815 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0631-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0631-4