Abstract
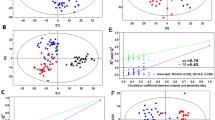
The clinical exploration of urinary metabonomic analysis on discriminating between the top-two-incidence urological cancers, bladder and kidney cancers (BC and KC), is still virgin land. In this study, we discovered and evaluated the clinical utility of holistic metabonomic profiling and current single biomarker methods, and ultimately suggested a potential screening test for BC and KC. Urine metabonomic profiling for 19 BC patients, 25 KC patients, and 24 healthy controls was carried out using an LC–MS based platform, which utilized both reversed phase chromatography and hydrophilic interaction chromatography. The holistic method that refers to orthogonal partial least-squares-discriminant analysis based on all qualified profile data, successfully classified BC, KC and healthy control groups, showing 100 % sensitivity and specificity. Taurine, hippuric acid, phenylacetylglutamine and carnitine species contributed most to the BC and KC discrimination. The predictive power of each above metabolite is evaluated using receiver operator characteristic technique. Hippuric acid was found 10-fold decrease in concentration relative healthy controls, and performed the best as a biomarker for BC diagnosis, with its sensitivity and specificity of 78.9 and 86.5 %, respectively. Carnitine C10:3 was found 1.5-fold decrease, and reached 84.0 % of sensitivity and 60.5 % of specificity for KC diagnosis. In view of both sensitivity and specificity, the holistic method is more accurate for detecting BC and KC, than current single metabonomic biomarker methods, and it could be advocated as a prescreen to other forms of more invasive or uncomfortable screening. Moreover, this approach also demonstrates attractive performance in diagnosis of early stage (ES) BC and KC patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BC:
-
Bladder cancer
- KC:
-
Kidney cancer
- RPLC:
-
Reversed phase liquid chromatography
- HILIC:
-
Hydrophilic interaction chromatography
- TNM:
-
Tumor nodes metastasis
- ESI:
-
Electrospray ionization
- TIC:
-
Total ion chromatogram
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- OPLS-DA:
-
Orthogonal partial least-squares-discriminant analysis
- ES:
-
Early stage
- HA:
-
Hippuric acid
- PAGN:
-
Phenylacetylglutamine
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- QC:
-
Quality control
- VIP:
-
Variable importance in the project
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
References
An, Z. L., Chen, Y. H., Zhang, R. P., Song, Y. M., Sun, J. H., He, J. M., et al. (2010). Integrated ionization approach for RRLC–MS/MS-based metabonomics: finding potential biomarkers for lung cancer. Journal of Proteome Research, 9(8), 4071–4081. doi:10.1021/pr100265g.
Beckonert, O., Monnerjahn, J., Bonk, U., & Leibfritz, D. (2003). Visualizing metabolic changes in breast-cancer tissue using 1H-NMR spectroscopy and self-organizing maps. NMR in Biomedicine, 16(1), 1–11. doi:10.1002/nbm.797.
Bruce, S. J., Jonsson, P., Antti, H., Cloarec, O., Trygg, J., Marklund, S. L., et al. (2008). Evaluation of a protocol for metabolic profiling studies on human blood plasma by combined ultra-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry: from extraction to data analysis. Analytical Biochemistry, 372(2), 237–249. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2007.09.037.
Bylesjö, M., Rantalainen, M., Cloarec, O., Nicholson, J. K., Holmes, E., & Trygg, J. (2006). OPLS discriminant analysis: combining the strengths of PLS-DA and SIMCA classification. Journal of Chemometrics, 20(8–10), 341–351. doi:10.1002/cem.1006.
Catchpole, G., Platzer, A., Weikert, C., Kempkensteffen, C., Johannsen, M., Krause, H., et al. (2011). Metabolic profiling reveals key metabolic features of renal cell carcinoma. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 15(1), 109–118. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00939.x.
Chen, J., Wang, W., Lv, S., Yin, P., Zhao, X., Lu, X., et al. (2009). Metabonomics study of liver cancer based on ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry with HILIC and RPLC separations. Analytica Chimica Acta, 650(1), 3–9. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2009.03.039.
Claudino, W. M., Quattrone, A., Biganzoli, L., Pestrin, M., Bertini, I., & Di Leo, A. (2007). Metabolomics: Available results, current research projects in breast cancer, and future applications. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 25(19), 2840–2846. doi:10.1200/Jco.2006.09.7550.
Clayton, T. A., Lindon, J. C., Cloarec, O., Antti, H., Charuel, C., Hanton, G., et al. (2006). Pharmaco-metabonomic phenotyping and personalized drug treatment. Nature, 440(7087), 1073–1077. doi:10.1038/nature04648.
Cohen, H. T., & McGovern, F. J. (2005). Renal-cell carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine, 353(23), 2477–2490. doi:10.1056/NEJMra043172.
Cubbon, S., Antonio, C., Wilson, J., & Thomas-Oates, J. (2010). Metabolomic applications of HILIC–LC–MS. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 29(5), 671–684. doi:10.1002/Mas.20252.
Cubbon, S., Bradbury, T., Wilson, J., & Thomas-Oates, J. (2007). Hydrophilic interaction chromatography for mass spectrometric metabonomic studies of urine. Analytical Chemistry, 79(23), 8911–8918. doi:10.1021/ac071008v.
Evan, G. I., & Vousden, K. H. (2001). Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature, 411(6835), 342–348. doi:10.1038/35077213.
Gamagedara, S., Shi, H., & Ma, Y. (2012). Quantitative determination of taurine and related biomarkers in urine by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 402(2), 763–770. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5491-4.
Gika, H. G., Theodoridis, G. A., & Wilson, I. D. (2008). Hydrophilic interaction and reversed-phase ultra-performance liquid chromatography TOF-MS for metabonomic analysis of Zucker rat urine. Journal of Separation Science, 31(9), 1598–1608. doi:10.1002/jssc.200700644.
Gika, H. G., Theodoridis, G. A., Wingate, J. E., & Wilson, I. D. (2007). Within-day reproducibility of an HPLC–MS-based method for metabonomic analysis: Application to human urine. Journal of Proteome Research, 6(8), 3291–3303. doi:10.1021/Pr070183p.
Greene, F. L., Page, D. L., Fleming, I. D., Fritz, A., Balch, C. M., Haller, D. G., et al. (Eds.). (2002). AJCC cancer staging manual (6th ed.). New York: Springer.
Issaq, H. J., Nativ, O., Waybright, T., Luke, B., Veenstra, T. D., Issaq, E. J., et al. (2008). Detection of bladder cancer in human urine by metabolomic profiling using high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. The Journal of Urology, 179(6), 2422–2426. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2008.01.084.
Kim, K., Aronov, P., Zakharkin, S. O., Anderson, D., Perroud, B., Thompson, I. M., et al. (2009). Urine metabolomics analysis for kidney cancer detection and biomarker discovery. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 8(3), 558–570. doi:10.1074/mcp.M800165-MCP200.
Kind, T., & Fiehn, O. (2010). Advances in structure elucidation of small molecules using mass spectrometry. Bioanalytical Reviews, 2(1), 23–60. doi:10.1007/s12566-010-0015-9.
Kind, T., Tolstikov, V., Fiehn, O., & Weiss, R. H. (2007). A comprehensive urinary metabolomic approach for identifying kidney cancer. Analytical Biochemistry, 363(2), 185–195. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2007.01.028.
Kutikov, A., Egleston, B. L., Wong, Y.-N., & Uzzo, R. G. (2010). Evaluating overall survival and competing risks of death in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma using a comprehensive nomogram. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 28(2), 311–317. doi:10.1200/jco.2009.22.4816.
Lin, L., Hang, W., Huang, Z. Z., Gao, Y., Yan, X. M., & Xing, J. C. (2011). LC–MS based serum metabonomic analysis for renal cell carcinoma diagnosis, staging, and biomarker discovery. Journal of Proteome Research, 10(3), 1396–1405. doi:10.1021/pr101161u.
Linehan, W. M., Walther, M. M., & Zbar, B. (2003). The genetic basis of cancer of the kidney. Journal of Urology, 170(6), 2163–2172. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000096060.92397.ed.
McClinton, S., Moffat, L. E., Horrobin, D. F., & Manku, M. S. (1991). Abnormalities of essential fatty acid distribution in the plasma phospholipids of patients with bladder cancer. British Journal of Cancer, 63(2), 314–316.
Michael, A., & Pandha, H. S. (2003). Renal-cell carcinoma: tumour markers, T-cell epitopes, and potential for new therapies. Lancet Oncology, 4(4), 215–223. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(03)01044-1.
Mitra, A. P., & Cote, R. J. (2010). Molecular screening for bladder cancer: progress and potential. Nature Reviews Urology, 7(1), 11–20. doi:10.1038/nrurol.2009.236.
Mohammed, S. I., & Rahman, M. (2008). Proteomics and genomics of urinary bladder cancer. Proteomics Clinical Application, 2(9), 1194–1207. doi:0.1002/prca.200780089.
Moreno, A., Rey, M., Montane, J. M., Alonso, J., & Arús, C. (1993). 1H NMR spectroscopy of colon tumors and normal mucosal biopsies; elevated taurine levels and reduced polyethyleneglycol absorption in tumors may have diagnostic significance. NMR in Biomedicine, 6(2), 111–118. doi:10.1002/nbm.1940060202.
Morrissey, J. J., London, A. N., Luo, J. Q., & Kharasch, E. D. (2010). Urinary biomarkers for the early diagnosis of kidney cancer. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 85(5), 413–421. doi:10.4065/mcp.20090709.
Nicholson, J. K., Lindon, J. C., & Holmes, E. (1999). ‘Metabonomics’: understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica, 29(11), 1181–1189. doi:10.1080/004982599238047.
Ott, O. J., Rödel, C., Weiss, C., Wittlinger, M., St. Krause, F., Dunst, J., et al. (2009). Radiochemotherapy for bladder cancer. Clinical Oncology, 21(7), 557–565. doi:10.1016/j.clon.2009.05.005.
Paik, M. J., Kim, J. W., Lee, G., Moon, S. M., Park, M. J., Hong, S. K., et al. (2010). Metabolomic screening and star pattern recognition by urinary amino acid profile analysis from bladder cancer patients. Metabolomics, 6(2), 202–206. doi:10.1007/s11306-010-0199-6.
Pasikanti, K. K., Esuvaranathan, K., Ho, P. C., Mahendran, R., Kamaraj, R., Wu, Q. H., et al. (2010). Noninvasive urinary metabonomic diagnosis of human bladder cancer. Journal of Proteome Research, 9(6), 2988–2995. doi:10.1021/Pr901173v.
Poynard, T., Halfon, P., Castera, L., Munteanu, M., Imbert-Bismut, F., Ratziu, V., et al. (2007). Standardization of ROC curve areas for diagnostic evaluation of liver fibrosis markers based on prevalences of fibrosis stages. Clinical Chemistry, 53(9), 1615–1622. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2007.085795.
Qin, F., Zhao, Y. Y., Sawyer, M. B., & Li, X. F. (2008). Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination of estrogen conjugates in human urine. Analytical Chemistry, 80(9), 3404–3411. doi:10.1021/ac702613k.
Quackenbush, J. (2006). Microarray analysis and tumor classification. New England Journal of Medicine, 354(23), 2463–2472. doi:10.1056/NEJMra042342.
Siegel, R., Ward, E., Brawley, O., & Jemal, A. (2011). Cancer statistics, 2011. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 61(4), 212–236. doi:10.3322/caac.20121.
Slupsky, C. M., Steed, H., Wells, T. H., Dabbs, K., Schepansky, A., Capstick, V., et al. (2010). Urine metabolite analysis offers potential early diagnosis of ovarian and breast cancers. Clinical Cancer Research, 16(23), 5835–5841. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-10-1434.
Spratlin, J. L., Serkova, N. J., & Eckhardt, S. G. (2009). Clinical applications of metabolomics in oncology: A review. Clinical Cancer Research, 15(2), 431–440. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-08-1059.
Srivastavaa, S., Roy, R., Singh, S., Kumar, P., Dalela, D., Sankhwarc, S. N., et al. (2010). Taurine—a possible fingerprint biomarker in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: A pilot study by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Cancer Biomarkers, 6(1), 11–20. doi:10.3233/CBM-2009-0115.
Theodoridis, G., Gika, H. G., & Wilson, I. D. (2011). Mass spectrometry-based holistic analytical approaches for metabolite profiling in systems biology studies. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 30(5), 884–906. doi:10.1002/mas.20306.
Umetrics, A. (2005). User’s guide to SIMCA-P, SIMCA-P+ version 12.0.
Wiklund, S., Johansson, E., Sjostrom, L., Mellerowicz, E. J., Edlund, U., Shockcor, J. P., et al. (2008). Visualization of GC/TOF-MS-based metabolomics data for identification of biochemically interesting compounds using OPLS class models. Analytical Chemistry, 80(1), 115–122. doi:10.1021/Ac0713510.
Yang, Q., Shi, X., Wang, Y., Wang, W., He, H., Lu, X., et al. (2010). Urinary metabonomic study of lung cancer by a fully automatic hyphenated hydrophilic interaction/RPLC–MS system. Journal of Separation Science, 33(10), 1495–1503. doi:10.1002/jssc.200900798.
Yin, P., Wan, D., Zhao, C., Chen, J., Zhao, X., Wang, W., et al. (2009). A metabonomic study of hepatitis B-induced liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma by using RP-LC and HILIC coupled with mass spectrometry. Molecular BioSystems, 5(8), 868–876. doi:10.1039/b820224a.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Department of Science & Technology of Fujian Province (2009D023), and the Medical Center Construction Foundation of Xiamen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Chen, Y., Hang, W. et al. Holistic metabonomic profiling of urine affords potential early diagnosis for bladder and kidney cancers. Metabolomics 9, 119–129 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0433-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0433-5