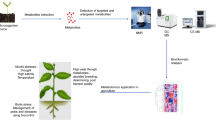
Abstract
The emerge of metabolomics within functional genomics has provided a new dimension in the study of biological systems. In regards to the study of agroecosystems, metabolomics enables monitoring of metabolic changes in association with biotic or abiotic agents such as agrochemicals. Focusing on crop protection chemicals, a great effort has been given towards the development of crop protection agents safer for consumers and the environment and more efficient than the existing ones. Within this framework, metabolomics has so far been a valuable tool for high-throughput screening of bioactive substances in order to discover those with high selectivity, unique modes-of-action, and acceptable eco-toxicological/toxicological profiles. Here, applications of metabolomics in the investigation of the modes-of-action and ecotoxicological–toxicological risk assessment of bioactive compounds, mining of biological systems for the discovery of bioactive metabolites, and the risk assessment of genetic modified crops are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, M. D., Celniker, S. E., Holt, R. A., et al. (2000). The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science, 287, 2185–2195.
Aharoni, A., de Vos, C. H. R., Verhoeven, H. A., et al. (2002). Non-targeted metabolome analysis by use of Fourier transform ion cyclotron mass spectrometry. OMICS, 6, 217–234.
Akiyama, K., Chikayama, E., Yuasa, H., et al. (2008). PRIMe: A Web site that assembles tools for metabolomics and transcriptomics. In Silico Biology, 8, 339–345.
Aliferis, K. A., & Chrysayi-Tokousbalides, M. (2006). Metabonomic strategy for the investigation of the mode of action of the phytotoxin (5S, 8R, 13S, 16R)-(−)-pyrenophorol using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance fingerprinting. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 54, 1687–1692.
Aliferis, K. A., & Jabaji, S. (2009). Metabolic fingerprinting of the plant-pathogen pathosystem, Rhizoctonia solani-Solanum tuberosum using Fourier transform mass spectrometry (FT-ICR/MS). In Proc. XIV congress on Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions (MPMI) (p. 32).
Aliferis, K. A., & Jabaji, S. (2010). 1H NMR and GC–MS metabolic fingerprinting of developmental stages of Rhizoctonia solani sclerotia. Metabolomics, 6, 96–108.
Aliferis, K. A., Materzok, S., Paziotou, G., & Chrysayi-Tokousbalides, M. (2009). Lemna minor L. as a model organism for ecotoxicological studies performing 1H NMR fingerprinting. Chemosphere, 76, 967–973.
Allen, J., Davey, H. M., Broadhurst, D., Rowland, J. J., Oliver, S. G., & Kell, D. B. (2004). Discrimination of modes of action of antifungal substances by use of metabolic footprinting. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 6157–6165.
Allen, J. K., Davey, H. M., Broadhurst, D., et al. (2003). High-throughput characterisation of yeast mutants for functional genomics using metabolic footprinting. Nature Biotechnology, 21, 692–696.
Allwood, J. W., Ellis, D. I., & Goodacre, R. (2008). Metabolomic technologies and their application to the study of plants and plant-host interactions. Physiologia Plantarum, 132, 117–135.
Allwood, J. W., Erban, A., de Koning, S., et al. (2009). Inter-laboratory reproducibility of fast gas chromatography-electron impact-time of flight mass spectrometry (GC-EI-TOF/MS) based plant metabolomics. Metabolomics, 5, 479–496.
Allwood, J. W., & Goodacre, R. (2010). HPLC instrumentation applied in plant metabolomic analyses. Phytochemical Analysis, 21, 33–47.
Aranibar, N., Singh, B. J., Stockton, G. W., & Ott, K. H. (2001). Automated mode of action detection by metabolic profiling. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 286, 150–155.
Atherton, H. J., Bailey, N. J., Zhang, W., et al. (2006). A combined 1H-NMR spectroscopy-and mass spectrometry-based metabolomic study of the PPAR-α null mutant mouse defines profound systemic changes in metabolism linked to the metabolic syndrome. Physiological Genomics, 27, 178–186.
Balba, H. (2007). Review of strobilurin fungicide chemicals. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, 42, 441–451.
Baran, R., Kochi, H., Saito, N., et al. (2006). MathDAMP: A package for differential analysis of metabolite profiles. BMC Bioinformatics, 7, 530.
Bednarek, P., Schneider, B., Svatos, A., Oldham, N. J., & Hahlbrock, K. (2005). Structural complexity, differential response to infection and tissue specificity of indolic and phenylpropanoid secondary metabolism in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiology, 138, 1058–1070.
Betz, F. S., Hammond, B. G., & Fuchs, R. L. (2000). Safety and advantages of Bacillus thuringiensis-protected plants to control insect pests. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 32, 156–173.
Bezemer, T. M., & van Dam, N. M. (2005). Linking aboveground and belowground interactions via induced plant defences. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 20, 617–624.
Biais, B., Allwood, J. W., Deborde, C., et al. (2009). 1H NMR, GC-EI-TOFMS, and data set correlation for fruit metabolomics: Application to spatial metabolite analysis in melon. Analytical Chemistry, 81, 2884–2894.
Böcker, S., Letzel, M. C., Lipták, Z., & Pervukhin, A. (2009). SIRIUS: Decomposing isotope patterns for metabolite identification. Bioinformatics, 25, 218–224.
Börner, J., Buchinger, S., & Schomburg, D. (2007). A high-throughput method for microbial metabolome analysis using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Analytical Biochemistry, 367, 143–151.
Breitling, R., Ritchie, S., Goodenowe, D., Stewart, M. L., & Barrett, M. P. (2006). Ab initio prediction of metabolic networks using Fourier transform mass spectrometry data. Metabolomics, 2, 155–164.
Broeckling, C. D., Reddy, I. R., Duran, A. L., Zhao, X., & Sumner, L. W. (2006). MET-IDEA: Data extraction tool for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4334–4341.
Bundy, J. G., Davey, M. P., & Viant, M. R. (2009). Environmental metabolomics: A critical review and future perspectives. Metabolomics, 5, 3–21.
Bundy, J. G., Lenz, E. M., Bailey, N. J., et al. (2002). Metabonomic assessment of toxicity of 4-fluoroaniline,3,5-difluoroaniline and 2-fluoro-4-methylaniline to the earthworm Eisenia veneta (Rosa): Identification of new endogenous biomarkers. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 21, 1966–1972.
Carraro, S., Giordano, G., Reniero, F., Perilongo, G., & Baraldi, E. (2009). Metabolomics: A new frontier for research in pediatrics. Journal of Pediatrics, 154, 638–644.
Caspi, R., Foerster, H., Fulcher, C. A., et al. (2008). The MetaCyc Database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, D623–D631.
Castrillo, J. I., Hayes, A., Mohammed, S., Gaskell, S. J., & Oliver, S. G. (2003). An optimized protocol for metabolome analysis in yeast using direct infusion electrospray mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry, 62, 929–937.
Catchpole, G. S., Beckmann, M., Enot, D. P., et al. (2005). Hierarchical metabolomics demonstrates substantial compositional similarity between genetically modified and conventional potato crops. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 14458–14462.
Cevallos-Cevallos, J. M., Reyes-De-Corcuera, J. I., Etxeberria, E., Danyluk, M. D., & Rodrick, G. E. (2009). Metabolomic analysis in food science: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 20, 557–566.
Chen, J. H., Linstead, E., Swamidass, S. J., Wang, D., & Baldi, P. (2007). ChemDB update-full-text search and virtual chemical space. Bioinformatics, 23, 2348–2351.
Choi, H.-K., Choi, Y. H., Verberne, M., Lefeber, A. W. M., Erkelens, C., & Verpoorte, R. (2004a). Metabolic fingerprinting of wild type and transgenic tobacco plants by 1H NMR and multivariate analysis techniques. Phytochemistry, 65, 857–864.
Choi, H.-C., Kim, H. K., Linthorst, H. J. M., et al. (2006). NMR metabolomics to revisit the tobacco mosaic virus infection in Nicotiana tobacum leaves. Journal of Natural Products, 69, 742–748.
Choi, Y. H., Tapias, E. C., Kim, H. K., et al. (2004b). Metabolic discrimination of Catharanthus roseus leaves infected by phytoplasma using 1H-NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Plant Physiology, 135, 2398–2410.
Chong, W. P. K., Goh, L. T., Reddy, S. G., et al. (2009). Metabolomics profiling of extracellular metabolites in recombinant Chinese hamster ovary fed-batch culture. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 23, 3763–3771.
Copping, L. G., & Duke, S. O. (2007). Natural products that have been used commercially as crop protection agents—a review. Pest Management Science, 63, 524–554.
Cuadros-Inostroza, Á., Caldana, C., Redestig, H., et al. (2009). TargetSearch-a Bioconductor package for the efficient preprocessing of GC–MS metabolite profiling data. BMC Bioinformatics, 10, 428.
Cui, Q., Lewis, I. A., Hegeman, A. D., et al. (2008). Metabolite identification via the Madison Metabolomics Consortium Database. Nature Biotechnology, 26, 162–164.
Dai, X., Wang, G., Yang, D. S., et al. (2010). TrichOME: A comparative omics database for plant trichomes. Plant Physiology, 152, 44–54.
Dayan, F. E., Cantrell, C. L., & Duke, S. O. (2009). Natural products in crop protection. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 17, 4022–4034.
Defernez, M., & Colquhoun, I. J. (2003). Factors affecting the robustness of metabolite fingerprinting using 1H NMR spectra. Phytochemistry, 62, 1009–1017.
Degtyarenko, K., de Matos, P., Ennis, M., et al. (2008). ChEBI: A database and ontology for chemical entities of biological interest. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, D344–D350.
Demyttenaere, J. C. R., Moriña, R. M., & Sandra, P. (2003). Monitoring and fast detection of mycotoxins-producing fungi based on headspace solid phase microextraction and headspace sorptive extraction of the volatile metabolites. Journal of Chromatography A, 985, 127–135.
Desneux, N., Decourtye, A., & Delpuech, J.-M. (2007). The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annual Review of Entomology, 52, 81–106.
Dixon, R. A. (2001). Natural products and plant disease resistance. Nature, 411, 843–847.
Dona, A., & Arvanitogiannis, I. S. (2009). Health risks of genetically modified foods. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 49, 164–175.
Duke, S. O. (2005). Taking stock of herbicide-resistant crops ten years after introduction. Pest Management Science, 61, 211–218.
Dunn, W. B. (2008). Current trends and future requirements for the mass spectrometric investigation of microbial, mammalian and plant metabolomes. Physical Biology, 5, 1–24.
Duran, A. L., Yang, J., Wang, L., & Sumner, L. W. (2003). Metabolomics spectral formatting, alignment and conversion tools (MSFACTs). Bioinformatics, 19, 2283–2293.
EFSA. (2005). Guidance document of the scientific panel on genetically modified organisms for the risk assessment of genetically modified plants and derived food feed. EFSA Journal, 99, 1–94.
Ekman, D. R., Keun, H. C., Eads, C. D., et al. (2006). Metabolomic evaluation of rat liver and testis to characterize the toxicity of triazole fungicides. Metabolomics, 2, 63–73.
Eriksson, L., Johansson, E., Kettaneh-Wold, N., & Wold, S. (2001). Multi- and megavariate data analysis. Principles and applications. Umeå, Sweden: Umetrics Academy.
Fahy, E., Sud, M., Cotter, D., & Subramaniam, S. (2007). LIPID MAPS online tools for lipid research. Nucleic Acids Research, 35, W606–W612.
FAO. (1996). Joint FAO/WHO Expert consultation on biotechnology and food safety. Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations. ftp://ftp.fao.org/es/esn/food/biotechnology.pdf.
FAO/WHO. (2000). Safety aspects of genetically modified foods of plant origin. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Foods Derived from Biotechnology. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO. ftp://ftp.fao.org/es/esn/food/gmreport.pdf.
FAO/WHO. (2001). Evaluation of allergenicity of genetically modified foods. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Foods Derived from Biotechnology. http://www.fao.org/es/esn/allergygm.pdf.
Fardet, A., Llorach, R., & Martin, J.-F. (2008). Liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight (LC-QTOF)-based metabolomic approach reveals new metabolic effects of catechin in rats fed high-fat diets. Journal of Proteome Research, 7, 2388–2398.
Fiehn, O., Kopka, J., Dormann, P., Altmann, T., Trethewey, R. N., & Willmitzer, L. (2000). Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nature Biotechnology, 18, 1157–1161.
Fiehn, O., Wohlgemuth, G., & Scholz, M. (2005). Setup and annotation of metabolomic experiments by integrating biological and mass spectrometric metadata. In B. Ludäscher & L. Raschid (Eds.), Data integration in the life sciences-lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 3615, pp. 224–239). Heidelberg: Springer Berlin.
Forgue, P., Halouska, S., Werth, M., Xu, K., Harris, S., & Powers, R. (2006). NMR metabolic profiling of Aspergillus nidulans to monitor drug and protein activity. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 1916–1923.
Frankart, C., Eullaffroy, P., & Vernet, G. (2002). Photosynthetic responses of Lemna minor exposed to xenobiotics, copper, and their combinations. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 53, 439–445.
Gaida, A., & Neumann, S. (2007). MetHouse: Raw and preprocessed mass spectrometry data. Journal of Integrative Bioinformatics, 4, 56.
Gao, J., Tarcea, V. G., Karnovsky, A., et al. (2010). Metscape: A Cytoscape plug-in for visualizing and interpreting metabolomic data in the context of human metabolic networks. Bioinformatics, 26, 971–973.
Garcia-Villalba, R., Leon, C., Dinelli, G., et al. (2008). Comparative metabolomic study of transgenic versus conventional soybean using capillary electrophoresis-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1195, 164–173.
Guillarme, D., Schappler, J., Rudaz, S., & Veuthey, J.-L. (2010). Coupling ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 29, 15–27.
Günther, S., Kuhn, M., Dunkel, M., et al. (2008). SuperTarget and Matador: Resources for exploring drug-target relationships. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, D919–D922.
Guo, Q., Sidhu, J. K., & Ebbels, T. M. D. (2009). Validation of metabolomics for toxic mechanism of action screening with the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. Metabolomics, 5, 72–83.
Hall, R. D., Brouwer, I. D., & Fitzgerald, M. A. (2008). Plant metabolomics and its potential application for human nutrition. Physiologia Plantarum, 132, 162–175.
Holt, R. A., Subramanian, G. M., Halpern, A., et al. (2002). The genome sequence of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Science, 298, 129–149.
Horai, H., Arita, M., & Nishioka, T. (2008). Comparison of ESI-MS spectra in MassBank database. Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Engineering Informatics, 2, 853–857.
Hu, Q., Noll, R. J., Li, H., et al. (2005). The Orbitrap: A new mass spectrometer. Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Physics, 40, 430–443.
Huang, K., Xia, L., Zhang, Y., Ding, X., & Zahn, J. A. (2009). Recent advances in the biochemistry of spinosyns. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82, 13–23.
Hunter, P. (2009). Reading the metabolic fine print. The application of metabolomics to diagnostics, drug research and nutrition might be integral to improved health and personalized medicine. EMBO Reports, 10, 20–23.
Iijima, Y., Nakamura, Y., Ogata, Y., et al. (2008). Metabolite annotations based on the integration of mass spectral information. Plant Journal, 54, 949–962.
International Organization for Standardization. (2003). Water quality-Determination of toxic effect of water constituents and waste water to duckweed ( Lemna minor )-Duckweed growth inhibition test. ISO/DIS 20079 (draft). Geneva, Switzerland.
Jansen, J. J., Allwood, J. W., Marsden-Edwards, E., van der Putten, W. H., Goodacre, R., & van Dam, N. M. (2009). Metabolomic analysis of the interaction between plants and herbivores. Metabolomics, 5, 150–161.
Jeschke, P., & Nauen, R. (2008). Neonicotinoids-from zero to hero in insecticide chemistry. Pest Management Science, 64, 1084–1098.
Junker, B. H., Klukas, C., & Schreiber, F. (2006). VANTED: A system for advanced data analysis and visualization in the context of biological networks. BMC Bioinformatics, 7, 109.
Jutsum, A. R., Heaney, S. P., Bob, M., et al. (1998). Pesticide resistance: Assessment of risk and the development and implementation of effective management strategies. Pesticide Science, 54, 435–446.
Kaddurah-Daouk, R., & Krishnan, K. R. R. (2009). Metabolomics: A global biochemical approach to the study of central nervous system diseases. Neuropsychopharmacology Review, 34, 173–186.
Kaderbhai, N. N., Broadhurst, D. I., Ellis, D. I., Goodacre, R., & Kell, D. B. (2003). Functional genomics via metabolic footprinting: Monitoring metabolite secretion by Escherichia coli tryptophan metabolism mutants using FT-IR and direct injection electrospray mass spectrometry. Comparative and Functional Genomics, 4, 376–391.
Kamleh, M. A., Hobani, Y., Dow, J. A. T., & Watson, D. G. (2008). Metabolomic profiling of Drosophila using liquid chromatography Fourier transform mass spectrometry. FEBS Letter, 582, 2916–2922.
Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., et al. (2006). From genomics to chemical genomics: New developments in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Research, 34, D354–D357.
Karp, P. D., Ouzounis, C. A., Moore-Kochlacs, C., et al. (2005). Expansion of the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases to 160 genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, 6083–6089.
Kastanias, M. A., & Chrysayi-Tokousbalides, M. (2000). Herbicidal potential of pyrenophorol isolated from a Drechslera avenae pathotype. Pest Management Science, 56, 227–232.
Katajamaa, M., Miettinen, J., & Orešič, M. (2006). MZmine: Toolbox for processing and visualization of mass spectrometry based molecular profile data. Bioinformatics, 22, 634–636.
Katz, J. E., Dumlao, D. S., Clarke, S., & Hau, J. (2004). A new technique (COMSPARI) to facilitate the identification of minor compounds in complex mixtures by GC/MS and LC/MS: Tools for the visualization of matched datasets. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 15, 580–584.
Kell, D. B., Brown, M., Davey, H. M., Dunn, W. B., Spasic, I., & Oliver, S. G. (2005). Metabolic footprinting and systems biology: The medium is the message. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 3, 557–565.
Kenneke, J. F., Ekman, D. R., Mazur, C. S., et al. (2010). Integration of metabolomics and in vitro metabolism assays for investigating the stereoselective transformation of triadimefon in rainbow trout. Chirality, 22, 183–192.
Kerber, A., Laue, R., Meringer, M., & Varmuza, K. (2001). MOLGEN-MS: Evaluation of low resolution electron impact mass spectra with MS classification and exhaustive structure generation. Advanced Mass Spectrometry, 15, 939–940.
Keseler, I. M., Bonavides-Martinez, C., & Collado-Vides, J. (2009). EcoCyc: A comprehensive view of Escherichia coli biology. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, D464–D470.
Kim, K.-B., Kim, S. H., & Um, S. Y. (2009). Metabolomics approach to risk assessment: Methoxyclor exposure in rats. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, 72, 1352–1368.
Kind, T., & Fiehn, O. (2007). Seven Golden Rules for heuristic filtering of molecular formulas obtained by accurate mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinformatics, 8, 105.
Klukas, C., & Schreiber, F. (2007). Dynamic exploration and editing of KEGG pathway diagrams. Bioinformatics, 23, 344–350.
Kopka, J., Schauer, N., Krueger, S., et al. (2005). GMDB@CSB.DB: The Golm Metabolome database. Bioinformatics, 21, 1635–1638.
Kos, M., van Loon, J. J., Dicke, M., & Vet, L. E. (2009). Transgenic plants as vital components of integrated pest management. Trends in Biotechnology, 27, 621–627.
Koulman, A., Woffendin, G., Narayana, V. K., et al. (2009). High-resolution extracted ion chromatography, a new tool for metabolomics and lipidomics using a second-generation Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 23, 1411–1418.
Kralya, J. R., Holcomba, R. E., Guana, Q., & Henry, C. S. (2009). Review: Microfluidic applications in metabolomics and metabolic profiling. Analytica Chimica Acta, 653, 23–35.
Krishnan, P., Kruger, N. J., & Ratcliffe, R. G. (2005). Metabolite fingerprinting and profiling in plants using NMR. Journal of Experimental Botany, 56, 255–265.
Kuhn, M., Szklarczyk, D., Franceschini, A., et al. (2010). STITCH 2: An interaction network database for small molecules and proteins. Nucleic Acids Research, 38, D552–D556.
Lange, L., & Lopez, C. S. (1996). Micro-organisms as a source of biologically active secondary metabolites. In L. G. Copping (Ed.), Crop protection agents from nature. Natural products and analogues (pp. 1–26). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Le Gall, G., Colquhoun, I. J., Davis, A. L., Collins, G. J., & Verhoeyen, M. E. (2003). Metabolite profiling of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) using 1H NMR spectroscopy as a tool to detect potential unintended effects following a genetic modification. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 51, 2447–2456.
Lee, S. H., Woo, H. M., & Jung, B. H. (2007). Metabolomic approach to evaluate the toxicological effects of nonylphenol with rat urine. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 6102–6110.
Leiss, K. A., Choi, Y. H., Abdel-Farid, I. B., Verpoorte, R., & Klinkhamer, P. G. L. (2009). NMR metabolomics of thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis) resistance in senecio hybrids. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 35, 219–229.
Leon, C., Rodriguez-Meizoso, I., Lucio, M., et al. (2009). Metabolomics of transgenic maize combining Fourier transform-ion cyclotron resonance-mass spectrometry, capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry and pressurized liquid extraction. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216, 7314–7323.
Li, X., Schuler, M. A., & Berenbaum, M. R. (2007). Molecular mechanisms of metabolic resistance to synthetic and natural xenobiotics. Annual Review of Entomology, 52, 231–253.
Lindon, J. C. (2003). HPLC-NMR-MS: Past, present and future. Drug Discovery Today, 8, 1021–1022.
Lindon, J. C., Holmes, E., & Nicholson, J. K. (2007). Metabonomics in pharmaceutical R&D. FEBS Journal, 274, 1140–1151.
Lindon, J. C., Keun, H. C., Ebbels, T. M., Pearce, J. M., Holmes, E., & Nicholson, J. K. (2005). The consortium for metabonomic toxicology (COMET): Aims, activities and achievements. Pharmacogenomics, 6, 691–699.
Lindon, J. C., & Nicholson, J. K. (2008a). Spectroscopic and statistical techniques for information recovery in metabonomics and metabolomics. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 1, 45–69.
Lindon, J. C., & Nicholson, J. K. (2008b). Analytical technologies for metabonomics and metabolomics, and multi-omic information recovery. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 27, 194–204.
Lindon, J. C., Nicholson, J. K., & Wilson, I. D. (2000). Directly coupled HPLC-NMR and HPLC-NMR-MS in pharmaceutical research and development. Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 748, 233–258.
Linstrom, P. J., & Mallard, W. G. (2001). The NIST Chemistry WebBook: A chemical data resource on the internet. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 46, 1059–1063.
Liu, Y., Wen, J., Wang, Y., Li, Y., & Xu, W. (2010). Postulating modes of action of compounds with antimicrobial activities through metabolomics analysis. Chromatographia, 71, 253–258.
López-Gresa, M. P., Maltese, F., Bellés, J. M., et al. (2010). Metabolic response of tomato leaves upon different plant-pathogen interactions. Phytochemical Analysis, 21, 89–94.
Lv, Y., Liu, X., Yan, S., et al. (2010). Metabolomic study of myocardial ischemia and intervention effects of compound Danshen tablets in rats using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 52, 129–135.
Ma, Z., & Michailides, T. J. (2005). Advances in understanding molecular mechanisms of fungicide resistance and molecular detection of resistant genotypes in phytopathogenic fungi. Crop Protection, 24, 853–863.
Malmendal, A., Overgaard, J., Bundy, J. G., et al. (2006). Metabolomic profiling of heat stress: Hardening and recovery of homeostasis in Drosophila. American Journal of Physiology: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 291, 205–212.
Manetti, C., Bianchetti, C., Casciani, L., et al. (2006). A metabonomic study of transgenic maize (Zea mays) seeds revealed variations in osmolytes and branched amino acids. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57, 2613–2625.
Markley, J. L. (2007). NMR analysis goes nano. Nature Biotechnology, 25, 750–751.
Mas, S., Villas-Bôas, S. G., Hansen, M. E., Åkesson, M., & Nielsen, J. (2007). A comparison of direct infusion MS and GC–MS for metabolic footprinting of yeast mutants. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 96, 1014–1022.
Masciocchi, J., Frau, G., Fanton, M., et al. (2009). MMsINC: A large-scale chemoinformatics database. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, 284–290.
McKelvie, J. R., Yuk, J., Xu, Y., Simpson, A. J., & Simpson, M. J. (2009). 1H NMR and GC/MS metabolomics of earthworm responses to sub-lethal DDT and endosulfan exposure. Metabolomics, 5, 84–94.
Michel, A., Johnson, R. D., Duke, S. O., & Scheffler, B. E. (2004). Dose-response relationships between herbicides with different modes of action and growth of Lemna paucicostata: An improved ecotoxicological method. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23, 1074–1079.
Miller, M. G. (2007). Environmental metabolomics: A SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats). Journal of Proteome Research, 6, 540–545.
Mirnezhad, M., Romero-González, R. R., Leiss, K. A., Choi, Y. H., Verpoorte, R., & Klinkhamer, P. G. L. (2010). Metabolomic analysis of host plant resistance to thrips in wild and cultivated tomatoes. Phytochemical Analysis, 21, 110–117.
Moco, S., Forshed, J., De Vos, R. C. H., et al. (2008). Intra- and inter-metabolite correlation spectroscopy of tomato metabolomics data obtained by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance. Metabolomics, 4, 202–215.
Mohan, B. S., & Hosetti, B. B. (1999). Aquatic plants for toxicity assessment. Environmental Research, 81, 259–274.
Mohler, R. E., Dombek, K. M., Hoggard, J. C., Pierce, K. M., Young, E. T., & Synovec, R. E. (2007). Comprehensive analysis of yeast metabolite GC×GC-TOFMS data: Combining discovery-mode and deconvolution chemometric software. Analyst, 132, 756–767.
Monton, M. R. N., & Soga, T. (2007). Metabolome analysis by capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1168, 237–246.
Nauen, R., & Bretschneider, T. (2002). New modes of action of insecticides. Pesticide Outlook, 13, 241–245.
OECD. (1993). Safety evaluation of foods derived by modern biotechnology, concepts and principles. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development. http://www.agbios.com/docroot/articles/oecd_fsafety_1993.pdf.
OECD. (2002a). Guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Revised proposal for a new guideline 221, Lemna sp. growth inhibition test. http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/16/51/1948054.pdf.
OECD. (2002b). Module II: Herbicide biochemistry, herbicide metabolism and the residues in glufosinate-ammonium (phosphinothricin)-tolerant transgenic plants. Series on harmonization of regulatory oversight in biotechnology No. 25 http://www.olis.oecd.org/olis/2002doc.nsf/LinkTo/env-jm-mono(2002)14.
Ohta, T., Masutomi, N., Tsutsui, N., et al. (2009). Untargeted metabolomic profiling as an evaluative tool of fenofibrate-induced toxicology in Fischer 344 male rats. Toxicologic Pathology, 37, 521–535.
Oikawa, A., Nakamura, Y., Ogura, T., et al. (2006). Clarification of pathway-specific inhibition by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance/mass spectrometry-based metabolic phenotyping studies. Plant Physiology, 142, 398–413.
Okada, T., Nakamura, Y., Kanaya, S., et al. (2009). Metabolome analysis of ephedra plants with different contents of ephedrine alkaloids by using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Planta Medica, 75, 1356–1362.
Ott, K. H., Aranibar, N., Singh, B., & Stockton, G. W. (2003). Metabonomics classifies pathways affected by bioactive compounds. Artificial neural network classification of NMR spectra of plant extracts. Phytochemistry, 62, 971–985.
Ott, M. A., & Vriend, G. (2006). Correcting ligands, metabolites, and pathways. BMC Bioinformatics, 7, 517.
Owen, M. D. K., & Zelaya, I. A. (2005). Herbicide-resistant crops and weed resistance to herbicides. Pest Management Science, 61, 301–311.
Pandher, R., Ducruix, C., Eccles, S. A., & Raynaud, F. I. (2009). Cross-platform Q-TOF validation of global exo-metabolomic analysis: Application to human glioblastoma cells treated with the standard PI 3-Kinase inhibitor LY294002. The Journal of Chromatography B, 877, 1352–1358.
Pedersen, K. S., Kristensen, T. N., Loeschcke, V., et al. (2008). Metabolomic signatures of inbreeding at benign and stressful temperatures in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics, 180, 1233–1243.
Piccioni, F., Capitani, D., Zolla, L., & Mannina, L. (2009). NMR metabolic profiling of transgenic maize with the Cry1Ab gene. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 57, 6041–6049.
Poole, R. L. (2008). The TAIR Database. In D. Edwards (Ed.), Methods in molecular biology, plant bioinformatics: Methods and protocols (pp. 179–212). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press Inc.
Raamsdonk, L. M., Teusink, B., & Broadhurst, D. (2001). A functional genomics strategy that uses metabolome data to reveal the phenotype of silent mutations. Nature Biotechnology, 19, 45–50.
Ramautar, R., Demirci, A., & de Jong, G. J. (2006). Capillary electrophoresis in metabolomics. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 25, 455–466.
Ratcliffe, R. G., & Shachar-Hill, Y. (2001). Probing plant metabolism with NMR. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 52, 499–526.
REACH. (2006). Registration, evaluation, authorisation and restriction of chemicals REACH, regulation no. 1907/2006. The European Parliament and The Council of The European Union.
Richards, S., Liu, Y., Bettencourt, B. R., et al. (2005). Comparative genome sequencing of Drosophila pseudoobscura: Chromosomal, gene, and cis-element evolution. Genome Research, 15, 1–18.
Robertson, D. G. (2005). Metabonomics in toxicology: A review. Toxicological Sciences, 85, 809–822.
Robertson, D. G., Reily, M. D., Sigler, R. E., Wells, D. F., Paterson, D. A., & Braden, T. K. (2000). Metabonomics: Evaluation of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and pattern recognition technology for rapid in vivo screening of liver and kidney toxicants. Toxicological Sciences, 57, 326–337.
Rosania, G. R., Crippen, G., Woolf, P., States, D., & Shedden, K. (2007). A cheminformatic toolkit for mining biomedical knowledge. Pharmaceutical Research, 24, 1791–1802.
Ruhland, M., Engelhardt, G., & Pawlizki, K. (2004). Distribution and metabolism of d/l-, l- and d-glufosinate in transgenic, glufosinate tolerant crops of maize (Zea mays L spp mays) and oilseed rape (Brassica napus L. var napus). Pest Management Science, 60, 691–696.
Sansone, S.-A., Fan, T., Goodacre, R., et al. (2007). The metabolomics standards initiative. Nature Biotechnology, 25, 846–848.
Schellenberger, J., Park, J. O., Conrad, T. C., & Palsson, B. Ø. (2010). BiGG: A biochemical genetic and genomic knowledgebase of large scale metabolic reconstructions. BMC Bioinformatics, 11, 213.
Schneider, D. (2000). Using drosophila as a model insect. Nature Reviews, 1, 218–226.
Scholz, M., & Fiehn, O. (2007). SetupX-a public study design database for metabolomic projects. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, 12, 169–180.
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., et al. (2003). Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Research, 13, 2498–2504.
Shinbo, Y., Nakamura, Y., Altaf-Ul-Amin, M., et al. (2006). KNApSAcK: A comprehensive species-metabolite relationship database. Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, 57, 166–181.
Smedsgaard, J., & Nielsen, J. (2005). Metabolite profiling of fungi and yeast: From phenotype to metabolome by MS and informatics. Journal of Experimental Botany, 56, 273–286.
Smith, C. A., O’Maille, G., Want, E. J., et al. (2005). METLIN: A metabolite mass spectral database. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 27, 747–751.
Smith, C. A., Want, E. J., O’Maille, G., Tong, G. C., Abagyan, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). XCMS: Processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 779–787.
Soga, T., Ohashi, Y., Ueno, Y., Naraoka, H., Tomita, M., & Nishioka, T. (2003). Quantitative metabolome analysis using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Journal of Proteome Research, 2, 488–494.
Sorrell, T. C., Wright, L. C., Malik, R., & Himmelreich, U. (2006). Application of proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to the study of Cryptococcus and cryptococcosis. FEMS Yeast Research, 6, 558–566.
Spratlin, J. L., Serkova, N. J., & Eckhardt, S. G. (2009). Clinical applications of metabolomics in oncology: A review. Clinical Cancer Research, 15, 431–440.
Suhre, K., & Schmitt-Kopplin, P. (2008). MassTRIX: Mass translator into pathways. Nucleic Acids Research, 36, W481–W484.
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., et al. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics, 3, 211–221.
Sun, B., Li, L., Wua, S., et al. (2009). Metabolomic analysis of biofluids from rats treated with Aconitum alkaloids using nuclear magnetic resonance and gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Analytical Biochemistry, 395, 125–133.
Taguchi, R., Nishijima, M., & Shimizu, T. (2007). Basic analytical systems for lipidomics by mass spectrometry in Japan. Methods in Enzymology, 432, 185–211.
Takahashi, H., Kai, K., Shinbo, Y., et al. (2008). Metabolomics approach for determining growth-specific metabolites based on Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 391, 2769–2782.
Tan, S., Evans, R., & Singh, B. (2006). Herbicidal inhibitors of amino acid biosynthesis and herbicide-tolerant crops. Amino Acids, 30, 195–204.
Taylor, C. F., Field, D., Sansone, S.-A., et al. (2008). Promoting coherent minimum reporting guidelines for biological and biomedical investigations: The MIBBI project. Nature Biotechnology, 26, 889–896.
Taylor, N. S., Weber, R. J. M., Southam, A. D., et al. (2009). A new approach to toxicity testing in Daphnia magna: Application of high throughput FT-ICR mass spectrometry metabolomics. Metabolomics, 5, 44–58.
Thimm, O., Bläsing, O., Gibon, Y., et al. (2004). MAPMAN: A user-driven tool to display genomics data sets onto diagrams of metabolic pathways and other biological processes. Plant Journal, 37, 914–939.
Thompson, G. D., Dutton, R., & Sparks, T. C. (2000). Spinosad-a case study: An example from a natural products discovery programme. Pest Management Science, 56, 696–702.
Tokimatsu, T., Sakurai, N., Suzuki, H., et al. (2005). KaPPA-View. A web-based analysis tool for integration of transcript and metabolite data on plant metabolic pathway maps. Plant Physiology, 138, 1289–1300.
Toyoda, T., & Wada, A. (2004). Omic space: Coordinate-based integration and analysis of genomic phenomic interactions. Bioinformatics, 20, 1759–1765.
Trethewey, R. N., Krotzky, A. J., & Willmitzer, L. (1999). Metabolic profiling: A Rosetta stone for genomics? Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2, 83–85.
Trygg, J., & Wold, S. (2002). Orthogonal projections to latent structures (OPLS). Journal of Chemometrics, 16, 119–128.
van Dam, N. M., & Raaijmakers, C. E. (2006). Local and systemic induced responses to cabbage root fly larvae (Delia radicum) in Brassica nigra and B. oleracea. Chemoecology, 16, 17–24.
van Iersel, M. P., Kelder, T., & Pico, A. R. (2008). Presenting and exploring biological pathways with PathVisio. BMC Bioinformatics, 9, 399.
van Ravenzwaay, B., Cunha, G. C.-P., Leibold, E., et al. (2007). The use of metabolomics for the discovery of new biomarkers of effect. Toxicology Letters, 172, 21–28.
van Vliet, E., Morath, S., Eskes, C., et al. (2008). A novel in vitro metabolomics approach for neurotoxicity testing, proof of principle for methyl mercury chloride and caffeine. Neurotoxicology, 29, 1–12.
Vastrik, I., D’Eustachio, P., Schmidt, E., et al. (2007). Reactome: A knowledge base of biologic pathways and processes. Genome Biology, 8, R39.
Viant, M. R., Bearden, D. W., Bundy, J. G., et al. (2009). International NMR-based environmental metabolomics intercomparison exercise. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 219–225.
Viant, M. R., Ludwig, C., & Günter, U. L. (2008). 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy: From metabolic fingerprinting to profiling. In W. J. Griffiths (Ed.), Metabolomics, metabonomics and metabolic profiling (pp. 44–70). Cambridge, UK: RSC Publishing.
Viant, M. R., Pincetich, C. A., Hinton, D. E., & Tjeerdema, R. S. (2006a). Toxic actions of dinoseb in medaka (Oryzias latipes) embryos as determined by in vivo 31P NMR, HPLC–UV and 1H NMR metabolomics. Aquatic Toxicology, 76, 329–342.
Viant, M. R., Pincetich, C. A., & Tjeerdema, R. S. (2006b). Metabolic effects of dinoseb, diazinon and esfenvalerate in eyed eggs and alevins of Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) determined by 1H NMR metabolomics. Aquatic Toxicology, 77, 359–371.
Villas-Bôas, S. G., Mas, S., Akesson, M., Smedsgaard, J., & Nielsen, J. (2005). Mass spectrometry in metabolome analysis. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 24, 613–646.
Vinayavekhin, N., Homan, E. A., & Saghatelian, A. (2010). Exploring disease through metabolomics. ACS Chemical Biology, 5, 91–103.
Ward, J. L., Baker, J. M., & Beale, M. H. (2007). Recent applications of NMR spectroscopy in plant metabolomics. FEBS Journal, 274, 1126–1131.
Ward, J. L., Baker, J. M., & Miller, S. J. (2010). An inter-laboratory comparison demonstrates that [1H]-NMR metabolite fingerprinting is a robust technique for collaborative plant metabolomic data collection. Metabolomics. doi:10.1007/s11306-010-0200-4.
Ward, E., & Bernasconi, P. (1999). Target-based discovery of crop protection chemicals. Nature Biotechnology, 17, 618–619.
Warne, M. A., Lenz, E. M., Osborn, D., Weeks, J. M., & Nicholson, J. K. (2000). An NMR-based metabonomic investigation of the toxic effects of 3-trifluoromethyl-aniline on the earthworm Eisenia veneta. Biomarkers, 5, 56–72.
Werner, E., Croixmarie, V., Umbdenstock, T., et al. (2008). Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: Accelerating the characterization of discriminating signals by combining statistical correlations and ultrahigh resolution. Analytical Chemistry, 80, 4918–4932.
Widarto, H. T., van Der Meijden, E., Lefeber, A. W. M., et al. (2006). Metabolomic differentiation of Brassica rapa following herbivory by different insect instars using two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 32, 2417–2428.
Williams, A. (1997). Chiral pesticides. Pesticide Outlook, 8, 15–19.
Wind, R. A., Hu, J. Z., & Majors, P. D. (2005). Slow-MAS NMR: A new technology for in vivo metabolomic studies. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies, 2, 291–294.
Wishart, D. S. (2008). Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 27, 228–237.
Wishart, D. S., Knox, C., & Guo, A. C. (2006). DrugBank: A comprehensive resource for in silico drug discovery and exploration. Nucleic Acids Research, 34, D668–D672.
Wishart, D. S., Tzur, D., Knox, C., et al. (2007). HMDB: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Research, 35, D521–D526.
Woo, H. M., Kim, K. M., Choi, M. H., et al. (2009). Mass spectrometry based metabolomic approaches in urinary biomarker study of women’s cancers. Clinica Chimica Acta, 400, 63–69.
Xia, J., Psychogios, N., Young, N., & Wishart, D. S. (2009). MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, W652–W660.
Yi, Z.-B., Yu, Y., Liang, Y.-Z., & Zeng, B. (2007). Evaluation of the antimicrobial mode of berberine by LC/ESI-MS combined with principal component analysis. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 44, 301–304.
Yu, Y., Yi, Z.-b., & Liang, Y.-Z. (2007). Main antimicrobial components of Tinospora capillipes, and their mode of action against Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Letter, 581, 4179–4183.
Zhang, P., Foerster, H., Tissier, C. P., et al. (2005). MetaCyc and AraCyc. Metabolic pathway databases for plant research. Plant Physiology, 138, 27–37.
Zhou, J., Ma, C., & Xu, H. (2009). Metabolic profiling of transgenic rice with cryIAc and sck genes: An evaluation of unintended effects at metabolic level by using GC–FID and GC–MS. The Journal of Chromatography B, 877, 725–732.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aliferis, K.A., Chrysayi-Tokousbalides, M. Metabolomics in pesticide research and development: review and future perspectives. Metabolomics 7, 35–53 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-010-0231-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-010-0231-x