Abstract
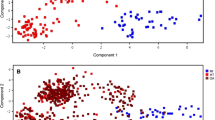
In this paper, a new strategy for processing GC/MS based metabolic profiling data via multivariate methods was proposed, which is applied to a small pilot study of impaired fasting glucose. The data obtained from plasma samples of impaired fasting glucose patients and healthy controls were first treated by principal component analysis and partial least squares-discriminant analysis to explore the differences and discriminators of the two groups. Subsequently, correlation analyses were employed to examine the relationships between blood glucose and the discriminators or their linear combination, thus may be considered as potential biomarkers of impaired fasting glucose. The results showed that the metabolic patterns of the two groups were different. Furthermore, eleven metabolites were screened as discriminators. Levels of nine of the eleven discriminators, say lactate, 2-ketoisocaproic acid, alanine, α-hydroxyisobutyric acid, urea, phosphoric acid, α-glycerophosphoric acid, palmitic acid and stearic acid, were found to be significantly higher in impaired fasting glucose patients, while 1-monopalmitin and 1-monostearin showed the opposite trend. Correlation analysis indicated that 2-ketoisocaproic acid, stearic acid were positively, while 1-monopalmitin and 1-monostearin were negatively correlated with blood glucose. Moreover, blood glucose correlated well with the linear combination of the eleven discriminators by canonical correlation analysis. The results have demonstrated that 2-ketoisocaproic acid, stearic acid and the linear combination of the eleven discriminators may be considered as the potential biomarkers of impaired fasting glucose and the proposed method may be useful in a larger study for exploring the metabolic alterations and biomarker candidates of diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- FBS:
-
Fasting blood sugar
- HDL:
-
High density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PLS-DA:
-
Partial least squares-discriminant analysis
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Total triglyceride
- WHR:
-
Waist-hip ratio
References
Alberti, K. G., & Zimmet, P. Z. (1998). Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO Consultation. Diabetic Medicine, 15, 539–553.
Barker, M., & Rayens, W. (2003). Partial least squares for discrimination. Journal of Chemometrics, 17, 166–173.
Bock, G., Chittilapilly, E., Basu, R., Toffolo, G., Cobelli, C., Chandramouli, V., et al. (2007). Contribution of hepatic and extrahepatic insulin resistance to the pathogenesis of impaired fasting glucose. Diabetes, 56, 1703–1711.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forest. Machine Learning, 45, 5–32.
Bruce, S. J., Jonsson, P., Antti, H., Cloarec, O., Trygg, J., Marklund, S. L., et al. (2008). Evaluation of a protocol for metabolic profiling studies on human blood plasma by combined ultra-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry: From extraction to data analysis. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 237–249.
Chan, E. C. Y., Koh, P. K., Mal, M., Cheah, P. Y., Eu, K. W., Backshall, A., et al. (2009). Metabolic profiling of human colorectal cancer using high-resolution magic spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS NMR) spectroscopy and gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Journal of Proteome Research, 8, 352–361.
De Jong, S. (1993). SIMPLS: An alternative approach to partial least squares regression. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 18, 251–263.
Dumas, M. E., Barton, R. H., Toye, A., Cloarec, O., Blancher, C., Rothwell, A., et al. (2006). Metabolic profiling reveals a contribution gut microbiota to fatty liver phenotype in insulin-resistance mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 103, 12511–12516.
Genuth, S. (2003). Lowering the criterion for impaired fasting glucose is in order. Diabetes Care, 26, 3331–3332.
Gong, F., Liang, Y. Z., Cui, H., Chau, F. T., & Chan, B. T. (2001). Determination of volatile components in peptic power by gas chromatograpy-mass spectrometry and chemometric resolution. Journal of Chromatography. A, 909, 237–247.
Harris, M. I., Flegal, K. M., Cowie, C. C., Eberhardt, M. S., Goldstein, D. E., Little, R. R., et al. (1998). Prevalence of diabetes, impaired fasting glucose, and impaired glucose tolerance in U.S. adults. The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care, 21, 518–524.
King, H., Aubert, R. E., & Herman, W. H. (1998). Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2005: Prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care, 21, 1414–1431.
Kvalheim, O. M., & Liang, Y. Z. (1992). Heuristic evolving latent projections: Resolving two-way multicomponent data. 1, selectivity, latent-projective graph, datascope, local rank, and unique resolution. Analytical Chemistry, 64, 936–946.
Liang, Y. Z., Kvalheim, O. M., Keller, H. R., Massart, D. L., Kiechle, P., & Erni, F. (1992). Heuristic evolving latent projections: Resolving two-way multicomponent data. 2, detection and resolution of minor constituents. Analytical Chemistry, 64, 946–953.
Mal, M., Koh, P. K., Cheah, P. Y., & Chan, E. C. Y. (2009). Development and validation of a gas chromatography/mass spectrometry method for the metabolic profiling of human colon tissue. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 23, 487–494.
McGarry, J. D. (2002). Banting lecture 2001: Dysregulation of fatty acid metabolism in the etiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes, 51, 7–18.
Meyer, C., Stumvoll, M., Nadkarni, V., Dostou, J., Mitrakou, A., & Gerich, J. (1998). Abnormal renal and hepatic glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 102, 619–624.
Nathan, D. M., Davidson, M. B., DeFronzo, R. A., Heine, R. J., Henry, R. R., Pratley, R., et al. (2007). Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care, 30, 753–759.
Pasikanti, K. K., Ho, P. C., & Chan, E. C. Y. (2008). Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry in metabolic profiling of biological fluids. Journal of Chromatography B, 871, 202–211.
Pongsuwan, W., Fukusaki, E., Bamba, T., Yonetani, T., Yamahara, T., & Kobayashi, A. (2007). Prediction of Japanese green tea ranking by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry-based hydrophilic metabolite fingerprinting. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 55, 231–236.
Rao, C. R. (1958). Some statistical methods for comparison of growth curves. Biometrics, 14, 1–17.
Rudell, D. R., Mattheis, J. P., & Curry, E. A. (2008). Prestorage ultraviolet-white light irradiation alters apple peel metabolome. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 56, 1138–1147.
Shepherd, T., Dobson, G., Verrall, S. R., Conner, S., Griffiths, D. W., McNicol, J. W., et al. (2007). Potato metabolomics by GC-MS: What are the limiting factors. Metabolomics, 3, 475–488.
Snehalatha, C., Ramachandran, A., Sivasankari, S., Satyavani, K., & Vijay, V. (2003). Insulin secretion and action show differences in impaired fasting glucose and in impaired glucose tolerance in Asian Indians. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, 19, 329–332.
Stone, M. (1974). Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 36, 111–147.
Wade, J. B., Dougherty, L. M., Hart, R. P., Rafii, A., & Price, D. D. (1992). A canonical correlation analysis of the influence of neuroticism and extroversion on chronic pain, suffering, and pain behavior. Pain, 51, 67–73.
Wang, C., Kong, H. W., Guan, Y. F., Yang, J., Gu, J. R., Yang, S. L., et al. (2005). Plasma phospholipid metabolic profiling and biomarkers of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray mass spectrometry and multivariate statistical analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 7, 4108–4116.
Webb, G. C., Akbar, M. S., Zhao, C. J., & Steiner, D. F. (2000). Expression profiling of pancreatic β-cells: glucose regulation of secretory and metabolic pathway genes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 97, 5773–5778.
Winder, C. L., Dunn, W. B., Schuler, S., Broadhurst, D., Jarvis, R., Stephens, G. M., et al. (2008). Global metabolic profiling of Escherichia coli cultures: An evaluation of methods for quenching and extraction of intracellular metabolites. Analytical Chemistry, 80, 2939–2948.
Wold, S., Esbensen, K., & Geladi, P. (1987). Principal component analysis. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2, 37–52.
Wold, S., Sjostrom, M., & Eriksson, L. (2001). PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 58, 109–130.
Xu, Q. S., & Liang, Y. Z. (2001). Monte Carlo cross validation. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 56, 1–11.
Zeng, M. M., Che, Z. H., Liang, Y. Z., Wang, B., Chen, X., Li, H. D., et al. (2009). GC-MS based plasma metabolic profiling of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chromatographia, 69, 941–948.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported financially by International Traditional Chinese Medicine Program for Cooperation in Science and Technology (No. 2006DFA41090 and 2007DFA40680), National Key Basic Research Program (No. 2006CB503901) founded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, M., Xiao, Y., Liang, Y. et al. Metabolic alterations of impaired fasting glucose by GC/MS based plasma metabolic profiling combined with chemometrics. Metabolomics 6, 303–311 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-009-0193-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-009-0193-z