Abstract
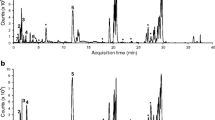
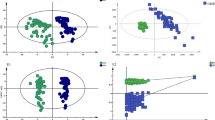
A metabonomics technique based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) coupled with Q-TOF mass spectrometry was employed to investigate the sera from 32 patients with chronic renal failure (CRF) without renal replacement therapy and 30 healthy volunteers in order to find potential disease biomarkers and reveal its pathophysiological changes. After data acquisition Waters MarkerLynx software was used to report retention time and m/z pairs for each metabolite peak, these data were exported to an excel table, then handled by using multivariate analysis and the statistical analysis in the SIMCA-P and the SPSS softwares to obtain potential biomarkers which were further identified by MS/MS. Seven potential biomarkers, creatinine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, kynurenine and three lysophosphatidylcholines, were identified. The results suggest that CRF can lead to the increase of reservation of creatinine in the body, and the abnormal metabolism of the two essential amino acids and lysophosphatidylcholines. It has indicated that metabonomics will be a powerful tool in the clinic research.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergstrom, J., Alvestrand, A., & Furst, P. (1990). Plasma and muscle free amino acid in maintenance hemodialysis patients without protein malnutrition. Kidney International, 38(1), 108–109.
Collins, A. J., Kasiske, B., Herzog, C., Chavers, B., Foley, R., Gilbertson, D., Grimm, R., Liu, J., & Louis, T. (2005). Excepts from the United States renal data system 2004 annual data report: Atlas of end-stage renal disease in the United States. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 45(suppl), A5–A7.
Constantinou, M. A., Papakonstantinou, E., & Spraul, M. (2005). 1H NMR-based metabonomics for the diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism in urine. Analytica Chimica Acta, 511, 303–312.
Coresh, J., Astor, B. C., & Greene, T. (2003). Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: The third National Health and Nutrition Examination survey. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 41, 1–12.
Coresh, J., Byrd-Holt, D., Astor, B. C., Briggs, J. P., Eggers, P. W., Lacher, D. A., & Hostetter, T. H. (2005). Chronic kidney disease awareness, prevalence, and trends among U.S. adults, 1999 to 2000. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 16, 180–188.
Desmond, O., & Russell, M.-S. (2006). High-throughput bioanalysis with simultaneous acquisition of metabolic route data using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 385(1), 114–121.
Dunn, W. B., Broadhurst, D. I., Deepak, S. M., Buch, M. H., McDowell, G., Spasic I., Ellis, D. I., Brooks, N., Kell, D. B., & Neyses L. (2007). Serum metabolomics reveals many novel metabolic markers of heart failure, including pseudouridine and 2-oxoglutarate. Metabolomics, 3, 413–426.
Duong, C. Q., Bared, S. M., Abu-Khader, A., Buechler, C., Schmitz, A., & Schmitz, G. (2004). Expression of the lysophopholipid receptor family and investigation of lysophopholipid-mediated responses in human macrophages. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1682, 112–119.
Eggers, P. W. (1999). Clinical aspects for which treatment with the artificial kidney to be considered. In R. A. Petting & N. G. Levinsky (Eds.), Kidney failure and the federal government (82 pp). Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Frank, R., & Hargreaves, R. (2003). Clinical biomarkers in drug discovery and development. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2, 566–580.
Gillett, M.-P. T., Obineche, E. N., Lakhani, M. S., Abdulle, A. M., Amirlak, I., Rukhaimi, M. A., & Suleiman, M. N. (2001). Levels of cholesteryl esters and other lipids in the plasma of patients with end-stage renal failure. Annals of Saudi Medicine, 21, 283–286.
Johnson, K. A., & Plumb, R. (2005). Investigating the human metabolism of acetaminophen using UPLC and exact mass oa-TOF MS. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 39, 805–810.
Jones, M. R., Kopple, J. D., & Swendseid, M. E. (1978). Phenylalanine metabolism in uremia and normal man. Kidney International, 14(2), 169.
Keun, H. C., Beckonert, O., Griffin, J. L., Richter, C., Moskau, D., Lindon, J. C., & Nicholson, J. K. (2002). Cryogenic probe C-13NMR spectroscopy of urine for metabonomic studies. Analytical Chemistry, 74, 4588–4593.
Khandelwal, P., Beyer, C. E., Lin, Q., McGonigle, P., Schechter, L. E., & Bach, A. C. (2004). Nanoprobe NMR spectroscopy and in vivo microdialysis: New analytical methods to study brain neurochemistry. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 133, 181–189.
Kuhara, T. (2005). Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric urinary metabolome analysis to study mutations of inborn errors of metabolism. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 24(6), 814–827.
Locatelli, F., Del Vecchio, L., Pozzoni, P., & Manzoni, C. (2006). Nephrology: Main advance in the last 40 years. Journal of Nephrology, 19, 6–11.
Monique, P., Christine, V.-S., Konstantinos, P., Claire, E., Jean-Paul, S., Aymeric, M., & Denis, B. (2003). ESI-MS/MS analysis of underivatised amino acids: a new tool for the diagnosis of inherited disorders of amino acid metabolism. Fragmentation study of 79 molecules of biological interest in positive and negative ionization mode. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 17, 1297–1331.
Morita, T., Saito, K., & Takemura, M. (2001). 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid, an l-tryptophan metabolite, induces apoptosis in monocyte-derived cells stimulated by interferon-gamma. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry, 38(pt3), 242–251.
Nicholson, J. K., Connelly, J., Lindon, J. C., & Holmes, E. (2002). Metabonomics: A platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 1(2), 153–162.
Nicholson, J. K., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., & Wilson, I. D. (2004). The challenges of modeling mammalian biocomplexity. Nature Biotechnology, 22(10), 1268–1274.
Oestvang, J., & Johansen, B. (2006). Phospholipase A2: A key regulator of inflammatory signaling and a connector to fibrosis development in atherosclerosis. Biochimica Biophysica Acta, 1761, 1309–1316.
Pawlak, D., Pawlak, K., Malyszko, J., Mysliwiec, M., & Buczko, W. (2001). Accumulation of toxic products degradation of kynurenine in hemodialyzed patients. International Urology and Nephrology, 33(2), 399–404.
Pawlak, D., Tankiewicz, A., Myslwiec, P., & Buczko, W. (2002). Tryptophan metabolism via the kynurenine pathway in experimental chronic renal failure. Nephron, 90(3), 328–335.
Plumb, R. S., Granger, J. H., & Stumpf, C. L. (2005). A rapid screening approach to metabonomics using UPLC and oa-TOF mass spectrometry: Application to age, gender,and diurnal variation in normal/Zucker obese rats and black, white, and nude mice. Analyst, 130(6), 844–849.
Pognan, F. (2004). Genomics, proteomics and metabonomics in toxicology: Hopefully not ‘fashionomics’. Pharmacogenomics, 5(7), 879–893.
Saito, K., Fujigaki, S., & Heyes, M. P. (2000). Mechanism of increased in l-kynurenine and quinolinic acid in renal insufficiency. American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology, 279(2), F565–F572.
Van der Greef, J., Davidov, E., Verheij, E. R., Vogels, J., Van der Heijden, R., Adourian, A. S., Oresic, M., Marple, E. W., & Naylor, S. (2003). The role of metabolomics in system biology. In G. G. Harrigan & R. Goodacre (Eds.), Metabolic profiling: Its role in biomarker discovery and gene function analysis (pp. 170–198). Boston, Dordrecht, London: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Van der Greef, J., Stroobant, P., & Van der Heijden, R. (2004). The role of analytical sciences in medical systems biology. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 8, 559–565.
Wang, C., Yang, J., Gao, P., Li, X., & Xu, G. W. (2005). Identification of phospholipids structures in human blood by direct-injection quadrupole-linear ion-trap mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 19, 2443–2453.
Want, E. J., Smith. C. A., Qin, C., Vanhorne, K. C., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). Phospholipid captune combined with non-linear chromatographic correction for improved serum metabolite profiling. Metabolomics, 2(2), 95–104.
Wilson, I. D., Nicholson, J. K., Castro-Perez, J., Granger, J. H., Johnson, K. A., Smith, B. W., & Plumb, R. S. (2005). High resolution “Ultra performance” liquid chromatography coupled to oa-TOF mass spectrometry as a tool for differential metabolic pathway profiling in functional genomic studies. Journal of Proteome Research, 4, 591–598.
Xu, Y., Xiao, Y. J., Zhu, K., Baudhuin, L. M., Lu, J., Hong, G., Kim, K. S., Cristina, K. L., Song, L., & William, F. S. (2003). Unfolding the pathophysiological role bioactive lysophospholipids. Current Drug Targets, 3(1), 23–32.
Xue, J. L., Ma, J. Z., Louis, T. A., & Collins, A. J. (2001). Forecast of the number of patients with end-stage renal disease in the United States to the year 2010. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 12, 2753–2758.
Yang, J., Zhao, X. J., Liu, X. L., Wang, C., Gao, P., Wang, J. S., Li, L. J., Gu, J. R., Yang, S. L., & Xu, G. W. (2006). High performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for metabonomics: Potential biomarkers for acute deterioration of liver function in chronic hepatitis B. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 554–561.
Yin, P. Y., Zhao, X. J., Ki, Q. R., Wang, J. S., Li, J. S., & Xu, G. W. (2006). Metabonomics study of intestinal fistulas based on ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with Q-TOF mass spectrometry (UPLC/Q-TOF MS). Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 2135–2143.
Zoccali, C. (2006). Traditional and emerging cardiovascular and renal risk factors: An epidemiologic perspective. Kidney International, 70, 26–33.
Acknowledgements
The study has been supported by the foundation (No. 20425516) for Distinguished Young Scholars and the foundation (No. 20675082) from National Natural Science Foundation of China, and National Basic Research Program of China (2006CB503902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, L., Chen, J., Yin, P. et al. Serum metabonomics study of chronic renal failure by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with Q-TOF mass spectrometry. Metabolomics 4, 183–189 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-008-0110-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-008-0110-x