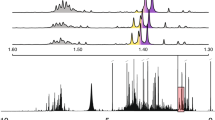
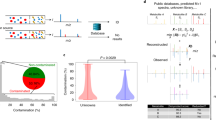
Abstract
Assignment of physical meaning to mass spectrometry (MS) data peaks is an important scientific challenge for metabolomics investigators. Improvements in instrumental mass accuracy reduce the number of spurious database matches, however, this alone is insufficient for accurate, unique high-throughput assignment. We present a method for clustering MS instrumental artifacts and a stochastic local search algorithm for the automated assignment of large, complex MS-based metabolomic datasets. Artifact peaks and their associated source peaks are grouped into “instrumental clusters.” Instrumental clusters, peaks grouped together by shared peak shape in the temporal domain, serve as a guide for the number of assignments necessary to completely explain a given dataset. We refine mass only assignments through the intersection of peak correlation pairs with a database of biochemically relevant interaction pairs. Further refinement is achieved through a stochastic local search optimization algorithm that selects individual assignments for each instrumental cluster. The algorithm works by choosing the peak assignment that maximally explains the connectivity of a given cluster. We demonstrate that this methodology provides a significant advantage over standard methods for the assignment of metabolites in a UPLC-MS diabetes dataset.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkin, A., Shen, P., & Ross, R. (1997). A test case of correlation metric construction of a reaction pathway from measurements. Science, 277, 1275–1279.
Breitling, R., Ritchie, S., Goodenowe, D., Stewart, M. L., & Barrett, M. P. (2006a). Ab initio prediction of metabolic networks using Fourier transform mass spectrometry data. Metabolomics, 2, 155–164.
Breitling, R., Pitt, A. R., & Barrett, M. P. (2006b). Precision mapping of the metabolome. Trends in Biotechnology, 24, 543–548.
Dettmer, K., Aronov, P. A., & Hammock, B. D. (2007). Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 26, 51–78.
Forster, J., Gomber, A. K., & Nielsen, J. (2002). A functional genomics approach using metabolomics and in silico pathway analysis. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 79, 703–712.
Goto, S., Nishioka, T., & Kanehisa, M. (1998). LIGAND: Chemical database for enzyme reactions. Bioinformatics, 14, 591–599.
Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Aoki-Kinoshita, K. F., Itoh, M., Kawashima, S., Katayama, T., Araki, M., & Hirakawa, M. (2006). From genomics to chemical genomics: New developments in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Research, 34, D354–D357.
Kell, D. B. (2004). Metabolomics and systems biology: Making sense of the soup. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 7, 296–307.
Kind, T., & Fiehn, O. (2006). Metabolomic database annotations via query of elemental compositions: Mass accuracy is insufficient even at less than 1 ppm. BMC Bioinformatics, 7, 234.
Kopka, J., Schauer, N., Krueger, S., Birkemeyer, C., Usadel, B., Bergmuller, E., Dormann, P., Weckwerth, W, Gibon, Y., Stitt, M., Willmitzer, L., Fernie, A. R., & Steinhauser, D. (2005). GMD@CSB.DB: The Golm metabolome database. Bioinformatics, 21, 1635–1638.
Mendes, P. (2002). Emerging bioinformatics for the metabolome. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 3, 134–145.
Smith, C. A., Want, E. J., O’Maille, G., Abagyan, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). XCMS: Processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 779–787.
Steuer, R. (2006). On the analysis and interpretation of correlations in metabolomic data. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 7, 151–158.
Steuer, R., Kurths, J., Fiehn, O., & Weckwerth, W. (2003a). Observing and interpreting correlations in metabolomic networks. Bioinformatics, 19, 1019–1026.
Steuer, R., Kurths, J., Fiehn, O., & Weckwerth, W. (2003b). Interpreting correlations in metabolomic networks. Biochemical Society Transactions, 31, 1476–1478.
Want, E. J., Cravatt, B. F., & Siuzdak, G. (2005). The expanding role of mass spectrometry in metabolite profiling and characterization. ChemBioChem, 6, 1941–1951.
Witten, I., & Frank E. (2000). Data mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques with Java implementations. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mike Hansen for providing the mouse urine samples and Mark Hodson for providing the LC method for LC-MS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gipson, G.T., Tatsuoka, K.S., Sokhansanj, B.A. et al. Assignment of MS-based metabolomic datasets via compound interaction pair mapping. Metabolomics 4, 94–103 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0096-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0096-9