Abstract
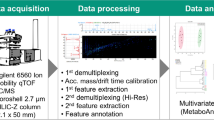
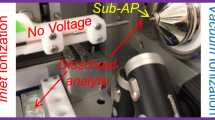
Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry (IMMS) was evaluated as an analytical method for metabolic profiling. The specific instrument used in these studies was a direct infusion (DI)-electrospray ionization (ESI)—ambient pressure ion mobility spectrometer (APIMS) coupled to a time-of-flight mass spectrometer (TOFMS). The addition of an ion mobility spectrometer to a mass spectrometer had several advantages over direct infusion electrospray mass spectrometry alone. This tandem instrument (ESI-IMMS) added a rapid separation step with high-resolution prior to mass spectrometric analysis of metabolite mixtures without extending sample preparation time or reducing the high through put potential of direct mass spectrometry. Further, IMMS also reduced the baseline noise common with ESI-MS analyses of complex samples and enabled rapid separation of isobaric metabolites. IMMS was used to analyze the metabolome of Escherichia coli (E. coli), containing a collection of extremely diverse chemical compounds including hydrophobic lipids, inorganic ions, volatile alcohols and ketones, amino and non-amino organic acids, and hydrophilic carbohydrates. IMMS data were collected as two-dimensional spectra showing both mobility and mass of each ion detected. Using direct infusion ESI-IMMS of a non-derivatized methanol extract of an E. coli culture, more than 500 features were detected, of which over 200 intracellular metabolites were tentatively assigned as E. coli metabolites. This analytical method also allowed simultaneous separation of isomeric metabolic features.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharoni, A., Ric de Vos, C. H., Verhoeven Harrie, A., Maliepaard Chris, A., Kruppa, G., Bino, R., & Goodenowe Dayan, B. (2002). Nontargeted metabolome analysis by use of Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Mass Spectrometry. Omics : A Journal of Integrative Biology, 6, 217–234.
Asbury, G. R., & Hill, H. H. (2000a). Evaluation of ultrahigh resolution ion mobility spectrometry as an analytical separation device in chromatographic terms. Journal of Microcolumn Separations, 12, 172–178.
Asbury, G. R., & Hill, H. H. (2000b). Using different drift cases to change separation factors (alpha) in ion mobility spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 72, 580–584.
Beegle, L. W., Kanik, I., Matz, L., & Hill, H. H. (2002). Effects of drift-gas polarizability on glycine peptides in ion mobility spectrometry. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 216, 257–268.
Belov, M. E., Buschbach, M. A., Prior, D. C., Tang, K., & Smith, R. D. (2007). Multiplexed ion mobility spectrometry-orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 2451–2462.
Bradbury, N. E., & Nielsen, R. A. (1936). Absolute values of the electron mobility in hydrogen. Physical Review, 49, 388.
Brown Stephen, C., Kruppa, G., & Dasseux, J.-L. (2005). Metabolomics applications of FT-ICR mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 24, 223–231.
Buchholz, A., Hurlebaus, J., Wandrey, C., & Takors, R. (2002). Metabolomics: Quantification of intracellular metabolite dynamics. Biomolecular Engineering, 19, 5–15.
Duarte, N. C., Becker, S. A., Jamshidi, N., Thiele, I., Mo, M. L., Vo, T. D., Srivas, R., & Palsson, B. O. (2007). Global reconstruction of the human metabolic network based on genomic and bibliomic data. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 1777–1782.
Dunn, W. B., Bailey, N. J. C., & Johnson, H. E. (2005). Measuring the metabolome: Current analytical technologies. Analyst, 130, 606–625.
Dunn, W. B., & Ellis, D. I. (2005). Metabolomics: Current analytical platforms and methodologies. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 24, 285–294.
Dwivedi, P., Bendiak, B. A., Clowers, B. H., & Hill, H. H. (2007). Rapid resolution of carbohydrate isomers by electrospray ionization ambient pressure ion mobility spectrometry-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ESI-APIMS-TOFMS). Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 18(7), 1163–1175.
Dwivedi, P., Wu, C., Matz, L. M., Clowers, B. H., Siems, W. F., & Hill, H. H. (2006). Gas-phase chiral separations by ion mobility spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 8200–8206.
Fiehn, O. (2002). Metabolomics – the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Molecular Biology, 48, 155–171.
Fiehn, O., Kopka, J., Dormann, P., Altmann, T., Trethewey, R. N., & Willmitzer, L. (2000). Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nature Biotechnology, 18, 1157–1161.
Goodacre, R., Vaidyanathan, S., Bianchi, G., & Kell, D. B. (2002). Metabolic profiling using direct infusion electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry for the characterisation of olive oils. Analyst, 127, 1457–1462.
Harrigan, G. G., LaPlante, R. H., Cosma, G. N., Cockerell, G., Goodacre, R., Maddox, J. F., Luyendyk, J. P., Ganey, P. E., & Roth, R. A. (2004). Application of high-throughput Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy in toxicology studies: Contribution to a study on the development of an animal model for idiosyncratic toxicity. Toxicology Letters, 146, 197–205.
Hollywood, K., Brison, D. R., & Goodacre, R. (2006). Metabolomics: Current technologies and future trends. Proteomics, 6, 4716–4723.
Johnson, H. E., Broadhurst, D., Kell, D. B., Theodorou, M. K., Merry, R. J., & Griffith, G. W. (2004). High-throughput metabolic fingerprinting of legume silage fermentations via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 1583–1592.
Kast, J., Gentzel, M., Wilm, M., & Richardson, K. (2003). Noise filtering techniques for electrospray quadrupole time of flight mass spectra. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 14, 766–776.
Kell, D. B. (2004). Metabolomics and systems biology: Making sense of the soup. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 7, 296–307.
Keseler, I. M., Collado-Vides, J., Gama-Castro, S., Ingraham, J., Paley, S., Paulsen, I. T., Peralta-Gil, M., & Karp, P. D. (2005). EcoCyc: A comprehensive database resource for Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, D334–337.
Koek, M. M., Muilwijk, B., van der Werf, M. J., & Hankemeier, T. (2006). Microbial metabolomics with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 1272–1281.
Louie, T. M., Webster, C. M., & Xun, L. Y. (2002). Genetic and biochemical characterization of a 2,4,6-trichlorophenol degradation pathway in Ralstonia eutropha JMP134. Journal of Bacteriology, 184, 3492–3500.
Merenbloom, S. I., Koeniger, S. L., Valentine, S. J., Plasencia, M. D., & Clemmer, D. E. (2006). IMS-IMS and IMS-IMS-IMS/MS for separating peptide and protein fragment ions. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 2802–2809.
Nordstrom, A., O’Maille, G., Qin, C., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). Nonlinear data alignment for UPLC-MS and HPLC-MS based metabolomics: Quantitative analysis of endogenous and exogenous metabolites in human serum. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 3289–3295.
Roessner, U., Wagner, C., Kopka, J., Trethewey, R. N., & Willmitzer, L. (2000). Simultaneous analysis of metabolites in potato tuber by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Plant Journal, 23, 131–142.
Soga, T., Ohashi, Y., Ueno, Y., Naraoka, H., Tomita, M., & Nishioka, T. (2003). Quantitative metabolome analysis using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Journal of Proteome Research, 2, 488–494.
Steiner, W. E., Clowers, B. H., Fuhrer, K., Gonin, M., Matz, L. M., Siems, W. F., Schultz, A. J., & Hill, H. H. (2001). Electrospray ionization with ambient pressure ion mobility separation and mass analysis by orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 15, 2221–2226.
Steiner, W. E., Clowers, B. H., & Hill, H. H. (2003). Rapid separation of phenylthiohydantoin amino acids: Ambient pressure ion-mobility mass spectrometry (IMMS). Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 375, 99–102.
Steiner, W. E., English, W. A., & Hill, H. H. (2005). Separation efficiency of a chemical warfare agent simulant in an atmospheric pressure ion mobility time-of-flight mass spectrometer (IM(tof)MS). Analytica Chimica Acta, 532, 37–45.
Vaidyanathan, S., Kell, D. B., & Goodacre, R. (2002). Flow-injection electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of crude cell extracts for high-throughput bacterial identification. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 13, 118–128.
Vaidyanathan, S., Rowland, J. J., Kell, D. B., & Goodacre, R. (2001). Discrimination of aerobic endospore-forming bacteria via electrospray-ionization mass spectrometry of whole cell suspensions. Analytical Chemistry, 73, 4134–4144.
Voyksner, R. D., & Lee, H. (1999). Investigating the use of an octupole ion guide for ion storage and high-pass mass filtering to improve the quantitative performance of electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 13, 1427–1437.
Wilson, I. D., Plumb, R., Granger, J., Major, H., Williams, R., & Lenz, E. A. (2005). HPLC-MS-based methods for the study of metabonomics. Journal of Chromatography B-Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 817, 67–76.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported in part by a research grant from Department of Health and Human Service: Public Health Services organization (Road Map Grant No. R21 DK070274). We also wish to express our appreciation to Dr. Al Schultz, Agnes Tempez, and Thomas F. Egan at IonWerks in Houston, TX for their help and discussions throughout this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, P., Wu, P., Klopsch, S.J. et al. Metabolic profiling by ion mobility mass spectrometry (IMMS). Metabolomics 4, 63–80 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0093-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0093-z