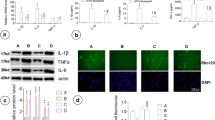
Abstract
Guanosine, a guanine-based purine, is an extracellular signaling molecule that is released from astrocytes and has been shown to promote central nervous system defenses in several in vivo and in vitro injury models. Our group recently demonstrated that guanosine exhibits glioprotective effects in the C6 astroglial cell line by associating the heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) signaling pathway with protection against azide-induced oxidative stress. Astrocyte overactivation contributes to the triggering of brain inflammation, a condition that is closely related to the development of many neurological disorders. These cells sense and amplify inflammatory signals from microglia and/or initiate the release of inflammatory mediators that are strictly related to transcriptional factors, such as nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB), that are modulated by HO-1. Astrocytes also express toll-like receptors (TLRs); TLRs specifically recognize lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which has been widely used to experimentally study inflammatory response. This study was designed to understand the glioprotective mechanism of guanosine against the inflammatory and oxidative damage induced by LPS exposure in primary cultures of hippocampal astrocytes. Treatment of astrocytes with LPS resulted in deleterious effects, including the augmentation of pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, NFκB activation, mitochondrial dysfunction, increased levels of oxygen/nitrogen species, and decreased levels of antioxidative defenses. Guanosine was able to prevent these effects, protecting the hippocampal astrocytes against LPS-induced cytotoxicity through activation of the HO-1 pathway. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory effects of guanosine were independent of the adenosinergic system. These results highlight the potential role of guanosine against neuroinflammatory-related diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orre M, Kamphuis W, Osborn LM, Jansen AH, Kooijman L, Bossers K, Hol EM (2014) Isolation of glia from Alzheimer’s mice reveals inflammation and dysfunction. Neurobiol Aging 35(12):2746–2760. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.06.004
Hansel G, Tonon AC, Guella FL, Pettenuzzo LF, Duarte T, Duarte MM, Oses JP, Achaval M, Souza DO (2014) Guanosine protects against cortical focal ischemia. involvement of inflammatory response. Response Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8978-0
Rizzo F, Riboldi G, Salani S, Nizzardo M, Simone C, Corti S, Hedlund E (2014) Cellular therapy to target neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 71(6):999–1015. doi:10.1007/s00018-013-1480-4
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8(4):382–397. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70062-6
Belanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ (2011) Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab 14(6):724–738. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.016
Maragakis NJ, Rothstein JD (2006) Mechanisms of disease: astrocytes in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2(12):679–689. doi:10.1038/ncpneuro0355
Parpura V, Heneka MT, Montana V, Oliet SHR, Schousboe A, Haydon PG Jr, Jr Stout RF, Spray DC, Reichenbach A, Pannicke T, Pekny M, Pekna M, Zorec R, Verkhratsky A (2012) Glial cells in (patho)physiology. J Neurochem 121:24. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07664.x
Villeda SA, Luo J, Mosher KI, Zou B, Britschgi M, Bieri G, Stan TM, Fainberg N, Ding Z, Eggel A, Lucin KM, Czirr E, Park JS, Couillard-Despres S, Aigner L, Li G, Peskind ER, Kaye JA, Quinn JF, Galasko DR, Xie XS, Rando TA, Wyss-Coray T (2011) The ageing systemic milieu negatively regulates neurogenesis and cognitive function. Nature 477(7362):90–94. doi:10.1038/nature10357
Farina C, Aloisi F, Meinl E (2007) Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol 28(3):138–145. doi:10.1016/j.it.2007.01.005
Guerra MC, Tortorelli LS, Galland F, Da Re C, Negri E, Engelke DS, Rodrigues L, Leite MC, Goncalves CA (2011) Lipopolysaccharide modulates astrocytic S100B secretion: a study in cerebrospinal fluid and astrocyte cultures from rats. J Neuroinflammation 8:128. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-8-128
Zong Y, Sun L, Liu B, Deng YS, Zhan D, Chen YL, He Y, Liu J, Zhang ZJ, Sun J, Lu D (2012) Resveratrol inhibits LPS-induced MAPKs activation via activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. PLoS One 7(8):e44107. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044107
Carpentier PA, Duncan DS, Miller SD (2008) Glial toll-like receptor signaling in central nervous system infection and autoimmunity. Brain Behav Immun 22(2):140–147. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2007.08.011
Ciccarelli R, Di Iorio P, Giuliani P, D’Alimonte I, Ballerini P, Caciagli F, Rathbone MP (1999) Rat cultured astrocytes release guanine-based purines in basal conditions and after hypoxia/hypoglycemia. Glia 25(1):93–98. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1136(19990101)25:1<93::AID-GLIA9>3.0.CO;2-N
Lara DR, Schmidt AP, Frizzo ME, Burgos JS, Ramirez G, Souza DO (2001) Effect of orally administered guanosine on seizures and death induced by glutamatergic agents. Brain Res 912(2):176–180. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(01)02734-2
Vinade ER, Schmidt AP, Frizzo ME, Izquierdo I, Elisabetsky E, Souza DO (2003) Chronically administered guanosine is anticonvulsant, amnesic and anxiolytic in mice. Brain Res 977(1):97–102. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(03)02769-0
Vinade ER, Schmidt AP, Frizzo ME, Portela LV, Soares FA, Schwalm FD, Elisabetsky E, Izquierdo I, Souza DO (2005) Effects of chronic administered guanosine on behavioral parameters and brain glutamate uptake in rats. J Neurosci Res 79(1–2):248–253. doi:10.1002/jnr.20327
Schmidt AP, Lara DR, Souza DO (2007) Proposal of a guanine-based purinergic system in the mammalian central nervous system. Pharmacol Ther 116(3):401–416. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.07.004
Schmidt AP, Tort AB, Silveira PP, Bohmer AE, Hansel G, Knorr L, Schallenberger C, Dalmaz C, Elisabetsky E, Crestana RH, Lara DR, Souza DO (2009) The NMDA antagonist MK-801 induces hyperalgesia and increases CSF excitatory amino acids in rats: reversal by guanosine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91(4):549–553. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2008.09.009
Chang R, Algird A, Bau C, Rathbone MP, Jiang S (2008) Neuroprotective effects of guanosine on stroke models in vitro and in vivo. Neurosci Lett 431(2):101–105. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.11.072
Oleskovicz SP, Martins WC, Leal RB, Tasca CI (2008) Mechanism of guanosine-induced neuroprotection in rat hippocampal slices submitted to oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neurochem Int 52(3):411–418. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2007.07.017
Dal-Cim T, Ludka FK, Martins WC, Reginato C, Parada E, Egea J, Lopez MG, Tasca CI (2013) Guanosine controls inflammatory pathways to afford neuroprotection of hippocampal slices under oxygen and glucose deprivation conditions. J Neurochem 126(4):437–450. doi:10.1111/jnc.12324
Pettifer KM, Kleywegt S, Bau CJ, Ramsbottom JD, Vertes E, Ciccarelli R, Caciagli F, Werstiuk ES, Rathbone MP (2004) Guanosine protects SH-SY5Y cells against beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis. Neuroreport 15(5):833–836
Ganzella M, de Oliveira ED, Comassetto DD, Cechetti F, Cereser VH Jr, Moreira JD, Hansel G, Almeida RF, Ramos DB, Figueredo YN, Souza DG, Oses JP, Worm PV, Achaval M, Netto CA, Souza DO (2012) Effects of chronic guanosine treatment on hippocampal damage and cognitive impairment of rats submitted to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Neurol Sci 33(5):985–997. doi:10.1007/s10072-011-0872-1
Moretto MB, Arteni NS, Lavinsky D, Netto CA, Rocha JB, Souza DO, Wofchuk S (2005) Hypoxic-ischemic insult decreases glutamate uptake by hippocampal slices from neonatal rats: prevention by guanosine. Exp Neurol 195(2):400–406. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.06.005
Rathbone MP, Saleh TM, Connell BJ, Chang R, Su C, Worley B, Kim M, Jiang S (2011) Systemic administration of guanosine promotes functional and histological improvement following an ischemic stroke in rats. Brain Res 1407:79–89. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.06.027
Hansel G, Ramos DB, Delgado CA, Souza DG, Almeida RF, Portela LV, Quincozes-Santos A, Souza DO (2014) The potential therapeutic effect of guanosine after cortical focal ischemia in rats. PLoS One 9(2):e90693. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090693
Schmidt AP, Lara DR, de Faria MJ, da Silveira PA, Onofre Souza D (2000) Guanosine and GMP prevent seizures induced by quinolinic acid in mice. Brain Res 864(1):40–43. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02106-5
Jackson EK, Cheng D, Jackson TC, Verrier JD, Gillespie DG (2013) Extracellular guanosine regulates extracellular adenosine levels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 304(5):C406–C421. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00212.2012
Quincozes-Santos A, Bobermin LD, de Souza DG, Bellaver B, Goncalves CA, Souza DO (2013) Gliopreventive effects of guanosine against glucose deprivation in vitro. Purinergic Signal 9(4):643–654. doi:10.1007/s11302-013-9377-0
Quincozes-Santos A, Bobermin LD, Souza DG, Bellaver B, Goncalves CA, Souza DO (2014) Guanosine protects C6 astroglial cells against azide-induced oxidative damage: a putative role of heme oxygenase 1. J Neurochem 130(1):61–74. doi:10.1111/jnc.12694
Cuadrado A, Rojo AI (2008) Heme oxygenase-1 as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases and brain infections. Curr Pharm Des 14(5):429–442. doi:10.2174/138161208783597407
Dang TN, Bishop GM, Dringen R, Robinson SR (2011) The metabolism and toxicity of hemin in astrocytes. Glia 59(10):1540–1550. doi:10.1002/glia.21198
Lee TS, Chau LY (2002) Heme oxygenase-1 mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of interleukin-10 in mice. Nat Med 8(3):240–246. doi:10.1038/nm0302-240
Bramanti V, Tomassoni D, Grasso S, Bronzi D, Napoli M, Campisi A, Li Volti G, Ientile R, Amenta F, Avola R (2012) Cholinergic precursors modulate the expression of heme oxigenase-1, p21 during astroglial cell proliferation and differentiation in culture. Neurochem Res 37(12):2795–2804. doi:10.1007/s11064-012-0873-3
Wakabayashi N, Slocum SL, Skoko JJ, Shin S, Kensler TW (2010) When NRF2 Talks, Who’s Listening? Antioxid Redox Signal. doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3216
Moncada S, Bolanos JP (2006) Nitric oxide, cell bioenergetics and neurodegeneration. J Neurochem 97(6):1676–1689. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03988.x
Bellaver B, Souza DG, Bobermin LD, Souza DO, Goncalves CA, Quincozes-Santos A (2015) Resveratrol Protects Hippocampal Astrocytes Against LPS-Induced Neurotoxicity Through HO-1, p38 and ERK Pathways. Neurochem Res 40(8):1600–1608. doi:10.1007/s11064-015-1636-8
Bellaver B, Souza DG, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A (2014) Resveratrol increases antioxidant defenses and deceases proinflammatory cytokines in hippocampal astocyte cultures from newborn, adult and aged Wistar rats. Toxicol in Vitro 28:479–484. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2014.01.006
Souza DG, Bellaver B, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A (2013) Characterization of adult rat astrocyte cutures. PLoS One 8:E60282. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060282
Reers M, Smiley ST, Mottola-Hartshorn C, Chen A, Lin M, Chen LB (1995) Mitochondrial membrane potential monitored by JC-1 dye. Methods Enzymol 260:406–417. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(95)60154-6
Santos CL, Bobermin LD, Souza DG, Bellaver B, Bellaver G, Arus BA, Souza DO, Goncalves CA, Quincozes-Santos A (2015) Lipoic acid and N-acetylcysteine prevent ammonia-induced inflammatory response in C6 astroglial cells: the putative role of ERK and HO1 signaling pathways. Toxicol In Vitro 29(7):1350–1357. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2015.05.023
Souza DG, Bellaver B, Raupp GS, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A (2015) Astrocytes from adult Wistar rats aged in vitro show changes in glial functions. Neurochem Int. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2015.07.016
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Jackson EK, Cheng D, Mi Z, Gillespie DG (2014) Guanosine regulates adenosine levels in the kidney. Physiol Rep. 2 (5). doi:10.14814/phy2.12028
Jackson EK, Gillespie DG (2013) Regulation of cell proliferation by the guanosine-adenosine mechanism: role of adenosine receptors. Physiol Rep 1(2):e00024. doi:10.1002/phy2.24
Jackson EK, Mi Z (2014) The guanosine-adenosine interaction exists in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 350(3):719–726. doi:10.1124/jpet.114.216978
Camandola S, Mattson MP (2007) NF-kappa B as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11(2):123–132. doi:10.1517/14728222.11.2.123
Ghosh A, Roy A, Liu X, Kordower JH, Mufson EJ, Hartley DM, Ghosh S, Mosley RL, Gendelman HE, Pahan K (2007) Selective inhibition of NF-kappaB activation prevents dopaminergic neuronal loss in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(47):18754–18759. doi:10.1073/pnas.0704908104
Rathbone MP, Middlemiss PJ, Gysbers JW, Andrew C, Herman MA, Reed JK, Ciccarelli R, Di Iorio P, Caciagli F (1999) Trophic effects of purines in neurons and glial cells. Prog Neurobiol 59(6):663–690. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(99)00017-9
Jiang S, Bendjelloul F, Ballerini P, D’Alimonte I, Nargi E, Jiang C, Huang X, Rathbone MP (2007) Guanosine reduces apoptosis and inflammation associated with restoration of function in rats with acute spinal cord injury. Purinergic Signal 3(4):411–421. doi:10.1007/s11302-007-9079-6
Di Iorio P, Ballerini P, Traversa U, Nicoletti F, D’Alimonte I, Kleywegt S, Werstiuk ES, Rathbone MP, Caciagli F, Ciccarelli R (2004) The antiapoptotic effect of guanosine is mediated by the activation of the PI 3-kinase/AKT/PKB pathway in cultured rat astrocytes. Glia 46(4):356–368. doi:10.1002/glia.20002
Traversa U, Bombi G, Di Iorio P, Ciccarelli R, Werstiuk ES, Rathbone MP (2002) Specific [(3)H]-guanosine binding sites in rat brain membranes. Br J Pharmacol 135(4):969–976. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704542
Bau C, Middlemiss PJ, Hindley S, Jiang S, Ciccarelli R, Caciagli F, Diiorio P, Werstiuk ES, Rathbone MP (2005) Guanosine stimulates neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells via activation of heme oxygenase and cyclic GMP. Purinergic Signal 1(2):161–172. doi:10.1007/s11302-005-6214-0
Dal-Cim T, Molz S, Egea J, Parada E, Romero A, Budni J, Martin de Saavedra MD, del Barrio L, Tasca CI, Lopez MG (2012) Guanosine protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against mitochondrial oxidative stress by inducing heme oxigenase-1 via PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta pathway. Neurochem Int 61(3):397–404. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2012.05.021
Haselkorn ML, Shellington DK, Jackson EK, Vagni VA, Janesko-Feldman K, Dubey RK, Gillespie DG, Cheng D, Bell MJ, Jenkins LW, Homanics GE, Schnermann J, Kochanek PM (2010) Adenosine A1 receptor activation as a brake on the microglial response after experimental traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neurotrauma 27(5):901–910. doi:10.1089/neu.2009.1075
Newell EA, Exo JL, Verrier JD, Jackson TC, Gillespie DG, Janesko-Feldman K, Kochanek PM, Jackson EK (2015) 2′,3′-cAMP, 3′-AMP, 2′-AMP and adenosine inhibit TNF-alpha and CXCL10 production from activated primary murine microglia via A2A receptors. Brain Res 1594:27–35. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.059
Kucher BM, Neary JT (2005) Bi-functional effects of ATP/P2 receptor activation on tumor necrosis factor-alpha release in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated astrocytes. J Neurochem 92(3):525–535. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02885.x
D’Alimonte I, Flati V, D’Auro M, Toniato E, Martinotti S, Rathbone MP, Jiang S, Ballerini P, Di Iorio P, Caciagli F, Ciccarelli R (2007) Guanosine inhibits CD40 receptor expression and function induced by cytokines and beta amyloid in mouse microglia cells. J Immunol 178(2):720–731. doi:10.4049/ jimmunol.178.2.720
Holmin S, Mathiesen T (2000) Intracerebral administration of interleukin-1beta and induction of inflammation, apoptosis, and vasogenic edema. J Neurosurg 92(1):108–120. doi:10.3171/jns.2000.92.1.0108
Olmos G, Llado J (2014) Tumor necrosis factor alpha: a link between neuroinflammation and excitotoxicity. Mediators Inflamm 2014:861231. doi:10.1155/2014/861231
de Rivero Vaccari JP, Dietrich WD, Keane RW (2014) Activation and regulation of cellular inflammasomes: gaps in our knowledge for central nervous system injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34(3):369–375. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2013.227
Pugazhenthi S, Zhang Y, Bouchard R, Mahaffey G (2013) Induction of an inflammatory loop by interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha involves NF-kB and STAT-1 in differentiated human neuroprogenitor cells. PLoS One 8(7):e69585. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069585
Stewart VC, Heales SJ (2003) Nitric oxide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: implications for neurodegeneration. Free Radic Biol Med 34(3):287–303. doi:10.1016/S0891584902013278
Brennan AM, Suh SW, Won SJ, Narasimhan P, Kauppinen TM, Lee H, Edling Y, Chan PH, Swanson RA (2009) NADPH oxidase is the primary source of superoxide induced by NMDA receptor activation. Nat Neurosci 12(7):857–863. doi:10.1038/nn.2334
Suh SW, Shin BS, Ma H, Van Hoecke M, Brennan AM, Yenari MA, Swanson RA (2008) Glucose and NADPH oxidase drive neuronal superoxide formation in stroke. Ann Neurol 64(6):654–663. doi:10.1002/ana.21511
Banerjee R, Vitvitsky V, Garg SK (2008) The undertow of sulfur metabolism on glutamatergic neurotransmission. Trends Biochem Sci 33(9):413–419. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2008.06.006
Halliwell B (2006) Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J Neurochem 97(6):1634–1658. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03907.x
Schulz JB, Lindenau J, Seyfried J, Dichgans J (2000) Glutathione, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Eur J Biochem 267(16):4904–4911. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01595.x
Lee M, Cho T, Jantaratnotai N, Wang YT, McGeer E, McGeer PL (2010) Depletion of GSH in glial cells induces neurotoxicity: relevance to aging and degenerative neurological diseases. FASEB J 24(7):2533–2545. doi:10.1096/fj.09-149997
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS), Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos (FINEP) – IBN Net (Instituto Brasileiro de Neurociências) 01.06.0842-00, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS), and Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia para Excitotoxicidade e Neuroproteção (INCTEN/CNPq).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellaver, B., Souza, D.G., Bobermin, L.D. et al. Guanosine inhibits LPS-induced pro-inflammatory response and oxidative stress in hippocampal astrocytes through the heme oxygenase-1 pathway. Purinergic Signalling 11, 571–580 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9475-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9475-2