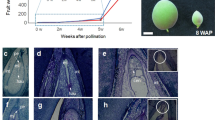
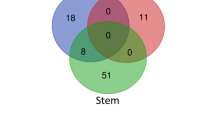
Abstract
Knowledge of post-zygotic hybrid incompatibility is essential to understand speciation. Although the genes and molecular mechanisms involved in hybrid incompatibility are being elucidated in model plants and crops, the information on woody non-model plants is lacking. In the seedlings of a cross between the most famous ornamental cherry cultivar Cerasus × yedoensis ‘Somei-yoshino’ and its closely related wild species Cerasus itosakura, we discovered a hybrid incompatibility characterized by a phenotype in which growth stops after the expansion of the first true leaves and the seedling eventually dies. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms related to this seedling necrosis, we performed a comprehensive expressed gene analysis on normal-growth and necrotic weak-growth (SW) hybrid seedlings. The RNA-seq results showed over 1500 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) specified for the SW. Numerous genes associated with plant defense response, such as pathogenesis-related genes, and several receptor-like protein kinases were included in SW-specific upregulated DEGs. The Gene Ontology enrichment analysis also showed the significant association of “defense response” in SW seedlings. These upregulated defense-related gene expressions were particularly observed in the hypocotyls. On the contrary, the reduction of photosynthesis-related gene expression and reduction in the gene expressions of cell division and cell cycle at specific parts of seedlings were also observed in the SW. Our results suggest that an upregulated defense-related gene expression suppresses the meristem growth and deviation, resulting in growth failure as an autoimmune response in hybrid cherry seedlings.





Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable.
Change history
22 July 2022
Handling editor name correction.
References
Acharya BR, Raina S, Maqbool SB, Jagadeeswaran G, Mosher SL, Appel HM, Schultz JC, Klessig DF, Raina R (2007) Overexpression of CRK13, an Arabidopsis cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase, results in enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae. Plant J 50:488–499. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03064.x
Alcázar R, García AV, Parker JE, Reymond M (2009) Incremental steps toward incompatibility revealed by Arabidopsis epistatic interactions modulating salicylic acid pathway activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:334–339. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0811734106
Bedre R, Mandadi K (2019) GenFam: a web application and database for gene family-based classification and functional enrichment analysis. Plant Direct 3:e00191. https://doi.org/10.1101/pld3.191
Bergelson J, Kreitman M, Stahl EA, Tian D (2001) Evolutionary dynamics of plant R-genes. Science 292:2281–2285. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1061337
Birkenbihl RP, Kracher B, Somssich IE (2017) Induced genome-wide binding of three Arabidopsis WRKY transcription factors during early MAMP-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 29:20–38. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00681
Bomblies K, Weigel D (2007) Hybrid necrosis: autoimmunity as a potential gene-flow barrier in plant species. Nat Rev Genet 8:382–393. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2082
Bomblies K, Lempe J, Epple P, Warthmann N, Lanz C, Dangl JL, Weigel D (2007) Autoimmune response as a mechanism for a Dobzhansky-Muller-type incompatibility syndrome in plants. PLoS Biol 5:e236. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0050236
Cesari S (2018) Multiple strategies for pathogen perception by plant immune receptors. New Phytol 219:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14877
Chae E, Bomblies K, Kim ST, Karelina D, Zaidem M, Ossowski S, Martín-Pizarro C, Laitinen RAE, Rowan BA, Tenenboim H et al (2014) Species-wide genetic incompatibility analysis identifies immune genes as hot spots of deleterious epistasis. Cell 159:1341–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.049
Chen H, Boutros PC (2011) VennDiagram: a package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinformatics 12:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-35
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Gu J (2018) fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34:i884–i890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Chen X, Li C, Wang H, Guo Z (2019) WRKY transcription factors: evolution, binding, and action. Phytopathol Res 1:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42483-019-0022-x
DeYoung BJ, Innes RW (2006) Plant NBS-LRR proteins in pathogen sensing and host defense. Nat Immunol 7:1243–1249. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1410
El-kereamy A, Jayasankar S, Taheri A, Errampalli D, Paliyath G (2009) Expression analysis of a plum pathogenesis related 10 (PR10) protein during brown rot infection. Plant Cell Rep 28:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0612-z
Encinas-Villarejo S, Maldonado AM, Amil-Ruiz F, de los Santos B, Romero F, Pliego-Alfaro F, Muñoz-Blanco J, Caballero JL (2009) Evidence for a positive regulatory role of strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) Fa WRKY1 and Arabidopsis At WRKY75 proteins in resistance. J Exp Bot 60:3043–3065. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp152
Hatano H, Mizuno N, Matsuda R, Shitsukawa N, Park P, Takumi S (2012) Dysfunction of mitotic cell division at shoot apices triggered severe growth abortion in interspecific hybrids between tetraploid wheat and Aegilops tauschii. New Phytol 194:1143–1154. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04125.x
Jones JD, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05286
Jung S, Lee T, Cheng CH, Buble K, Zheng P, Yu J, Humann J, Ficklin SP, Gasic K, Scott K et al (2019) 15 years of GDR: new data and functionality in the Genome Database for Rosaceae. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D1137–D1145. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1000
Kato S, Matsumoto A, Yoshimura K, Katsuki T, Iwamoto K, Kawahara T, Mukai Y, Tsuda Y, Ishio S, Nakamura K et al (2014) Origins of Japanese flowering cherry (Prunus subgenus Cerasus) cultivars revealed using nuclear SSR markers. Tree Genet Genome 10:477–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-014-0697-1
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Li J, Brader G, Palva ET (2004) The WRKY70 transcription factor: a node of convergence for jasmonate-mediated and salicylate-mediated signals in plant defense. Plant Cell 16:319–331. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.016980
Li J, Brader G, Kariola T, Palva ET (2006) WRKY70 modulates the selection of signaling pathways in plant defense. Plant J 46:477–491. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02712.x
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W (2014) featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30:923–930. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AKM (2006) The family 10 of plant pathogenesis-related proteins: their structure, regulation, and function in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 68:3–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2006.06.004
Mauch F, Dudler R (1993) Differential induction of distinct glutathione-S-transferases of wheat by xenobiotics and by pathogen attack. Plant Physiol 102:1193–1201. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.4.1193
Mizuno N, Hosogi N, Park P, Takumi S (2010) Hypersensitive response-like reaction is associated with hybrid necrosis in interspecific crosses between tetraploid wheat and Aegilops tauschii Coss. PLoS ONE 5:e11326. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011326
Mizuno N, Shitsukawa N, Hosogi N, Park P, Takumi S (2011) Autoimmune response and repression of miotic cell division occur in inter-specific crosses between tetraploid wheat and Aegilops tauschii Coss. that show low temperature-induced hybrid necrosis. Plant J 68:114–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04667.x
Montanari S, Brewer L, Lamberts R, Velasco R, Malnoy M, Perchepied L, Guérif P, Durel CE, Bus VGM, Gardiner SE, Chagné D (2016) Genome mapping of postzygotic hybrid necrosis in an interspecific pear population. Hortic Res 3:15064. https://doi.org/10.1038/hortres.2015.64
Morimoto T, Inaoka M, Banno K, Itai A (2020) Genetic mapping of a locus controlling the intergeneric hybridization barrier between apple and pear. Tree Genet Genome 16:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-019-1397-7
Nakano H, Mizuno N, Tosa Y, Yoshida K, Park P, Takumi S (2015) Accelerated senescence and enhanced disease resistance in hybrid chlorosis lines derived from interspecific crosses between tetraploid wheat and Aegilops tauschii. PLoS ONE 10:e0121583. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121583
Ohba H, Kawasaki T, Tanaka H, Kihara H (2007) Flowering cherries of Japan, Newth. Yama-kei Publishers, Tokyo (in Japanese)
Orr HA (1996) Dobzhansky, Bateson, and the genetics of speciation. Genetics 144:1331–1335
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST©) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.9.e36
Pühringer H, Moll D, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Watillon B, Katinger H, da Câmara Machado ML (2000) The promoter of an apple Ypr10 gene, encoding the major allergen Mal d 1, is stress- and pathogen-inducible. Plant Sci 152:35–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00222-8
Rieseberg LH, Blackman BK (2010) Speciation genes in plants. Ann Bot 106:439–455. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq126
Rieseberg LH, Willis JH (2007) Plant speciation. Science 317:910–914. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1137729
Robinson MD, Oshlack A (2010) A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol 11:R25. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r25
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139–140. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Wenger AM, Zehir A, Mesirov JP (2017) Variant review with the integrative genomics viewer. Cancer Res 77:e31–e34. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0337
Rushton PJ, Somssich IE, Ringler P, Shen QJ (2010) WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 15:247–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2010.02.006
Sherif S, Paliyath G, Jayasankar S (2012) Molecular characterization of peach PR genes and their induction kinetics in response to bacterial infection and signaling molecules. Plant Cell Rep 31:697–711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1188-6
Shirasawa K, Esumi T, Hirakawa H, Tanaka H, Itai A, Ghelfi A, Nagasaki H, Isobe S (2019) Phased genome sequence of an interspecific hybrid flowering cherry, ‘Somei-Yoshino’ (Cerasus × yedoensis). DNA Res 26:379–389. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsz016
Shirasawa K, Harada D, Hirakawa H, Isobe S, Kole C (2021) Chromosome-level de novo genome assemblies of over 100 plant species. Breed Sci 71:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.20146
Su W, Sun J, Shimizu K, Kadota K (2019) TCC-GUI: a Shiny-based application for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq count data. BMC Res Notes 12:133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-019-4179-2
Takamatsu K, Iehisa JC, Nishijima R, Takumi S (2015) Comparison of gene expression profiles and responses to zinc chloride among inter-and intraspecific hybrids with growth abnormalities in wheat and its relatives. Plant Mol Biol 88:487–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0338-6
Tian D, Traw MB, Chen JQ, Kreitman M, Bergelson J (2003) Fitness costs of R-gene-mediated resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 423:74–77. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01588
Tian T, Liu Y, Yan H, You Q, Yi X, Du Z, Xu W, Su Z (2017) agriGO v2.0: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W122–W129. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx382
Tochigi K, Shuri K, Kikuchi S, Naoe S, Koike S, Nagamitsu T (2021) Phenological shift along an elevational gradient and dispersal of pollen and seeds maintain a hybrid zone between two cherry tree species. Plant Species Biol 36:230–245. https://doi.org/10.1111/1442-1984.12311
Tsuruta M, Mukai Y (2015) Hybrid seedling inviability locus (HIs1) mapped on linkage group 4 of the Japanese flowering cherry, Cerasus × yedoensis ‘Somei-yoshino.’ Tree Genet Genome 11:88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0910-x
Tsuruta M, Mukai Y (2019) Fine mapping of a locus presumably involved in hybrid inviability (HIs-1) between flowering cherry cultivar Cerasus × yedoensis ‘Somei-yoshino’ and its wild relative C. spachiana. Breed Sci 69:658–664. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.19078
Tsuruta M, Wang C, Kato S, Mukai Y (2017) Map based estimation of the origin of Japanese flowering cherry cultivar, Cerasus × yedoensis ‘Somei-yoshino’ Fujino with an assignment for each chromosome. J Japan For Soc 99:210–213 (In Japanese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.4005/jjfs.99.210
Ülker B, Mukhtar MS, Somssich IE (2007) The WRKY70 transcription factor of Arabidopsis influences both the plant senescence and defense signaling pathways. Planta 226:125–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0474-y
van Hulten M, Pelser M, Van Loon LC, Pieterse CM, Ton J (2006) Costs and benefits of priming for defense in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:5602–5607. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0510213103
van Loon LC, Rep M, Pieterse CM (2006) Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:135–162. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.070505.143425
Verde I, Jenkins J, Dondini L, Micali S, Pagliarani G, Vendramin E, Paris R, Aramini V, Gazza L, Rossini L et al (2017) The Peach v2.0 release: high-resolution linkage mapping and deep resequencing improve chromosome-scale assembly and contiguity. BMC Genomics 18:225. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3606-9
Wagner U, Edwards R, Dixon DP, Mauch F (2002) Probing the diversity of the Arabidopsis glutathione S-transferase gene family. Plant Mol Biol 49:515–532. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015557300450
Wan WL, Kim ST, Castel B, Charoennit N, Chae E (2021) Genetics of autoimmunity in plants: an evolutionary genetics perspective. New Phytol 229:1215–1233. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16947
Wang J, Liu W, Zhu D, Hong P, Zhang S, Xiao S, Tan Y, Chen X, Xu L, Zong X et al (2020) Chromosome-scale genome assembly of sweet cherry (Prunus aviumL.) cv Tieton obtained using long-read and Hi-C sequencing. Hortic Res 7:122. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-020-00343-8
Watanabe K, Yoshikawa K (1967) Notes on variation and self-incompatibility in Japanese flowering cherries. Bot Mag Tokyo 80:257–260. https://doi.org/10.15281/jplantres1887.80.257
Xu X, Chen C, Fan B, Chen Z (2006) Physical and functional interactions between pathogen-induced Arabidopsis WRKY18, WRKY40, and WRKY60 transcription factors. Plant Cell 18:1310–1326. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.037523
Yadeta KA, Elmore JM, Creer AY, Feng B, Franco JY, Rufian JS, He P, Phinney B, Coaker G (2017) A cysteine-rich protein kinase associates with a membrane immune complex and the cysteine residues are required for cell death. Plant Physiol 173:771–787. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01404
Yamamoto E, Takashi T, Morinaka Y, Lin S, Wu J, Matsumoto T, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Ashikari M (2010) Gain of deleterious function causes an autoimmune response and Bateson-Dobzhansky-Muller incompatibility in rice. Mol Genet Genomics 283:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-010-0514-y
Ye J, Coulouris G, Zaretskaya I, Cutcutache I, Rozen S, Madden T (2012) Primer-BLAST: a tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinformatics 13:134. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-13-134
Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A (2010) Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol 11:R14. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14
Ziadi S, Poupard P, Brisset MN, Paulin JP, Simoneau P (2001) Characterization in apple leaves of two subclasses of PR-10 transcripts inducible by acibenzolar-S-methyl, a functional analogue of salicylic acid. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 59:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1006/pmpp.2001.0343
Zubini P, Zambelli B, Musiani F, Ciurli S, Bertolini P, Baraldi E (2009) The RNA hydrolysis and the cytokinin binding activities of PR-10 proteins are differentially performed by two isoforms of the Pru p 1 peach major allergen and are possibly functionally related. Plant Physiol 150:1235–1247. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.139543
Zuo C, Liu H, Lv Q, Chen Z, Tian Y, Mao J, Chu M, Ma Z, An Z, Chen B (2020) Genome-wide analysis of the apple (Malus domestica) cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase (CRK) family: annotation, genomic organization, and expression profiles in response to fungal infection. Plant Mol Biol Rep 38:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-019-01179-w
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the staff of the University of Tokyo Tanashi Forest for providing the cherry trees for artificial pollination; Dr. S-I. Miyazawa, Senior Researcher of FFPRI, for the advising in qPCR analysis; and Dr. D. Tsugama, Associate Professor of ARC-BRES, the University of Tokyo, for the kind support in the first step of next-generation sequencing analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP18K14489.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.T. designed and carried out the experiments and wrote draft manuscripts. C.L. and Y.M. provided critical advice for experiments and analysis. All authors discussed the results and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Data Archiving Statement
The raw sequence data of RNA-seqs were deposited in the DDBJ Sequence Read Archive (DRA) with accession numbers DRA 011866 and DRA011867.
Additional information
Communicated by: C. Dardick
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuruta, M., Lian, C. & Mukai, Y. Upregulation of defense-related gene expressions associated with lethal growth failure in the hybrid seedlings of Japanese flowering cherry. Tree Genetics & Genomes 18, 21 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-022-01552-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-022-01552-z