Abstract
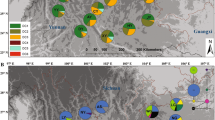
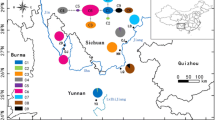
Dalbergia cochinchinensis Pierre ex Laness. (Fabaceae) is a commercially important tree in Southeast Asia. Although this species is under legal protections, illegal logging and disorderly developments have reduced its populations, and the conservation of this species is currently of much concern. In this study, we determined nucleotide sequences at six chloroplasts and ten nuclear loci in four populations of D. cochinchinensis in Cambodia, followed by population genetic analyses. The average silent nucleotide diversity over the nuclear loci, excluding one with an exceptionally high value, was 0.0057 in the entire population, and the mean F ST across the nuclear loci between each population pair was between 0.135 and 0.467. Thus, the nucleotide diversity in the studied populations was not low compared with that in other tree species, and the level of population differentiation was high. Neutrality test statistics indicated a recent reduction of population size and a subdivision of the population within this species. The divergence times and migration rates were estimated with a likelihood-based method assuming the isolation with migration model. Based on the results, the three populations split 68,000–138,000 years ago, possibly corresponding to the start of the last glacial period, and the level of gene flow among the populations was very low thereafter. Moreover, after the split, population sizes were reduced considerably. Notably, the nucleotide diversity in an insertion sequence in a noncoding region of nuclear C4H was much higher than the mean nucleotide diversity in silent sites across other nuclear genes, indicating that the region was affected by selection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B Methodol 57(1):289–300. https://doi.org/10.2307/2346101
Chen AH, Chai YR, Li JN, Chen L (2007) Molecular cloning of two genes encoding cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) from oilseed rape (Brassica Napus). J Biochem Mol Biol 40(2):247–260
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA (2000) TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol Ecol 9(10):1657–1659. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.2000.01020.x
Cook GC, Jones RT (2012) Paleoclimate dynamics in continental Southeast Asia over the last ~30,000 Cal yrs BP. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 339–341:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.03.025
Core Team R (2016) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. In: R foundation for statistical computing, Vienna. URL https://www.R-project.org/
Demesure B, Sodzi N, Petit RJ (1995) A set of universal primers for amplification of polymorphic non-coding regions of mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA in plants. Mol Ecol 4(1):129–131. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.1995.tb00201.x
Dunning LT, Savolainen V (2010) Broad-scale amplification of matK for DNA barcoding plants, a technical note. Bot J Linn Soc 164(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.2010.01071.x
Earl DA, vonHoldt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4(2):359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14(8):2611–2620
Fay JC, Wu CI (2000) Hitchhiking under positive Darwinian selection. Genetics 155(3):1405–1413
Fu YX (1997) Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 147(2):915–925
Fu YX, Li WH (1993) Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations. Genetics 133(3):693–709
Hamilton MB (1999) Four primer pairs for the amplification of chloroplast intergenic regions with intraspecific variation. Mol Ecol 8(3):521–523. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.1999.00510.x
Hey J (2010) Isolation with migration models for more than two populations. Mol Biol Evol 27:905–920
Hey J, Nielsen R (2004) Multilocus methods for estimating populations sizes, migration rates and divergence time, with application to the divergence of Drosophila pseudooscura and D. persimillis. Genetics 167:747–760
Hien VTT, Phong DT (2012) Genetic diversity among endangered rare Dalbergia cochinchinensis (Fabaceae) genotypes in Vietnam revealed by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and inter simple sequence repeats (ISSR) markers. Afr J Biotechnol 11(35):8632–8644. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.3598
Hubisz MJ, Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2009) Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol Ecol Resour 9:1322–1332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02591.x
Hudson RR, Slatkin M, Maddison WP (1992) Estimation of levels of gene flow from DNA sequence data. Genetics 132:583–589
Iwanaga H, Teshima KM, Khatab IA, Inomata N, Finkeldey R, Siregar IZ, Szmidt AE (2012) Population structure and demographic history of a tropical lowl and rainforest tree species Shorea parvifolia (Dipterocarpaceae) from southeastern Asia. Ecol Evol 2(7):1663–1675. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.284
Kimura M, Crow JF (1964) The number of alleles that can be maintained in a finite population. Genetics 49:725–738
Kopelman NM, Mayzel J, Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA, Mayrose I (2015) CLUMPAK: a program for identifying clustering modes and packaging population structure inferences across K. Mol Ecol Resour 15(5):1179–1191. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12387
Kress WJ, Erickson DL (2007) A two-locus global DNA barcode for land plants: the coding rbcL gene complements the non-coding trnH-psbA spacer region. PLoS One 2(6):e508. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000508
Lavin M, Herendeen PS, Wojciechowski MF (2005) Evolutionary rates analysis of Leguminosae implicates a rapid diversification of lineages during the tertiary. Syst Biol 54(4):575–594. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150590947131
Lee C, Wen J (2004) Phylogeny of panax using chloroplast trnC-trnD intergenicregion and the utility of trnC-trnD in interspecific studies of plants. Mol Phylogenet Evol 31(3):894–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2003.10.009
Levin RA, Wagner WL, Hoch PC, Nepokroeff M, Pires JC, Zimmer EA, Sytsma KJ (2003) Family-level relationships of Onagraceae based on chloroplast rbcL and ndhF data. Am J Bot 90(1):107–115. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.90.1.107
Lewis G, Schrire B, Mackinder B, Lock M (2005) Legumes of the world. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25(11):1451–1452. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187; 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187
Louys J, Meijaard E (2010) Palaeoecology of southeast Asian megafauna-bearing sites from the Pleistocene and a review of environmental changes in the region. J Biogeogr 37(8):1432–1449. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2010.02297.x
Lynch M (2006) The origins of eukaryotic gene structure. Mol Biol Evol 23(2):450–468. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msj050
Meaux J, JY H, Tartler U, Goebel U (2008) Structurally different alleles of the ath-MIR824 microRNA precursor are maintained at high-frequency in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(26):8994–8999. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0803218105
Miyazawa Y, Tateishi M, Komatsu H, Ma V, Kajisa T, Sokh H, Mizoue N, Kumagai T (2014) Tropical tree water use under seasonal waterlogging and drought in central Cambodia. J Hydrol 515:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.04.049
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8(19):4321–4325. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Nielsen R, Beaumont MA (2009) Statistical inferences in phylogeogrphy. Mol Ecol 18:2034–1047
Niyomdham C, Pham Hoang Hô, Dy Phon P, Vidal JE (1997) Flore du Cambodge du Laos et du Vietnam vol. 29, Leguminoseae-Papilionoïdeae Dalbergieae. Paris: Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle
Nozawa M, Miura S, Nei M (2012) Origins and evolution of microRNA genes in plant species. Genome Biol Evol 4(3):230–239. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evs002
Penny D (2001) A 40,000 year palynological record from north-east Thailand: implications for biogeography and paleo-environmental reconstruction. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 171:97–128
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Simonsen KL, Churchill GA, Aquadro CF (1995) Properties of statistical tests of neutrality for DNA polymorphism data. Genetics 141:413–429
So T (2011) Improving reforestation success of high-value and key forest species by direct seeding in Southeast Asia and Western Australia. School of Biological Sciences and Biotechnology, Faculty of Science, Engineering and Sustainability, Murdoch University. Thesis
Soonhuae P (1994) Estimation of genetic variation in Thailand rosewood (Dalbergia cochinchinensis Pierre). Kasetsart University, Thailand. Thesis. doi:10.14288/1.0099229Taberlet
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991) Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol 17(5):1105–1109. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037152
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123(3):585–595
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121; 10.1093/molbev/msr121
The IUCN red list of threatened species. Version 2013.2. http://www.iucnredlist.org/
White JC, Penny D, Kealhoefer L, Maloney B (2004) Vegetation changes from the late Pleistocene through the Holocene from three areas of archaeology significance in Thailand. Quat Int 113:111–132
Yahara T, Javadi F, Onoda Y et al (2013) Global legume diversity assessment: concepts, key indicators and strategies. Taxon 62:249–266. 10.12705/622.12
Yooyuen R, Duangjai S, Changtragoon S (2012) Chloroplast DNA phylogeography of Dalbergia cochinchinensis Pierre in Thailand and Laos. (ISSN 1016-3263, ISBN 978-3-902762-15-3)
Acknowledgements
We cordially thank the Forestry Administration of Cambodia for the permits and support of our fieldwork in Cambodia.
Data archiving statement
All sequences are deposited with EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ under the accession numbers AB850618–AB850637 for the chloroplast loci and KX428531–KX429590 for the nuclear loci.
Funding
The Environment Research and Technology Development Fund (S9) of the Ministry of Environment, Japan, and JSPS KAKENHI grant numbers JP26291082 and JP16H02553 supported this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. B. Neale
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 516 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moritsuka, E., Chhang, P., Tagane, S. et al. Genetic variation and population structure of a threatened timber tree Dalbergia cochinchinensis in Cambodia. Tree Genetics & Genomes 13, 115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1199-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1199-8