Abstract
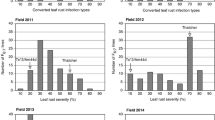
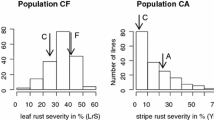
Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTL) for resistance to Melampsora leaf rust was performed in two willow families: the progeny from a backcross between Salix viminalis and a hybrid S. viminalis × Salix schwerinii (population S1), and the F1 progeny of a cross between two S. viminalis (population S3). Disease levels were scored in the field for three consecutive years. In the laboratory, five different rust strains were sprayed onto leaf disks and the following resistance components were scored: latent period, diameter and number of uredinia, and flecking. One major QTL and 14 smaller were identified in the S1 host population. One rust strain, that represents a Melampsora form with limited incidence on S. viminalis, showed lower aggressiveness to the S1 host population together with a different pattern in QTLs. In the S3 host population, we detected 13 QTLs for rust resistance, of which two were located to the same genomic regions as those found for the S1 population. We showed that the strongest QTL co-segregated with a gene homologous to a known Toll/interleukin receptor-nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat resistance gene in poplar. The importance of the identified QTLs is discussed in relation to breeding for durable resistance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åhman I (1997) Growth, herbivory and disease in relation to gender in Salix viminalis L. Oecologia 111:61–68
Åhman I, Bertholdsson N-O (2001) Biomass willow cultivars and local variation in attacks by herbivores and rust. Aspects Appl Biol 65:205–214
Berlin S, Lagercrantz U, von Arnold S, Öst T, Rönnberg-Wästljung AC (2010) High-density linkage mapping and evolution of paralogs and orthologs in Salix and Populus. BMC Genomics 11:129
Dowkiw A, Bastien C (2004) Characterization of two major genetic factors controlling quantitative resistance to Melampsora larici-populina leaf rust in hybrid poplars: strain specificity, field expression, combined effects, and relationship with a defeated qualitative resistance gene. Phytopathology 94:1358–1367
Dowkiw A, Bastien C (2007) Presence of defeated qualitative resistance genes frequently has a major impact on quantitative resistance to Melampsora larici-populina leaf rust in P. × interamericana hybrid poplars. Tree Genet Genomes 3:261–274
Dowkiw A, Husson C, Frey P, Pinon J, Bastien C (2003) Partial resistance to Melampsora larici-populina leaf rust in hybrid poplars: genetic variability in inoculated excised leaf disk bioassay and relationship with complete resistance. Phytopathology 93:421–427
Dowkiw A, Voisin E, Bastien C (2010) Potential of Eurasian poplar rust to overcome a major quantitative resistance factor. Plant Pathol 59:523–534
Höglund S, Larsson S, Wingsle G (2005) Both hypersensitive and non-hypersensitive responses are associated with resistance in Salix viminalis against the gall midge Dasineura marginemtorquens. J Exp Bot 56:3215–3222
Jorge V, Dowkiw A, Faivre-Rampant P, Bastien C (2005) Genetic architecture of qualitative and quantitative Melampsora larici-populina leaf rust resistance in hybrid poplar: genetic mapping and QTL detection. New Phytol 167:113–127
Knott SA, Neale DB, Sewell MM, Haley CS (1997) Multiple marker mapping of quantitative trait loci in an outbred pedigree of loblolly pine. Theor Appl Genet 94:810–820
Kohler A, Rinaldi C, Duplessis S, Baucher M, Geelen D, Hellsten U, Duchaussoy F, DiFazio S, Boerjan W, Martin F (2008) Genome-Wide identification of NBS resistance genes in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Mol Biol 66:619–636
Lascoux M, Ramstedt M, Åström B, Gullberg U (1996) Components of resistance of leaf rust (Melampsora laricii-epitea Kleb./Melampsora ribesii-viminalis Kleb.) in Salix viminalis L. Theor Appl Genet 93:1310–1318
Lefèvre F, Pichot C, Pinon J (1994) Intra- and interspecific inheritance of some components of the resistance to leaf rust (Melampsora larici-epitea Kleb.) in poplars. Theor Appl Genet 88:501–507
Lefèvre F, Goué-Mourier MC, Faivre-Rampant P, Villar M (1998) A single gene cluster controls incompatibility and partial resistance to various Melampsora larici-populina races in hybrid poplars. Phytopathology 88:156–163
McCracken AR, Dawson WM (1998) Short rotation coppice willow in Northern Ireland since 1973: development of the use of mixtures in the control of foliar rust (Melampsora spp.). Eur J For Pathol 28:241–250
McDonald B, Linde C (2002) Pathogen population genetics, evolutionary potential, and durable resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:349–379
Pei MH, Royle DJ, Hunter T (1996) Pathogen specialization in Melampsora epitea var. epitea on Salix. Plant Pathol 45:679–690
Pei MH, Yuan ZW, Hunter T, Ruiz C (2000) Heterogeneous nature of a’new’ pathotype of Melampsora rust on Salix revealed by AFLP. Eur J Plant Pathol 106:771–779
Pei MH, Kevin Lindegaard K, Ruiz C, Bayon C (2008) Rust resistance of some varieties and recently bred genotypes of biomass willows. Biomass Bioenerg 32:453–459
Pei MH, Ruiz C, Shield I, Macalpine W, Lindegaard K, Bayon C, Karp A (2010) Mendelian inheritance of rust resistance to Melampsora larici-epitea in crosses between Salix sachalinensis and S. viminalis. Plant Pathol 59:862–872
Pinon J, Frey P (2005) Interactions between poplar clones and Melampsora populations and their implications for breeding for durable resistance. In: Pei MH, McCracken AR (eds) Rust diseases of Willow and Poplar. CAB International, Wallingford, UK, pp 139–154
Pinon J, van Dam C, Genetet I, de Kam M (1987) Two pathogenic races of Melampsora larici-populina in north-western Europe. Eur J For Path 17(1):47–53
Rönnberg-Wästljung AR, Samils B, Tsarouhas V, Gullberg U (2008) Resistance to Melampsora larici-epitea leaf rust in Salix: analyses of quantitative trait loci. J Appl Genet 49:321–331
Samils B, Lagercrantz U, Lascoux M, Gullberg U (2001) Genetic structure of Melampsora epitea populations in Swedish Salix viminalis plantations. Eur J Plant Pathol 107:399–409
Samils B, Lagercrantz U, Gullberg U (2002) Genetic relationships among genetically distinct forms of Melampsora larici-epitea and related species based on AFLP data. Forest Pathol 32:379–386
Tsarouhas V, Gullberg U, Lagercrantz U (2002) An AFLP and RFLP linkage map and quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis of growth traits in Salix. Theor Appl Genet 105:277–288
Van Ooijen J (2009) MapQTL 6. Software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations of diploid species. Kyazma, Wageningen, Netherlands
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap version 3.0: software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen, Netherlands
van Ooijen JW, Boer MP, Jansen RC, Maliepaard C (2002) MapQTL 4.0. Software for the calculation of QTL positions on genetic maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen, Netherlands
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: Software for the Graphical Presentation of Linkage Maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Yin TM, Di Fazio SP, Gunter LE, Jawdy SS, Boerjan W, Tuskan GA (2004) Genetic and physical mapping of Melampsora rust resistance genes in Populus and characterization of linkage disequilibrium and flanking genomic sequence. New Phytol 164:95–105
Acknowledgment
We highly appreciate the assistance by Dr. Merje Toome, Solveig Höglund, and Marika Pettersson in the infection experiment work, the assistance by Urban Pettersson in the greenhouse work and by Dr. Katarina Ihrmark and Dr. Rena Gadjieva in the sequencing work. The study was supported by grants from the Swedish Energy Agency, Lantmännen Agroenergi AB and the Faculty of Natural Resources and Agricultural Sciences at the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W. Boerjan
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Disease resistance-like proteins in genomic regions of Populus trichocarpa corresponding to genomic regions of leaf rust resistance QTLs in the Salix genome (DOC 81 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samils, B., Rönnberg-Wästljung, AC. & Stenlid, J. QTL mapping of resistance to leaf rust in Salix . Tree Genetics & Genomes 7, 1219–1235 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-011-0408-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-011-0408-0