Abstract
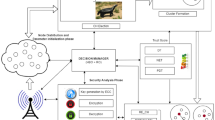
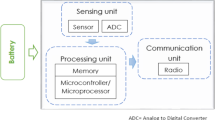
Many application domains require that sensor node to be deployed in harsh or hostile environments, such as active volcano area tracking endangered species, etc. making these nodes more prone to failures. The most challenging problem is monitoring the illegal movement within the sensor networks. Attacker prefers mobile malicious node because by making the diversity of path intruder maximize his impact. The emerging technology of sensor network expected Intrusion detection technique for a dynamic environment. In this paper, a defective mechanism based on three-step negotiation is performed for identifying the mobile malicious node using the mobile agent. In many approaches, the multi-mobile agents are used to collect the data from all the sensor nodes after verification. But it is inefficient to verify all the sensor nodes (SNs) in the network, because of mobility, energy consumption, and high delay. In the proposed system this can be solved by grouping sensor nodes into clusters and a single mobile agent performs verification only with all the cluster heads instead of verifying all the SNs. The simulation result shows the proposed system shows a better result than the existing system.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fissaoui, M. E., Beni-Hssane, A., & Saadi, M. (2018). Multi-mobile agent itinerary planning-based energy and fault aware data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-018-1099-0
Chen, M., Yang, L. T., Kwon, T., Zhou, L., & Jo, M. (2011). Itinerary planning for energy-efficient agent communications in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 60(7), 3290–3299.
Chen, M., Kwon, T., Yuan, Y., Choi, Y., & Leung, V. C. M. (2007). Mobile agent-based directed diffusion in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP Journal Application on Signal Processing. https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/3687
Lohani, D., & Varma, S. (2016). Energy efficient data aggregation in mobile agent based wireless sensor network. Wireless Person Communication, 89(4), 1165–1176.
Gandhimathi, L., & Murugaboopathi, G. (2016). Cross layer intrusion detection and prevention of multiple attacks in wireless sensor network using mobile agent. In International conference on communication and embedded systems. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICES.2016.7518935.
Xu, Y., & Qi, H. (2007). Dynamic mobile agent migration in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing, 2(1/2), 73–82.
Lingaraj, K., Biradar, R. V., & Patil, V. C. (2017). Eagilla: An enhanced mobile agent middleware for wireless sensor networks. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 57(3), 1197–1204.
Khaleghi, B., Khamis, A., Karray, F. O., & Razavi, S. N. (2013). Multisensor data fusion: A review of the state-of-the-art. Information Fusion, 14(1), 28–44.
Xu, Y., & Qi, H. (2008). Mobile agent migration modeling and design for target tracking in wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Network, 6(1), 1–16.
Kai Lin, M., Chen, S., Zeadally, J., & Rodrigues, J. P. C. (2012). Balancing energy consumption with mobile agents in wireless sensor networks. Future Generation Computer Systems, 28(2), 446–456.
Zhang, S., Sun, Y., & Huang, H. (2012). Cooperative data processing algorithm based on mobile agent in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 8(6), 1–9.
Yang, T., Mu, D., Hu, W., & Zhang, H. (2014). Energy-efficient border intrusion detection using wireless sensors network. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1499-2014-46
Wu, Q., Rao, N. S., Barhen, J., Iyengar, S. S., Vaishnavi, V. K., Qi, H., & Chakrabarty, K. (2004). On computing mobile agent routes for data fusion in distributed sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 16(6), 740–753.
Hairong, Q., & Feiyi, W. (2001). Optimal itinerary analysis for mobile agents in ad hoc wireless sensor networks. University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Advanced Networking Group MCNC. Research Triangle Park, 18(5), 147–153.
Bendjima, M., & Feham, M. (2012). Optimal itinerary planning for mobile multiple agents in WSN. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications. https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2012.031103.
Chen, J., Li, J., & Ten, HLai. (2013). Trapping mobile targets in wireless sensor networks: An energy-efficient perspective. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 62(7), 3287–3300.
Ho, J. W., Wright, M., & Das, S. K. (2012). Distributed detection of mobile malicious node attacks in wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 10(3), 512–523.
Bajaber, F., & Awan, I. (2008). Dynamic/static clustering protocol for wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the IEEE second UKSIM European symposium on computer modeling and simulation (pp. 524–529).
Tayyab, K., et al. (2019). A novel and comprehensive trust estimation clustering based approach for large scale wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2914769
Ismail, A., & Amin, R. (2019). Malicious cluster head detection mechanism in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 108, 2117–2135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06512-w
Pitchaimanickam, B., & Murugaboopathi, G. (2020). A hybrid firefly algorithm with particle swarm optimization for energy efficient optimal cluster head selection in wireless sensor networks. Neural Computing & Applications, 32, 7709–7723.
Narayanan, S. S., & Murugaboopathi, G. (2020). Prevention of rushing attack in MANET using threshold-based approach. International Journal of Internet Technology and Secured Transactions, 10(5), 576–584.
Sunder, A. J. C., & Shanmugam, A. (2019). Jensen–Shannon divergence based independent component analysis to detect and prevent black hole attacks in healthcare WSN. Wireless Personal Communications, 107, 1607–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06347-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandhimathi, L., Murugaboopathi, G. Mobile Malicious Node Detection Using Mobile Agent in Cluster-Based Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 117, 1209–1222 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07918-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07918-7