Abstract
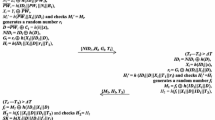
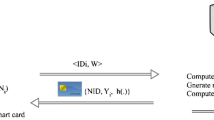
The telecare medical information system (TMIS) offers remote healthcare services to the patients at their doorstep. Including this serenity, it is compulsory to preserve privacy and to give guaranty to the patients for secured TMIS communication. Authentication protocols are usually exploited to ensure privacy and protect communication between patients and remote assistance. Currently, we observe the inaccuracy of an authentication protocol for TMIS. The scheme is recently proposed by Qiu et al. to realize healthcare services. We find that their protocol is vulnerable to offline password guessing, replay, and anonymity violation attacks. To avoid these weaknesses, we have developed an improved biometric-based protocol. Our proposed protocol is capable to prevent the said attacks. We validate the security of our proposed protocol using Burrows–Abadi–Needham logic. We compare the performance of the proposed protocol with the preceding protocols and conclude that the proposed protocol is more secure and efficient as compared to its former counterparts.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lamport, L. (1981). Password authentication with insecure communication. Communications of the ACM, 24, 770–771.
Shimizu, A. (1990). A dynamic password authentication method by one-way function. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, J73-D-I, 630–636.
Shimizu, A., Horioka, T., & Inagaki, H. (1998). A password authentication method for contents communication on the Internet. IEICE Transactions on Communication, E81-B, 1666–1763.
Haller, N. M. (1995). The S/KEY one-time password system. RFC1760.
Mitchell, C. J., & Chen, L. (1996). Comments on the S/KEY user authentication scheme. ACMOSR (12–16)
Hwang, M. S., & Li, L. H. (2000). A new remote user authentication scheme using smart card. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 46, 28–30.
Lovis, C., Baud, R. H., & Scherrer, R. H. (1998). Internet integrated in the daily medical practice within an electronic patient record. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 28(5), 567–579.
Lambrinoudakis, C., & Gritzalis, S. (2000). Managing medical and insurance information through a smart-card-based information system. Journal of Medical Systems, 24(4), 213–234.
Elberg, P. B. (2001). Electronic patient records and innovation in health care services. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 64(2–3), 201–205.
Wu, Z. Y., Lee, Y. C., Lai, F., Lee, H. C., & Chun, Y. (2012). A secure authentication scheme for telecare medicine information systems. Journal of Medical Systems, 36(3), 1529–1535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9614-9.
Xu, X., Zhu, P., Wen, Q., Jin, Z., Zhang, H., & He, L. (2013). A secure and efficient authentication and key agreement scheme based on ECC for telecare medicine information systems. Journal of Medical Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-013-9994-8.
Islam, S. H., & Khan, M. K. (2014). Cryptanalysis and improvement of authentication and key agreement protocols for telecare medicine information systems. Journal of Medical Systems, 38(10), 135.
Chaudhry, S. A., Naqvi, H., Shon, T., Sher, M., & Farash, M. S. (2015). Cryptanalysis and improvement of an improved two factor authentication protocol for telecare medical information systems. Journal of Medical Systems, 39(6), 66.
Qiu, S., Xu, G., Ahmad, H., & Wang, L. (2018). A robust mutual authentication scheme based on elliptic curve cryptography for telecare medical information systems. IEEE Access, 6, 7452–7463.
Jin, A. T. B., Ling, D. N. C., & Goh, A. (2004). Biohashing: Two factor authentication featuring fingerprint data and tokenised random number. Pattern Recognition, 37(11), 2245–2255.
Nanni, L., Brahnam, S., & Lumini, A. (2011). Biohashing applied to orientation-based minutia descriptor for secure fingerprint authentication system. Electronics Letters, 47(15), 851–853.
Moon, J., Choi, Y., Kim, J., & Won, D. (2016). An improvement of robust and efficient biometrics based password authentication scheme for telecare medicine information systems using extended chaotic maps. Journal of Medical Systems, 40(3), 70.
Wang, D., He, D., Wang, P., & Chu, C.-H. (2015). Anonymous two-factor authentication in distributed systems: Certain goals are beyond attainment. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 12(4), 428–442.
Wang, D., & Wang, P. (2018). Two birds with one stone: Two-factor authentication with security beyond conventional bound. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 15(4), 708–722.
Burrows, M., Abadi, M., & Needham, R. M. (1989). A logic of authentication. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 426(1871), 233–271.
He, D. (2012). An efficient remote user authentication and key agreement protocol for mobile client–server environment from pairings. Ad Hoc Networks, 10(6), 1009–1016.
Kumari, S., Chaudhary, P., Chen, C. M., & Khan, M. K. (2019). Questioning key compromise attack on Ostad-Sharif et al.’s authentication and session key generation scheme for healthcare applications. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2905731.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, S., Renuka, K. Design of a Password Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme to Access e-Healthcare Services. Wireless Pers Commun 117, 27–45 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06755-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06755-7