Abstract
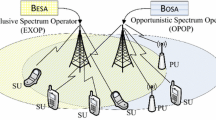
Energy and spectrum optimization for massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO) cognitive femtocell based fifth generation (5G) mobile network is developed using auction game. In 5G massive MIMO, multiple numbers of antennas are used to transmit the signal with same time frequency to maximize the number of users, who can communicate with less number of channels. Cognitive radio network (CRN) also increases spectrum efficiency by sharing primary users channel to transmit data for secondary users. In this article, cognitive femtocell base stations are treated as secondary base stations to win a channel by using auction game with utility function. Femtocell base stations bid for a channel with pricing value to the MIMO base station spectrum manager and the spectrum manager allocates spectrum to the femtocell base station based on maximum pricing value. Opportunistic spectrum access by femtocell using cognitive approach decreases number of active antennas in massive MIMO based network which reduces energy consumption. Simulation results show that the proposed network reduces ~ 70% power consumptions than the existing CRN and only MIMO CRN based strategies. Simulation results also presents that the massive MIMO cognitive femtocell network increases signal to interference plus noise ratio and spectral efficiency ~ 13% and ~ 20% respectively than the existing CRN and only MIMO CRN based approaches.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agiwal, M., Roy, A., & Saxena, N. (2016). Next generation 5G wireless networks: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 18(3), 1617–1655.
Ramazanali, H., Mesodiakaki, A., Vinel, A., & Verikoukis, C. (2016). Survey of user association in 5G HetNets. In 2016 8th IEEE Latin-American conference on communications (LATINCOM) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Mukherjee, A., Bhattacherjee, S., Pal, S., & De, D. (2013). Femtocell based green power consumption methods for mobile network. Computer Networks, 57(1), 162–178.
Han, F., Zhao, S., Zhang, L., & Wu, J. (2016). Survey of strategies for switching off base stations in heterogeneous networks for greener 5G systems. IEEE Access, 4, 4959–4973.
Muirhead, D., Imran, M. A., & Arshad, K. (2016). A survey of the challenges, opportunities and use of multiple antennas in current and future 5G small cell base stations. IEEE Access, 4, 2952–2964.
Zhang, L., Xiao, M., Wu, G., Alam, M., Liang, Y. C., & Li, S. (2017). A Survey of Advanced Techniques for Spectrum Sharing in 5G Networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 24(5), 44–51.
Tang, M., & Xin, Y. (2016). Energy efficient power allocation in cognitive radio network using coevolution chaotic particle swarm optimization. Computer Networks, 100, 1–11.
Bengtsson, E. L., Rusek, F., Malkowsky, S., Tufvesson, F., Karlsson, P. C., & Edfors, O. (2017). A Simulation Framework for Multiple-Antenna Terminals in 5G Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Access, 5, 26819–26831.
Elderini, T., Kaabouch, N., & Reyes, H. (2017). Channel quality estimation metrics in cognitive radio networks: a survey. IET Communications, 11(8), 1173–1179.
Wang, H., Song, R., & Leung, S. H. (2016). Optimal uplink access in cognitive femtocell networks with adaptive modulation. IEEE Communications Letters, 20(5), 1050–1053.
Ho, T. M., Tran, N. H., Kazmi, S. A., & Hong, C. S. (2016). Distributed resource allocation for interference management and QoS guarantee in underlay cognitive femtocell networks. In Network operations and management symposium (APNOMS), 2016 18th Asia-Pacific (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Liu, Z., Li, S., Ma, K., Guan, X., & Li, X. (2017). Robust power allocation based on hierarchical game with consideration of different user requirements in two-tier femtocell networks. Computer Networks, 122, 179–190.
Hao, W., & Yang, S. (2017). Small cell cluster-based resource allocation for wireless backhaul in two-tier heterogeneous networks with massive MIMO. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(1), 509–523.
Zhang, Q., Yang, H. H., Quek, T. Q., & Lee, J. (2017). Heterogeneous Cellular Networks with LoS and NLoS Transmissions—The Role of Massive MIMO and Small Cells. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 16(12), 7996–8010.
Liu, Y., & Dong, L. (2014). Spectrum sharing in MIMO cognitive radio networks based on cooperative game theory. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(9), 4807–4820.
Liu, D., Wang, L., Chen, Y., Zhang, T., Chai, K. K., & Elkashlan, M. (2015). Distributed energy efficient fair user association in massive MIMO enabled HetNets. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(10), 1770–1773.
Guozhen, X., An, L., Wei, J., Haige, X., & Wu, L. (2015). Energy-efficient beamforming for two-tier massive MIMO downlink. China Communications, 12(10), 64–75.
Cui, M., Hu, B. J., Li, X., Chen, H., Hu, S., & Wang, Y. (2017). Energy-efficient power control algorithms in massive MIMO cognitive radio networks. IEEE Access, 5, 1164–1177.
Cui, M., Hu, B. J., Tang, J., & Wang, Y. (2017). Energy-efficient Joint Power Allocation in Uplink Massive MIMO Cognitive Radio Networks with Imperfect CSI. IEEE Access, 5, 27611–27621.
Hao, W., Muta, O., Gacanin, H., & Furukawa, H. (2017). Power allocation for massive MIMO cognitive radio networks with pilot sharing under SINR requirements of primary users. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(2), 1174–1186.
Zhang, H., Jiang, C., Cheng, J., Peng, M., & Leung, V. C. (2017). Game Theory for 5G Wireless Networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 22(3), 526–528.
Eraslan, B., Gozupek, D., & Alagoz, F. (2011). An auction theory based algorithm for throughput maximizing scheduling in centralized cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 15(7), 734–736.
Wang, X., Li, Z., Xu, P., Xu, Y., Gao, X., & Chen, H. H. (2010). Spectrum sharing in cognitive radio networks—An auction-based approach. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 40(3), 587–596.
Jayaweera, S. K., Bkassiny, M., & Avery, K. A. (2011). Asymmetric cooperative communications based spectrum leasing via auctions in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(8), 2716–2724.
Chen, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, B., & Liu, K. R. (2010). Spectrum auction games for multimedia streaming over cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 58(8), 2381–2390.
Feng, M., Mao, S., & Jiang, T. (2017). BOOST: Base station on-off switching strategy for green massive MIMO HetNets. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 16(11), 7319–7332.
Hossain, M. A., Cavdar, C., Bjornson, E., & Jantti, R. (2017). Energy saving game for massive MIMO: Coping with daily load variation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(3), 2301–2313.
Badoi, C. I., Prasad, N., Croitoru, V., & Prasad, R. (2011). 5G based on cognitive radio. Wireless Personal Communications, 57(3), 441–464.
Prasad, R. (2014). 5G: 2020 and beyond. London: River Publishers.
Anwar, S., & Prasad, R. (2018). Framework for future telemedicine planning and infrastructure using 5G technology. Wireless Personal Communications, 100, 1–16.
Prasad, R. (2015). 5G Revolution through WISDOM. Wireless Personal Communications, 81(4), 1351–1357.
Prasad, R. (Ed.). (2016). 5G outlook-innovations and applications. London: River Publishers.
Badoi, C. I., Prasad, N., & Prasad, R. (2016). Virtualization and Scheduling Methods for 5G Cognitive Radio Based Wireless Networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 89(2), 599–619.
Rao, S. K., & Prasad, R. (2018). Impact of 5G technologies on smart city implementation. Wireless Personal Communications, 100, 1–16.
Tripathi, P. S. M., & Prasad, R. (2018). Spectrum for 5G services. Wireless Personal Communications, 100, 1–17.
Rao, S. K., & Prasad, R. (2018). Impact of 5G technologies on industry. Wireless Personal Communications, 100, 1–15.
Agiwal, M., Saxena, N., & Roy, A. (2018). Ten Commandments of Emerging 5G Networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 98(3), 2591–2621.
Gonzalez-Coma, J. P., Rodriguez-Fernandez, J., Gonzalez-Prelcic, N., Castedo, L., & Heath, R. W. (2018). Channel estimation and hybrid precoding for frequency selective multiuser mmWave MIMO systems. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 12(2), 353–367.
Rajoria, S., Trivedi, A., & Godfrey, W. W. (2018). A comprehensive survey: Small cell meets massive MIMO. Physical Communication, 26, 40–49.
Hao, W., Muta, O., Gacanin, H., & Furukawa, H. (2017). Dynamic small cell clustering and non-cooperative game-based precoding design for two-tier heterogeneous networks with massive MIMO. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 66(2), 675–687.
C.V., R. K. & Bagadi, K. P. (2017). Design of MC-CDMA receiver using radial basis function network to mitigate multiple access interference and nonlinear distortion. Neural Computing and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3127-0.
Bagadi, K. P. (2017). MC–CDMA receiver design using recurrent neural networks for eliminating multiple access interference and nonlinear distortion. International Journal of Communication Systems, 30(16), e3328.
Bagadi, K. P., Annepu, V., & Das, S. (2016). Recent trends in multiuser detection techniques for SDMA–OFDM communication system. Physical Communication, 20, 93–108.
Bagadi, K. P., & Das, S. (2014). Minimum symbol error rate multiuser detection using an effective invasive weed optimization for MIMO/SDMA–OFDM system. International Journal of Communication Systems, 27(12), 3837–3854.
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Department of Science and Technology (DST) for sanctioning a research Project entitled “Dynamic Optimization of Green Mobile Networks: Algorithm, Architecture and Applications” under Fast Track Young Scientist Scheme Reference No.: SERB/F/5044/2012-2013, DST FIST Reference No.: SR/FST/ETI-296/2011 and TEQIP III (Grant No. 2018/makaut,wb) of MHRD a world bank project under which this paper has been completed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., De, D. & Deb, P. Energy and Spectrum Optimization for 5G Massive MIMO Cognitive Femtocell Based Mobile Network Using Auction Game Theory. Wireless Pers Commun 106, 555–576 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06179-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06179-3