Abstract
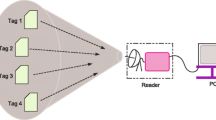
In this paper, we study radio frequency identification tag identification problems using framed slotted ALOHA protocol. Each tag will be assumed to participate in the contention with a certain probability. Then, the frame size and the probability will be dynamically controlled by the reader in every reading round so that all the tags can be detected in a short period of time. Moreover, we propose a practical way of controlling the probability in terms of transmit power control, assuming Additive White Gaussian Noise channel or flat Rayleigh fading channel. Computer simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finkenzeller, K. (2003). RFID Handbook: Fundamentals and applications in contactless smart cards and identification. New York: Wiley.
Angeles, R. (2005). RFID technologies: Supply-chain applications and implementations issues. Information Systems Management, 22(1), 51–65.
Molnar, D., & Wagner, D. (2004). Privacy and security in library RFID: Issues, practices, and architectures. Proceedings of the 11th ACM conference on computer and communication, security, pp. 210–219.
Hush, D., & Wood, C. (1998, August). Analysis of tree algorithm for RFID arbitration. Proceedings of the IEEE international symposium on information theory p. 107.
Roberts, L. G. (1975). ALOHA packet system with and without slots and capture. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 5, 28–42.
EPC global radio frequency identity protocols class-1 generation-2 UHF RFID protocol for communications at 860MHz-960MHz version 1.2.0, Technical, Report, (2008). http://www.gsl.org/gsmp/kc/epcglobal/uhfc1g2/uhfc1g2_1_2_0-standard-20080511.pdf
Cui, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2008, May). Mathematical analysis for binary tree algorithm in RFID. Proceedings of the IEEE vehicular technology conference VTC, pp. 2725–2729.
Law, C., Lee, K., & Siu, K.-Y. (2000, August). Efficient memoryless protocol for tag identification. Proceedings of the 4th international workshop on discrete algorithms and methods for mobile computing and communications (p. 7584) ACM.
Auto-ID Center. (2003). Draft protocol specification for a 900MHz class 0 radio frequency identification tag.
Chen, W.-T. (2008). Performance comparison of binary search tree and framed aloha algorithms for RFID anti-collision. IEICE Transactions on Communications, E91–B(4), 1168–1171.
Zhu, L., & Yum, T.-S. P. (2010). The optimal reading strategy for EPC Gen-2 RFID anti-collision systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 58(9), 2725–2733.
Choi, S. S., & Kim, S. (2009). A dynamic framed slotted ALOHA algorithm using collision factor for RFID identification. IEICE Transactions on Communications, E92–B(3), 1023–1026.
Deng, D.-Z., & Tsao, H.-W. (2010). Optimal dynamic framed slotted ALOHA based anti-collision algorithm for RFID systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 59(1), 109–122.
Fan, X., Song, I., & Chang, K. (2008, December). Gen2-based hybrid tag anti-collision Q algorithm using Chebyshev’s inequality for passivie RFID systems. Proceedings of the 19th IEEE international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, PIMRC, pp. 1–5.
Floerkemeier, C. (2007, March). Bayesian transmission strategy for framed ALOHA based RFID protocols. Proceedings of IEEE international conference on RFID, pp. 228–235.
Chen, W.-T. (2009). An accurate tag estimate method for improving the performance of an RFID anticollision algorithm based on dynamic frame length ALOHA. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 6(1), 9–15.
Cha, J-R, & Kim, J-H (2006). Dynamic framed slotted ALOHA algorithms using fast tag estimation method for RFID system. Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE conference on consumer communications and networking vol. 2, pp. 768–772.
Vogt, H. (2002, April). Efficient object identification with passive RFID tags. Proceedings of international conference on, pervasive computing pp. 98–113.
Bolíc, M., Simplot-Ryl, D., & Stojmenovíc, I. (2010). RFID systems: Research trends and challenges. New York: Wiley.
Qian, C., Ngan, H., Liu, Y., & Ni, L. M. (2011). Cardinality estimation for large-scale RFID systems. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 22(9), 1441–1454.
Auto-ID Center. (2003). 13.56 MHz ISM band class 1 radio frequence identification tag interface specification, version 1.0. HF RFID standard. http://www.epcglobalinc.org/standards/specs/.
Ali, K., Hassanein, H., & Taha, A.-E. M. (2007, October). RFID anti-collision protocol for dense passive tag enviroments. Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE conference on local, computer networks, pp. 819–824.
Xin-qing, Y., Zhou-ping, Y., & You-lun, X. (2008, October). QTS ALOHA: A hybrid collision resolution protocol for dense RFID networks. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on e-business engineering pp. 557–562.
Sze, W.-K., Lau, W.-C., & Yue, O.-C. (2009, June). Fast RFID counting under unreliable radio channel. Proceedings of the IEEE internation conference in, communications, pp. 1–5.
Mansouri, V. S., & Wong, V. W. S. (2011). Cardinality estimation in RFID systems with multiple readers. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 10(5), 1458–1469.
Kim, D.-Y., Yoon, H.-G., Jang, B.-J., & Yook, J.-G. (2009). Effects of reader-to-reader interference on the UHF RFID interrogation range. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 57(7), 2337–2346.
Pourbagheri, S., Bakhtiar, M. S., & Atarodi, M. (2008, December). Cellular design for a dense RFID reader environment. Proceedings of the IEEE Asia pacific conference on circuits and systems pp. 1124–1127.
Al-Fagih, A. E., Al-Turjman, F. M., Hassanein, H. S., & Alsalih, W. M. (2012, June). Coverage-based placement in RFID networks: An overview. Proceedings of the third FTRA international conference on mobile, ubiquitous and intelligent computing pp. 1124–1127.
Kodialam, M., & Nandagopal, T. (2006, September). Fast and reliable estimation schemes in RFID systems. Proceedings of the 12th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking, pp. 322–333.
Schoute, F. C. (1983). Dynamic frame length ALOHA. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 31(4), 565–568.
Kim, J., Lee, W., Kim, E., Kim, D., & Suh, K. (2007). Optimized transmission power control of interrogators for collision arbitration in UHF RFID systems. IEEE Communications Letters, 11(1), 22–24.
Philips Semiconductors. I-CODE smart label RFID tags. http://www.semiconductors.philips.com/acrobat_download/other/identification/SL092030.pdf.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, C.T., Hayashi, K., Kaneko, M. et al. Probabilistic Dynamic Framed Slotted ALOHA for RFID Tag Identification. Wireless Pers Commun 71, 2947–2963 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0981-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0981-z